A 5' Noncoding Exon Containing Engineered Intron Enhances Transgene Expression from Recombinant AAV Vectors in vivo
- PMID: 27903072
- PMCID: PMC5278795
- DOI: 10.1089/hum.2016.140
A 5' Noncoding Exon Containing Engineered Intron Enhances Transgene Expression from Recombinant AAV Vectors in vivo
Abstract
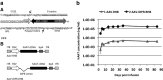
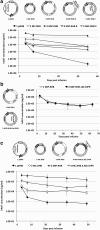
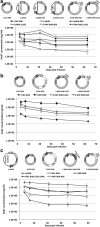
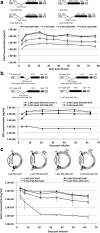
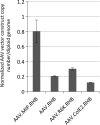
We previously developed a mini-intronic plasmid (MIP) expression system in which the essential bacterial elements for plasmid replication and selection are placed within an engineered intron contained within a universal 5' UTR noncoding exon. Like minicircle DNA plasmids (devoid of bacterial backbone sequences), MIP plasmids overcome transcriptional silencing of the transgene. However, in addition MIP plasmids increase transgene expression by 2 and often >10 times higher than minicircle vectors in vivo and in vitro. Based on these findings, we examined the effects of the MIP intronic sequences in a recombinant adeno-associated virus (AAV) vector system. Recombinant AAV vectors containing an intron with a bacterial replication origin and bacterial selectable marker increased transgene expression by 40 to 100 times in vivo when compared with conventional AAV vectors. Therefore, inclusion of this noncoding exon/intron sequence upstream of the coding region can substantially enhance AAV-mediated gene expression in vivo.
Keywords: AAV vectors; enhance transgene expression; intron; mini-intronic plasmid; miniorigins.
Conflict of interest statement
Author Disclosure James Williams and Jeremy Luke have an equity interest in Nature Technology Corporation. Jiamiao Lu, Feijie Zhang, Kirk Chu, and Mark Kay declare that no other competing financial interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Improving cell and gene therapy safety and performance using next-generation Nanoplasmid vectors.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Apr 7;32:494-503. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.04.003. eCollection 2023 Jun 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37346980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A mini-intronic plasmid (MIP): a novel robust transgene expression vector in vivo and in vitro.Mol Ther. 2013 May;21(5):954-63. doi: 10.1038/mt.2013.33. Epub 2013 Mar 5. Mol Ther. 2013. PMID: 23459514 Free PMC article.
-
High-titer, wild-type free recombinant adeno-associated virus vector production using intron-containing helper plasmids.J Virol. 2000 Dec;74(24):11456-63. doi: 10.1128/jvi.74.24.11456-11463.2000. J Virol. 2000. PMID: 11090141 Free PMC article.
-
JSRV Intragenic Enhancer Element Increases Expression from a Heterologous Promoter and Promotes High Level AAV-mediated Transgene Expression in the Lung and Liver of Mice.Viruses. 2020 Nov 6;12(11):1266. doi: 10.3390/v12111266. Viruses. 2020. PMID: 33172105 Free PMC article.
-
Towards effective non-viral gene delivery vector.Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2015 Apr-Oct;31(1-2):82-107. doi: 10.1080/02648725.2016.1178011. Biotechnol Genet Eng Rev. 2015. PMID: 27160661 Review.
Cited by
-
Adeno-associated virus as a delivery vector for gene therapy of human diseases.Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024 Apr 3;9(1):78. doi: 10.1038/s41392-024-01780-w. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2024. PMID: 38565561 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Selection of viral capsids and promoters affects the efficacy of rescue of Tmprss3-deficient cochlea.Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023 Aug 11;30:413-428. doi: 10.1016/j.omtm.2023.08.004. eCollection 2023 Sep 14. Mol Ther Methods Clin Dev. 2023. PMID: 37663645 Free PMC article.
-
Intravitreal Injection of AAV for the Transduction of Mouse Retinal Ganglion Cells.Methods Mol Biol. 2023;2708:155-174. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-3409-7_17. Methods Mol Biol. 2023. PMID: 37558970
-
Improving cell and gene therapy safety and performance using next-generation Nanoplasmid vectors.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023 Apr 7;32:494-503. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2023.04.003. eCollection 2023 Jun 13. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2023. PMID: 37346980 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The AAV capsid can influence the epigenetic marking of rAAV delivered episomal genomes in a species dependent manner.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 28;14(1):2448. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-38106-3. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37117181 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bigger BW, Tolmachov O, Collombet JM, et al. . An araC-controlled bacterial cre expression system to produce DNA minicircle vectors for nuclear and mitochondrial gene therapy. J Biol Chem 2001;276:23018–23027 - PubMed
-
- Chen ZY, He CY, Ehrhardt A, et al. . Minicircle DNA vectors devoid of bacterial DNA result in persistent and high-level transgene expression in vivo. Mol Ther 2003;8:495–500 - PubMed
-
- Chen ZY, He CY, Kay MA. Improved production and purification of minicircle DNA vector free of plasmid bacterial sequences and capable of persistent transgene expression in vivo. Hum Gene Ther 2005;16:126–131 - PubMed
-
- Darquet AM, Cameron B, Wils P, et al. . A new DNA vehicle for nonviral gene delivery: supercoiled minicircle. Gene Ther 1997;4:1341–1349 - PubMed
-
- Mayrhofer P, Blaesen M, Schleef M, et al. . Minicircle-DNA production by site specific recombination and protein-DNA interaction chromatography. J Gene Med 2008;10:1253–1269 - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


