Effect of Ibuprofen on BrainAGE: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Response Exploratory Study
- PMID: 29941380
- PMCID: PMC6510235
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bpsc.2018.05.002
Effect of Ibuprofen on BrainAGE: A Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Dose-Response Exploratory Study
Abstract
Background: The age of a person's brain can be estimated from structural brain images using an aggregate measure of variation in morphology across the whole brain. The brain age gap estimation (BrainAGE) score is computed as the difference between kernel-estimated brain age and chronological age. In this exploratory study, we investigated the application of the BrainAGE measure to identify potential novel effects of pharmacological agents on brain morphology.
Methods: Twenty healthy participants (23-47 years of age) completed three structural magnetic resonance imaging scans 45 minutes after administration of placebo or 200 or 600 mg of ibuprofen in a double-blind, crossover study. An externally derived BrainAGE model from a sample of 480 healthy participants was used to examine the acute effect of ibuprofen on temporary neuroanatomical changes in healthy individuals.
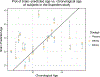
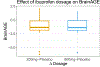
Results: The BrainAGE model produced age prediction for each participant with a mean absolute error of 6.7 years between the estimated and chronological age. The intraclass correlation coefficient for BrainAGE was 0.96. Relative to placebo, 200 and 600 mg of ibuprofen significantly decreased BrainAGE by 1.18 and 1.15 years, respectively (p < .05). The trained BrainAGE model identified the medial prefrontal cortex to be the strongest age predictor.
Conclusions: BrainAGE is a potentially useful construct to examine neurological effects of therapeutic drugs. Ibuprofen temporarily reduces BrainAGE by approximately 1 year, which is likely due to its acute anti-inflammatory effects.
Trial registration: ClinicalTrials.gov NCT02507219.
Keywords: BrainAGE; Ibuprofen; Pharmacological manipulation; Prefrontal cortex; Structural imaging; Support vector.
Copyright © 2018 Society of Biological Psychiatry. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors report no biomedical financial interests or potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
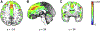
Similar articles
-
Changes of individual BrainAGE during the course of the menstrual cycle.Neuroimage. 2015 Jul 15;115:1-6. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.04.036. Epub 2015 Apr 23. Neuroimage. 2015. PMID: 25913700
-
Sex differences in predictors and regional patterns of brain age gap estimates.Hum Brain Mapp. 2022 Oct 15;43(15):4689-4698. doi: 10.1002/hbm.25983. Epub 2022 Jul 5. Hum Brain Mapp. 2022. PMID: 35790053 Free PMC article.
-
Advanced BrainAGE in older adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.Front Aging Neurosci. 2013 Dec 17;5:90. doi: 10.3389/fnagi.2013.00090. eCollection 2013. Front Aging Neurosci. 2013. PMID: 24381557 Free PMC article.
-
BrainAGE in Mild Cognitive Impaired Patients: Predicting the Conversion to Alzheimer's Disease.PLoS One. 2013 Jun 27;8(6):e67346. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0067346. Print 2013. PLoS One. 2013. PMID: 23826273 Free PMC article.
-
BrainAGE, brain health, and mental disorders: A systematic review.Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024 Apr;159:105581. doi: 10.1016/j.neubiorev.2024.105581. Epub 2024 Feb 13. Neurosci Biobehav Rev. 2024. PMID: 38354871 Review.
Cited by
-
Decoding MRI-informed brain age using mutual information.Insights Imaging. 2024 Aug 26;15(1):216. doi: 10.1186/s13244-024-01791-9. Insights Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39186199 Free PMC article.
-
Association between inflammation, reward processing, and ibuprofen-induced increases of miR-23b in astrocyte-enriched extracellular vesicles: A randomized, placebo-controlled, double-blind, exploratory trial in healthy individuals.Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022 Dec 24;27:100582. doi: 10.1016/j.bbih.2022.100582. eCollection 2023 Feb. Brain Behav Immun Health. 2022. PMID: 36605933 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimaging-Based Brain Age Estimation: A Promising Personalized Biomarker in Neuropsychiatry.J Pers Med. 2022 Nov 5;12(11):1850. doi: 10.3390/jpm12111850. J Pers Med. 2022. PMID: 36579560 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Is musical engagement enough to keep the brain young?Brain Struct Funct. 2023 Mar;228(2):577-588. doi: 10.1007/s00429-022-02602-x. Epub 2022 Dec 27. Brain Struct Funct. 2023. PMID: 36574049 Free PMC article.
-
Peripheral inflammation levels associated with degree of advanced brain aging in schizophrenia.Front Psychiatry. 2022 Aug 12;13:966439. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2022.966439. eCollection 2022. Front Psychiatry. 2022. PMID: 36032250 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Rainsford KD (2013): Ibuprofen: From invention to an OTC therapeutic mainstay. Int J Clin Pract Suppl (178):9–20. - PubMed
-
- Rainsford KD (2009): Ibuprofen: Pharmacology, efficacy and safety. Inflammopharmacology 17:275–342. - PubMed
-
- Delaney JA, Biggs ML, Kronmal RA, Psaty BM (2011): Demographic, medical, and behavioral characteristics associated with over the counter non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drug use in a population-based cohort: Results from the Multi-Ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 20:83–89. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous


