Gene-environment interaction study for BMI reveals interactions between genetic factors and physical activity, alcohol consumption and socioeconomic status
- PMID: 28873402
- PMCID: PMC5600404
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pgen.1006977
Gene-environment interaction study for BMI reveals interactions between genetic factors and physical activity, alcohol consumption and socioeconomic status
Abstract
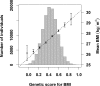
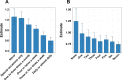
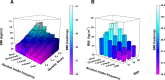
Previous genome-wide association studies (GWAS) have identified hundreds of genetic loci to be associated with body mass index (BMI) and risk of obesity. Genetic effects can differ between individuals depending on lifestyle or environmental factors due to gene-environment interactions. In this study, we examine gene-environment interactions in 362,496 unrelated participants with Caucasian ancestry from the UK Biobank resource. A total of 94 BMI-associated SNPs, selected from a previous GWAS on BMI, were used to construct weighted genetic scores for BMI (GSBMI). Linear regression modeling was used to estimate the effect of gene-environment interactions on BMI for 131 lifestyle factors related to: dietary habits, smoking and alcohol consumption, physical activity, socioeconomic status, mental health, sleeping patterns, as well as female-specific factors such as menopause and childbirth. In total, 15 lifestyle factors were observed to interact with GSBMI, of which alcohol intake frequency, usual walking pace, and Townsend deprivation index, a measure of socioeconomic status, were all highly significant (p = 1.45*10-29, p = 3.83*10-26, p = 4.66*10-11, respectively). Interestingly, the frequency of alcohol consumption, rather than the total weekly amount resulted in a significant interaction. The FTO locus was the strongest single locus interacting with any of the lifestyle factors. However, 13 significant interactions were also observed after omitting the FTO locus from the genetic score. Our analyses indicate that many lifestyle factors modify the genetic effects on BMI with some groups of individuals having more than double the effect of the genetic score. However, the underlying causal mechanisms of gene-environmental interactions are difficult to deduce from cross-sectional data alone and controlled experiments are required to fully characterise the causal factors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The association of cigarette smoking and alcohol drinking with body mass index: a cross-sectional, population-based study among Chinese adult male twins.BMC Public Health. 2016 Apr 11;16:311. doi: 10.1186/s12889-016-2967-3. BMC Public Health. 2016. PMID: 27068329 Free PMC article.
-
Gene-environment interactions and obesity traits among postmenopausal African-American and Hispanic women in the Women's Health Initiative SHARe Study.Hum Genet. 2013 Mar;132(3):323-36. doi: 10.1007/s00439-012-1246-3. Epub 2012 Nov 29. Hum Genet. 2013. PMID: 23192594 Free PMC article.
-
Interaction between Social/Psychosocial Factors and Genetic Variants on Body Mass Index: A Gene-Environment Interaction Analysis in a Longitudinal Setting.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017 Sep 29;14(10):1153. doi: 10.3390/ijerph14101153. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2017. PMID: 28961216 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of Gene-Environment Interaction on Obesity among Chinese Adults Born in the Early 1960s.Genes (Basel). 2021 Feb 13;12(2):270. doi: 10.3390/genes12020270. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33668547 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Body Mass Index With Cardiometabolic Disease in the UK Biobank: A Mendelian Randomization Study.JAMA Cardiol. 2017 Aug 1;2(8):882-889. doi: 10.1001/jamacardio.2016.5804. JAMA Cardiol. 2017. PMID: 28678979 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Assessment of Adolescents' Overweight and Obesity Risk Factors Among Alabnaa Schools in Tabuk City, Saudi Arabia.Cureus. 2024 Jun 2;16(6):e61533. doi: 10.7759/cureus.61533. eCollection 2024 Jun. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38957243 Free PMC article.
-
How do lifestyle factors modify the association between genetic predisposition and obesity-related phenotypes? A 4-way decomposition analysis using UK Biobank.BMC Med. 2024 Jun 10;22(1):230. doi: 10.1186/s12916-024-03436-6. BMC Med. 2024. PMID: 38853248 Free PMC article.
-
Risk factors affecting polygenic score performance across diverse cohorts.medRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Apr 10:2023.05.10.23289777. doi: 10.1101/2023.05.10.23289777. medRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38645167 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Expanding the Scope: In-depth Review of Interaction in Regression Models.Ann Clin Epidemiol. 2023 Jun 10;6(2):25-32. doi: 10.37737/ace.24005. eCollection 2024. Ann Clin Epidemiol. 2023. PMID: 38606039 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
Advances in DNA, histone, and RNA methylation mechanisms in the pathophysiology of alcohol use disorder.Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2023 Feb 15;3:10871. doi: 10.3389/adar.2023.10871. eCollection 2023. Adv Drug Alcohol Res. 2023. PMID: 38389820 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hunter DJ. Gene-environment interactions in human diseases. Nat Rev Genet. 2005;6: 287–298. doi: 10.1038/nrg1578 - DOI - PubMed
-
- Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development. OECD: Obestiy Update 2014. OECD Heal Stat. 2014; 8.
-
- Willer CJ, Speliotes EK, Loos RJF, Li S, Lindgren CM, Heid IM, et al. Six new loci associated with body mass index highlight a neuronal influence on body weight regulation. Nat Genet. 2009;41: 25–34. doi: 10.1038/ng.287 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Locke AE, Kahali B, Berndt SI, Justice AE, Pers TH, Day FR, et al. Genetic studies of body mass index yield new insights for obesity biology. Nature. 2015;518: 197–206. doi: 10.1038/nature14177 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Speliotes EK, Willer CJ, Berndt SI, Monda KL, Thorleifsson G, Jackson AU, et al. Association analyses of 249,796 individuals reveal 18 new loci associated with body mass index. Nat Genet. 2010;42: 937–948. doi: 10.1038/ng.686 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


