Assessment of pulmonary artery pressure by echocardiography-A comprehensive review
- PMID: 28616542
- PMCID: PMC5454185
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ijcha.2016.05.011
Assessment of pulmonary artery pressure by echocardiography-A comprehensive review
Abstract
Pulmonary hypertension is a pathological haemodynamic condition defined as an increase in mean pulmonary arterial pressure ≥ 25 mmHg at rest, assessed using gold standard investigation by right heart catheterisation. Pulmonary hypertension could be a complication of cardiac or pulmonary disease, or a primary disorder of small pulmonary arteries. Elevated pulmonary pressure (PAP) is associated with increased mortality, irrespective of the aetiology. The gold standard for diagnosis is invasive right heart catheterisation, but this has its own inherent risks. In the past 30 years, immense technological improvements in echocardiography have increased its sensitivity for quantifying pulmonary artery pressure (PAP) and it is now recognised as a safe and readily available alternative to right heart catheterisation. In the future, scores combining various echo techniques can approach the gold standard in terms of sensitivity and accuracy, thereby reducing the need for repeated invasive assessments in these patients.
Keywords: Pulmonary acceleration time; Pulmonary hypertension by echo; Pulmonary pressure by echocardiography; Pulmonary vascular resistance by echo; Tricuspid Regurgitation Vmax.
Figures
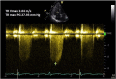

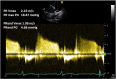
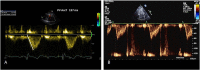
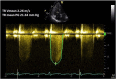
Similar articles
-
Two simple echo-Doppler measurements can accurately identify pulmonary hypertension in the large majority of patients with chronic heart failure.J Heart Lung Transplant. 2005 Jun;24(6):745-54. doi: 10.1016/j.healun.2004.03.026. J Heart Lung Transplant. 2005. PMID: 15949736
-
Cardiomyopathy in children: Can we rely on echocardiographic tricuspid regurgitation gradient estimates of right ventricular and pulmonary arterial pressure?Cardiol Young. 2016 Oct;26(7):1406-13. doi: 10.1017/S1047951116000020. Epub 2016 Mar 4. Cardiol Young. 2016. PMID: 26940013
-
Combined automated 3D volumetry by pulmonary CT angiography and echocardiography for detection of pulmonary hypertension.Eur Radiol. 2019 Nov;29(11):6059-6068. doi: 10.1007/s00330-019-06188-7. Epub 2019 Apr 8. Eur Radiol. 2019. PMID: 30963276
-
[Noninvasive diagnosis of pulmonary arterial hypertension in chronic respiratory insufficiency].Rev Mal Respir. 1985;2(5):263-77. Rev Mal Respir. 1985. PMID: 2938231 Review. French.
-
Echocardiographic Evaluation of Pulmonary Pressures and Right Ventricular Function after Pediatric Cardiac Surgery: A Simple Approach for the Intensivist.Front Pediatr. 2017 Aug 29;5:184. doi: 10.3389/fped.2017.00184. eCollection 2017. Front Pediatr. 2017. PMID: 28900614 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Imatinib Mesylate Causes Potential Cardiac Dysfunction in Patients With Chronic Myeloid Leukemia: the Results of a Case-control Study.Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2024 Oct;40(4):558-563. doi: 10.1007/s12288-024-01797-9. Epub 2024 Jul 8. Indian J Hematol Blood Transfus. 2024. PMID: 39469155
-
Peak Tricuspid Regurgitation Jet Velocity and Kidney Outcomes in Patients With Heart Failure With Preserved Ejection Fraction.Kidney Int Rep. 2024 Jul 17;9(10):3035-3044. doi: 10.1016/j.ekir.2024.07.009. eCollection 2024 Oct. Kidney Int Rep. 2024. PMID: 39430198 Free PMC article.
-
Interpreting Diastolic Dynamics and Evaluation through Echocardiography.Life (Basel). 2024 Sep 12;14(9):1156. doi: 10.3390/life14091156. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39337939 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Realistic Aspects of Cardiac Ultrasound in Rats: Practical Tips for Improved Examination.J Imaging. 2024 Sep 6;10(9):219. doi: 10.3390/jimaging10090219. J Imaging. 2024. PMID: 39330439 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Breathing patterns during sleep and their relationship with FEV1 in pediatric patients with cystic fibrosis residing at high altitude.Front Pediatr. 2024 Aug 15;12:1360227. doi: 10.3389/fped.2024.1360227. eCollection 2024. Front Pediatr. 2024. PMID: 39210986 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Galiè N., Humbert M., Vachiery J.-L. 2015 ESC/ERS guidelines for the diagnosis and treatment of pulmonary hypertension. Eur. Heart J. August 2015;29 (published online)
-
- Bossone E., D'Andrea A., D'Alto M. Echocardiography in pulmonary arterial hypertension: from diagnosis to prognosis. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2013;26(1):1–14. - PubMed
-
- Haddad F., Hunt S.A., Rosenthal D.N. Right ventricular function in cardiovascular disease, part I: anatomy, physiology, aging, and functional assessment of the right ventricle. Circulation. 2008;117(11):1436–1448. - PubMed
-
- Lafitte S., Pillois X., Reant P. Estimation of pulmonary pressures and diagnosis of pulmonary hypertension by Doppler echocardiography: a retrospective comparison of routine echocardiography and invasive hemodynamics. J. Am. Soc. Echocardiogr. 2013;26(5):457–463. - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


