Herbal Medicine Cordyceps sinensis Improves Health-Related Quality of Life in Moderate-to-Severe Asthma
- PMID: 28050193
- PMCID: PMC5165155
- DOI: 10.1155/2016/6134593
Herbal Medicine Cordyceps sinensis Improves Health-Related Quality of Life in Moderate-to-Severe Asthma
Abstract
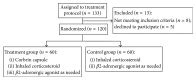
Moderate-to-severe asthma has a substantial impact on the health-related quality of life (HR-QOL) of the patients. Cordyceps sinensis is a traditional Chinese medicine that is evaluated clinically for the treatment of many diseases, such as chronic allograft nephropathy, diabetic kidney disease, and lung fibrosis. In order to investigate the effects of Cordyceps sinensis on patients with moderate-to-severe persistent asthma, 120 subjects were randomized to receive Corbin capsule containing Cordyceps sinensis for 3 months (treatment group, n = 60), whereas the control group (n = 60) did not receive treatment with Corbin capsule. Inhaled corticosteroid and as-needed β-agonists were used in the treatment of both groups. HR-QOL was measured with the Juniper's Asthma Quality of Life Questionnaire (AQLQ). The incidence of asthma exacerbation, pulmonary function testing, and serum measurements of inflammatory mediators were also evaluated. The results showed that the treatment group indicated a significant increase in AQLQ scores and lung function compared with the control group. The expression levels of the inflammation markers IgE, ICAM-1, IL-4, and MMP-9 in the serum were decreased and IgG increased in the treatment group compared with the control group. Therefore, the conclusion was reached that a formulation of Cordyceps sinensis improved the HR-QOL, asthma symptoms, lung function, and inflammatory profile of the patients with moderate-to-severe asthma. This trial is registered with ChiCTR-IPC-16008730.
Conflict of interest statement
There is no conflict of interests in this study.
Figures
Similar articles
-
[Pharmacological effects of Bailing capsule and its application in lung disease research].Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010 Oct;35(20):2777-81. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi. 2010. PMID: 21246839 Chinese.
-
[Effect of Cordyceps sinensis on expressions of HIF-1α and VEGF in the kidney of rats with diabetic nephropathy].Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013 May;38(5):448-57. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-7347.2013.05.003. Zhong Nan Da Xue Xue Bao Yi Xue Ban. 2013. PMID: 23719521 Chinese.
-
[The use of Juniper's asthma quality of life questionnaire in Chinese asthmatics].Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2003 Nov;42(11):760-3. Zhonghua Nei Ke Za Zhi. 2003. PMID: 14636472 Chinese.
-
Impact of omalizumab on quality-of-life outcomes in patients with moderate-to-severe allergic asthma.Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006 Feb;96(2):316-26. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61242-2. Ann Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2006. PMID: 16498854 Review.
-
Mechanism of Cordyceps sinensis and its Extracts in the Treatment of Diabetic Kidney Disease: A Review.Front Pharmacol. 2022 May 13;13:881835. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.881835. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35645822 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early Trends to Show the Efficacy of Cordyceps militaris in Mild to Moderate COVID Inflammation.Cureus. 2023 Aug 18;15(8):e43731. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43731. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37727187 Free PMC article.
-
The Role and Mechanisms of Traditional Chinese Medicine for Airway Inflammation and Remodeling in Asthma: Overview and Progress.Front Pharmacol. 2022 Jul 15;13:917256. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2022.917256. eCollection 2022. Front Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35910345 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Tussah silkmoth pupae improve anti-tumor properties of Cordyceps militaris (L.) Link by increasing the levels of major metabolite cordycepin.RSC Adv. 2019 Feb 13;9(10):5480-5491. doi: 10.1039/c8ra09491h. eCollection 2019 Feb 11. RSC Adv. 2019. PMID: 35515955 Free PMC article.
-
New Insights Into the Biosynthesis of Typical Bioactive Components in the Traditional Chinese Medicinal Fungus Cordyceps militaris.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021 Dec 17;9:801721. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2021.801721. eCollection 2021. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2021. PMID: 34976991 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Yarsagumba is a Promising Therapeutic Option for Treatment of Pulmonary Hypertension due to the Potent Anti-Proliferative and Vasorelaxant Properties.Medicina (Kaunas). 2020 Mar 16;56(3):131. doi: 10.3390/medicina56030131. Medicina (Kaunas). 2020. PMID: 32188043 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Leff J. A., Baer J. W., Bodman M. E., Kirkman J. M., Shanley P. F., Patton L. M. Interleukin-1-induced lung neutrophil accumulation and oxygen metabolite-mediated lung leak in rats. American Journal of Physiology. 1994;266(1, part 1):L2–L8. - PubMed
-
- Richman-Eisenstat J. B. Y., Jorens P. G., Hebert C. A., Ueki I., Nadel J. A. Interleukin-8: an important chemoattractant in sputum of patients with chronic inflammatory airway diseases. American Journal of Physiology—Lung Cellular and Molecular Physiology. 1993;264(4, part 1):L413–L418. - PubMed
-
- Heo J. C., Nam S. H., Nam D. Y., Kim J. G., Lee K. G., Yeo J. H. Anti-asthmatic activities in mycelial extract and culture filtrate of Cordyceps sphecocephala J201. International Journal of Molecular Medicine. 2010;26(3):351–356. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous