Negative Feedback Phosphorylation of Gγ Subunit Ste18 and the Ste5 Scaffold Synergistically Regulates MAPK Activation in Yeast
- PMID: 29719261
- PMCID: PMC5987779
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2018.03.135
Negative Feedback Phosphorylation of Gγ Subunit Ste18 and the Ste5 Scaffold Synergistically Regulates MAPK Activation in Yeast
Abstract
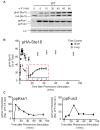
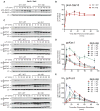
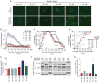
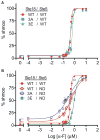
Heterotrimeric G proteins (Gαβγ) are essential transducers in G protein signaling systems in all eukaryotes. In yeast, G protein signaling differentially activates mitogen-activated protein kinases (MAPKs)-Fus3 and Kss1-a phenomenon controlled by plasma membrane (PM) association of the scaffold protein Ste5. Here, we show that phosphorylation of the yeast Gγ subunit (Ste18), together with Fus3 docking on Ste5, controls the rate and stability of Ste5/PM association. Disruption of either element alone by point mutation has mild but reciprocal effects on MAPK activation. Disabling both elements results in ultra-fast and stable bulk Ste5/PM localization and Fus3 activation that is 6 times faster and 4 times more amplified compared to wild-type cells. These results further resolve the mechanism by which MAPK negative feedback phosphorylation controls pathway activation and provides compelling evidence that Gγ subunits can serve as intrinsic regulators of G protein signaling.
Keywords: G protein; G protein γ; MAPK; Ste18; Ste5; feedback; phosphorylation; scaffold; signaling; subunit; synergistic.
Copyright © 2018 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
MAPK modulation of yeast pheromone signaling output and the role of phosphorylation sites in the scaffold protein Ste5.Mol Biol Cell. 2019 Apr 1;30(8):1037-1049. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E18-12-0793. Epub 2019 Feb 6. Mol Biol Cell. 2019. PMID: 30726174 Free PMC article.
-
Mutational analysis suggests that activation of the yeast pheromone response mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway involves conformational changes in the Ste5 scaffold protein.Mol Biol Cell. 2000 Nov;11(11):4033-49. doi: 10.1091/mbc.11.11.4033. Mol Biol Cell. 2000. PMID: 11071925 Free PMC article.
-
Persistent activation by constitutive Ste7 promotes Kss1-mediated invasive growth but fails to support Fus3-dependent mating in yeast.Mol Cell Biol. 2004 Oct;24(20):9221-38. doi: 10.1128/MCB.24.20.9221-9238.2004. Mol Cell Biol. 2004. PMID: 15456892 Free PMC article.
-
The Ste5p scaffold.J Cell Sci. 2001 Nov;114(Pt 22):3967-78. doi: 10.1242/jcs.114.22.3967. J Cell Sci. 2001. PMID: 11739629 Review.
-
Scaffold proteins as dynamic integrators of biological processes.J Biol Chem. 2022 Dec;298(12):102628. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.102628. Epub 2022 Oct 20. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 36273588 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Glucose-6-phosphate 1-Epimerase CrGlu6 Contributes to Development and Biocontrol Efficiency in Clonostachys chloroleuca.J Fungi (Basel). 2023 Jul 20;9(7):764. doi: 10.3390/jof9070764. J Fungi (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37504752 Free PMC article.
-
Mechanism of commitment to a mating partner in Saccharomyces cerevisiae.Mol Biol Cell. 2022 Oct 1;33(12):ar112. doi: 10.1091/mbc.E22-02-0043. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Mol Biol Cell. 2022. PMID: 35947501 Free PMC article.
-
Enhancing the Discovery of Functional Post-Translational Modification Sites with Machine Learning Models - Development, Validation, and Interpretation.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2499:221-260. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2317-6_12. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35696084
-
Directed yeast genome evolution by controlled introduction of trans-chromosomic structural variations.Sci China Life Sci. 2022 Sep;65(9):1703-1717. doi: 10.1007/s11427-021-2084-1. Epub 2022 May 25. Sci China Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 35633480
-
Combinatorial phosphorylation modulates the structure and function of the G protein γ subunit in yeast.Sci Signal. 2021 Jun 22;14(688):eabd2464. doi: 10.1126/scisignal.abd2464. Sci Signal. 2021. PMID: 34158397 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bargmann CI. Comparative chemosensation from receptors to ecology. Nature. 2006;444:295–301. - PubMed
-
- Bhattacharyya RP, Reményi A, Good MC, Bashor CJ, Falick AM, Lim WA. The Ste5 scaffold allosterically modulates signaling output of the yeast mating pathway. Science. 2006;311:822–826. - PubMed
-
- Cabrera-Vera TM, Vanhauwe J, Thomas TO, Medkova M, Preininger A, Mazzoni MR, Hamm HE. Insights into G protein structure, function, and regulation. Endocr Rev. 2003;24:765–781. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases


