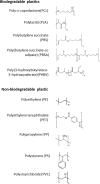
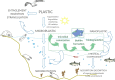
Degradation of plastics and plastic-degrading bacteria in cold marine habitats
- PMID: 29992436
- PMCID: PMC6132502
- DOI: 10.1007/s00253-018-9195-y
Degradation of plastics and plastic-degrading bacteria in cold marine habitats
Abstract
Synthetic plastics present in everyday materials constitute the main anthropogenic debris entering the Earth's oceans. The oceans provide important and valuable resources such as food, energy, and water. They are also the main way of international trade and the main stabilizer of the climate. Hence, changes in the marine ecosystem caused by anthropogenic influences such as plastic pollution can have a dramatic impact on a global scale. Although the problem of plastics still remains unsolved, different ways are being considered to reduce their impact on the environment. One of them is to use microorganisms capable of degradation of plastic. A particularly interesting area is the application of microorganisms isolated from cold regions in view of their unique characteristics. Nevertheless, the interactions between plastic and microorganisms are still poorly known. Here, we present a review of current knowledge on plastic degradation and plastic-microorganism interactions in cold marine habitats. Moreover, we highlight the advantages of microorganisms isolated from this environment for eliminating plastic waste from ecosystems.
Keywords: Biodegradation; Biofilm; Cold marine environment; Microorganisms; Plastic wastes.
Conflict of interest statement
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Competing interests
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Human Health and Ocean Pollution.Ann Glob Health. 2020 Dec 3;86(1):151. doi: 10.5334/aogh.2831. Ann Glob Health. 2020. PMID: 33354517 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Plastic-Degrading Potential across the Global Microbiome Correlates with Recent Pollution Trends.mBio. 2021 Oct 26;12(5):e0215521. doi: 10.1128/mBio.02155-21. Epub 2021 Oct 26. mBio. 2021. PMID: 34700384 Free PMC article.
-
Plastic-microbe interaction in the marine environment: Research methods and opportunities.Environ Int. 2023 Jan;171:107716. doi: 10.1016/j.envint.2022.107716. Epub 2022 Dec 22. Environ Int. 2023. PMID: 36587499 Review.
-
Microbial biotechnology addressing the plastic waste disaster.Microb Biotechnol. 2017 Sep;10(5):1232-1235. doi: 10.1111/1751-7915.12775. Epub 2017 Jul 17. Microb Biotechnol. 2017. PMID: 28714254 Free PMC article.
-
A review of plastic waste biodegradation.Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2005 Oct-Dec;25(4):243-50. doi: 10.1080/07388550500346359. Crit Rev Biotechnol. 2005. PMID: 16419620 Review.
Cited by
-
Isolation and Identification of Four Strains of Bacteria with Potential to Biodegrade Polyethylene and Polypropylene from Mangrove.Microorganisms. 2024 Oct 2;12(10):2005. doi: 10.3390/microorganisms12102005. Microorganisms. 2024. PMID: 39458314 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated approaches for plastic waste management.Front Microbiol. 2024 Sep 26;15:1426509. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1426509. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39391604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Durably Superhydrophobic Magnetic Cobalt Ferrites for Highly Efficient Oil-Water Separation and Fast Microplastic Removal.Langmuir. 2024 Oct 15;40(41):21533-21546. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.4c02420. Epub 2024 Oct 6. Langmuir. 2024. PMID: 39370649 Free PMC article.
-
Degradation Behaviors of Polylactic Acid, Polyglycolic Acid, and Their Copolymer Films in Simulated Marine Environments.Polymers (Basel). 2024 Jun 21;16(13):1765. doi: 10.3390/polym16131765. Polymers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39000621 Free PMC article.
-
Dual Application of p-Nitrophenol Alkanoate-Based Assay for Soil Selection and Screening of Microbial Strains for Bioplastic Degradation.J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024 Jul 28;34(7):1530-1543. doi: 10.4014/jmb.2403.03013. Epub 2024 May 30. J Microbiol Biotechnol. 2024. PMID: 38973389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Artham T, Sudhakar M, Venkatesan R, Madhavan Nair C, Murty KVG, Doble M. Biofouling and stability of synthetic polymers in sea water. Int Biodeterior Biodegradation. 2009;63:884–890. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2009.03.003. - DOI
-
- Austin HP, Allen MD, Donohoe BS, Rorrer NA, Kearns FL, Silveira RL, Pollard BC, Dominick G, Duman R, El Omari K, Mykhaylyk V, Wagner A, Michener WE, Amore A, Skaf MS, Crowley MF, Thorne AW, Johnson CW, Woodcock HL, McGeehan JE, Beckham GT. Characterization and engineering of a plastic-degrading aromatic polyesterase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2018;115:E4350–E4357. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1718804115. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources