A Study on Curing Kinetics of Nano-Phase Modified Epoxy Resin
- PMID: 29445228
- PMCID: PMC5813017
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-018-21208-0
A Study on Curing Kinetics of Nano-Phase Modified Epoxy Resin
Abstract
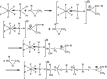
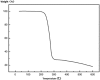
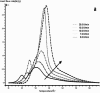
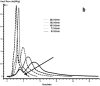
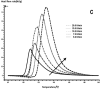
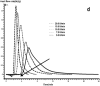
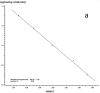
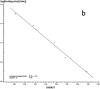
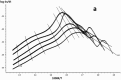
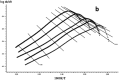
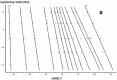
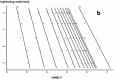
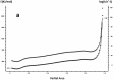
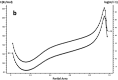
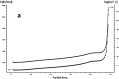
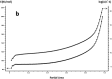
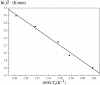
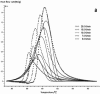
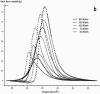
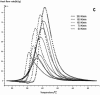
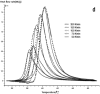
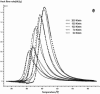
In this paper, DSC curves at different heating rates were measured by DSC, the characteristic curing temperature was determined, and the optimum curing conditions were obtained. The KAS method, Friedman method and FWO method were used to analyze the DSC curves respectively. The kinetic parameters and the reaction mechanism function of the curing system were obtained, and the results of different analytical methods were compared and analyzed. Result from fitting and verification of the curing kinetic model for the curing system of the nano-phase modified epoxy resin further demonstrates that the nano-particle could play a catalytic role in the curing reaction of the epoxy resin and could reduce the apparent activation energy of the system, thus it is considered as a breakthrough in the field of resin research.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Kinetic Analysis of the Curing Process of Biobased Epoxy Resin from Epoxidized Linseed Oil by Dynamic Differential Scanning Calorimetry.Polymers (Basel). 2021 Apr 14;13(8):1279. doi: 10.3390/polym13081279. Polymers (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33919970 Free PMC article.
-
Thiourea modified low molecular polyamide as a novel room temperature curing agent for epoxy resin.RSC Adv. 2022 Jun 21;12(28):18215-18223. doi: 10.1039/d2ra02693g. eCollection 2022 Jun 14. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35800299 Free PMC article.
-
The Curing Kinetics of E-Glass Fiber/Epoxy Resin Prepreg and the Bending Properties of Its Products.Materials (Basel). 2021 Aug 19;14(16):4673. doi: 10.3390/ma14164673. Materials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34443194 Free PMC article.
-
Kinetic Analysis of the Curing of a Partially Biobased Epoxy Resin Using Dynamic Differential Scanning Calorimetry.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Feb 27;11(3):391. doi: 10.3390/polym11030391. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 30960375 Free PMC article.
-
Curing Regime-Modulating Insulation Performance of Anhydride-Cured Epoxy Resin: A Review.Molecules. 2023 Jan 5;28(2):547. doi: 10.3390/molecules28020547. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 36677605 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Predicting the Properties of High-Performance Epoxy Resin by Machine Learning Using Molecular Dynamics Simulations.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jul 9;12(14):2353. doi: 10.3390/nano12142353. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35889577 Free PMC article.
-
Curing and Molecular Dynamics Simulation of MXene/Phenolic Epoxy Composites with Different Amine Curing Agent Systems.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022 Jun 30;12(13):2249. doi: 10.3390/nano12132249. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2022. PMID: 35808085 Free PMC article.
-
Cardanol-Derived Epoxy Resins as Biobased Gel Polymer Electrolytes for Potassium-Ion Conduction.ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2022 May 13;4(5):3855-3865. doi: 10.1021/acsapm.2c00335. Epub 2022 Apr 29. ACS Appl Polym Mater. 2022. PMID: 35601462 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of organic-modified nickel phyllosilicate on the non-isothermal cure kinetics and flame retardancy properties of epoxy composites.RSC Adv. 2022 Feb 15;12(9):5415-5427. doi: 10.1039/d1ra08466f. eCollection 2022 Feb 10. RSC Adv. 2022. PMID: 35425577 Free PMC article.
-
Preparation and Properties of 3D Printing Light-Curable Resin Modified with Hyperbranched Polysiloxane.ACS Omega. 2021 Sep 9;6(37):23683-23690. doi: 10.1021/acsomega.1c01232. eCollection 2021 Sep 21. ACS Omega. 2021. PMID: 34568648 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Li, T. Q. et al. Engineering Superior Toughness in Commercially Viable Block Copolymer Modified Epoxy Resin. Journal of Polymer Science, Part B: Polymer Physics. 1–16 (2015).
-
- Ruan Z, Liu ZH, Deng ZP. etc., Functionalization of epoxy resin system research. Equipment Environmental Engineering. 2015;12(1):51–58.
-
- Feng ZC, et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Solid Bisphenol A Epoxy Resin. Thermosetting Resins. 2010;11(6):33–34.
-
- Tian C, Yang L, Ma HB. Propertiesof nano-silica toughened epoxy resin. Journal of Southwest University of Science and Technology. 2012;4:11–15.
-
- Hong Z, et al. Epoxy resin amine curing agent research. New Chemical Materials. 2014;42(8):12–15.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


