The First Negative Allosteric Modulator for Dopamine D2 and D3 Receptors, SB269652 May Lead to a New Generation of Antipsychotic Drugs
- PMID: 28265019
- PMCID: PMC5438131
- DOI: 10.1124/mol.116.107607
The First Negative Allosteric Modulator for Dopamine D2 and D3 Receptors, SB269652 May Lead to a New Generation of Antipsychotic Drugs
Abstract
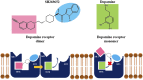
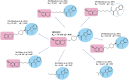
D2 and D3 dopamine receptors belong to the largest family of cell surface proteins in eukaryotes, the G protein-coupled receptors (GPCRs). Considering their crucial physiologic functions and their relatively accessible cellular locations, GPCRs represent one of the most important classes of therapeutic targets. Until recently, the only strategy to develop drugs regulating GPCR activity was through the identification of compounds that directly acted on the orthosteric sites for endogenous ligands. However, many efforts have recently been made to identify small molecules that are able to interact with allosteric sites. These sites are less well-conserved, therefore allosteric ligands have greater selectivity on the specific receptor. Strikingly, the use of allosteric modulators can provide specific advantages, such as an increased selectivity for GPCR subunits and the ability to introduce specific beneficial therapeutic effects without disrupting the integrity of complex physiologically regulated networks. In 2010, our group unexpectedly found that N-[(1r,4r)-4-[2-(7-cyano-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroisoquinolin-2-yl)ethyl]cyclohexyl]-1H-indole-2-carboxamide (SB269652), a compound supposed to interact with the orthosteric binding site of dopamine receptors, was actually a negative allosteric modulator of D2- and D3-receptor dimers, thus identifying the first allosteric small molecule acting on these important therapeutic targets. This review addresses the progress in understanding the molecular mechanisms of interaction between the negative modulator SB269652 and D2 and D3 dopamine receptor monomers and dimers, and surveys the prospects for developing new dopamine receptor allosteric drugs with SB269652 as the leading compound.
U.S. Government work not protected by U.S. copyright.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Distinctive binding properties of the negative allosteric modulator, [3H]SB269,652, at recombinant dopamine D3 receptors.Eur J Pharmacol. 2018 Jan 15;819:181-189. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2017.12.002. Epub 2017 Dec 6. Eur J Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29223348
-
Dopamine D2 Receptors Dimers: How can we Pharmacologically Target Them?Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018 Jan 30;16(2):222-230. doi: 10.2174/1570159X15666170518151127. Curr Neuropharmacol. 2018. PMID: 28521704 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The action of a negative allosteric modulator at the dopamine D2 receptor is dependent upon sodium ions.Sci Rep. 2018 Jan 19;8(1):1208. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-19642-1. Sci Rep. 2018. PMID: 29352161 Free PMC article.
-
The structural determinants of the bitopic binding mode of a negative allosteric modulator of the dopamine D2 receptor.Biochem Pharmacol. 2018 Feb;148:315-328. doi: 10.1016/j.bcp.2018.01.002. Epub 2018 Jan 9. Biochem Pharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29325769 Free PMC article.
-
Bitropic D3 Dopamine Receptor Selective Compounds as Potential Antipsychotics.Curr Pharm Des. 2015;21(26):3700-24. doi: 10.2174/1381612821666150724100830. Curr Pharm Des. 2015. PMID: 26205291 Review.
Cited by
-
Review on allosteric modulators of dopamine receptors so far.Health Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 18;7(3):e1984. doi: 10.1002/hsr2.1984. eCollection 2024 Mar. Health Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38505681 Free PMC article.
-
Allosteric Modulators of Dopamine D2 Receptors for Fine-Tuning of Dopaminergic Neurotransmission in CNS Diseases: Overview, Pharmacology, Structural Aspects and Synthesis.Molecules. 2022 Dec 25;28(1):178. doi: 10.3390/molecules28010178. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 36615372 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Allosteric modulation of dopamine D2L receptor in complex with Gi1 and Gi2 proteins: the effect of subtle structural and stereochemical ligand modifications.Pharmacol Rep. 2022 Apr;74(2):406-424. doi: 10.1007/s43440-021-00352-x. Epub 2022 Jan 22. Pharmacol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35064921 Free PMC article.
-
Evidence for Two Modes of Binding of the Negative Allosteric Modulator SB269,652 to the Dopamine D2 Receptor.Biomedicines. 2021 Dec 23;10(1):22. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines10010022. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 35052702 Free PMC article.
-
Integration and Spatial Organization of Signaling by G Protein-Coupled Receptor Homo- and Heterodimers.Biomolecules. 2021 Dec 3;11(12):1828. doi: 10.3390/biom11121828. Biomolecules. 2021. PMID: 34944469 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Aloisi G, Silvano E, Rossi M, Millan MJ, Maggio R. (2011) Differential induction of adenylyl cyclase supersensitivity by antiparkinson drugs acting as agonists at dopamine D1/D2/D3 receptors vs D2/D3 receptors only: Parallel observations from co-transfected human and native cerebral receptors. Neuropharmacology 60:439–445. - PubMed
-
- Bonaventura J, Navarro G, Casadó-Anguera V, Azdadc K, Reab W, Moreno E, Brugarolas M, Mallol J, Canela EI, Lluís C, et al. (2015) Allosteric interactions between agonists and antagonists within the adenosine A2A receptor-dopamine D2 receptor heterotetramer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 112:E3609–E3618. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Carrillo JJ, Pediani J, Milligan G. (2003) Dimers of class A G protein-coupled receptors function via agonist-mediated trans-activation of associated G proteins. J Biol Chem 278:42578–42587. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources

