Cosmic Influence on the Sun-Earth Environment
- PMID: 27873955
- PMCID: PMC3790986
- DOI: 10.3390/s8127736
Cosmic Influence on the Sun-Earth Environment
Abstract
SOHO satellite data reveals geophysical changes before sudden changes in the Earth's Sun-Earth environment. The influence of extragalactic changes on the Sun as well as the Sun-Earth environment seems to be both periodic and episodic. The periodic changes in terms of solar maxima and minima occur every 11 years, whereas the episodic changes can happen at any time. Episodic changes can be monitored by cosmic ray detectors as a sudden increase or decrease of activity. During these solar and cosmic anomaly periods the environment of the Earth is affected. The Star-Sun-Earth connection has the potential to influence the thermosphere, atmosphere, ionosphere and lithosphere. Initial correlation of the cosmic and Sun-Earth connection has shown the possibility of predicting earthquakes, sudden changes in atmospheric temperatures and erratic rainfall/snowfall patterns.
Keywords: SOHO satellite data; change in atmosphere; cosmic; earthquake; extragalactic.
Figures
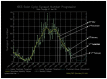
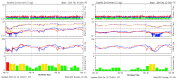
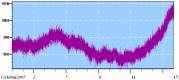
Similar articles
-
Cosmic ray impact on extrasolar earth-like planets in close-in habitable zones.Astrobiology. 2005 Oct;5(5):587-603. doi: 10.1089/ast.2005.5.587. Astrobiology. 2005. PMID: 16225432
-
[Correlation between the microbiological (S. aureus) and seismic activities with regard to the sun-earth interactions and neutron flux generation].Aviakosm Ekolog Med. 2005 May-Jun;39(3):20-6. Aviakosm Ekolog Med. 2005. PMID: 16193922 Russian.
-
Cosmic rays, clouds, and climate.Science. 2002 Nov 29;298(5599):1732-7. doi: 10.1126/science.1076964. Science. 2002. PMID: 12459578
-
Exposure to galactic cosmic radiation and solar energetic particles.Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007;125(1-4):407-11. doi: 10.1093/rpd/ncm317. Epub 2007 Sep 9. Radiat Prot Dosimetry. 2007. PMID: 17846031 Review.
-
Role of the ionosphere for the atmospheric evolution of planets.Astrobiology. 2007 Oct;7(5):783-800. doi: 10.1089/ast.2007.0140. Astrobiology. 2007. PMID: 17963477 Review.
References
References and Notes
-
- Bochnicek J., Hejda P. The winter NAO pattern changes in association with solar and geomagnetic activity. Journal of Atmospheric and Solar –Terrestrial Physics. 2005;67(1-2):17–32.
-
- Chapman S., Ferraro V.C.A. A new theory of magnetic storms. Nature. 1930;126:129.
-
- Eden P. Weather wise. Macmillan. 1995:323.
-
- Kudela K., Stronini M., Hofer M.Y., Belov A.V. Cosmic rays and space weather. Space Sciences Review. 2000;93(1-2):153–174.
-
- Kunze P., Zeits F. The Relativistic Increase in Ionization of High Energy Electrons and Mesotrons. Phys. Rev. 1945;67:269–272.
Suggested Notes
-
- Tinsley B.A. Do Effects of Global Atmospheric Electricity on Clouds Cause Climate Change? EOS. 1997;78:341–349.
-
- Tinsley B.A., Rohrbaugh R.P., Hei M., Beard K.V. Effects of Image Charges on the Scavenging of Aerosol Particles by Cloud Droplets, and on Droplet Charging and Possible Ice Nucleation Processes. J. Atmos. Sci. 2000;57:2118–2134.
-
- Tinsley B.A. Influence of Solar Wind on the Global Electric Circuit, and Inferred effects on Cloud Microphysics, Temperature, and Dynamics in the Troposphere. Space Science Reviews. 2000;94(1-2):231–258.
-
- Tinsley B.A., Rohrbaugh R.P., Hei M. Electroscavenging in Clouds with Broad Droplet Size Distributions and Weak Electrification. Atmospheric Research. 2001;59-60:115–135.
-
- Tinsley B.A., Yu F. Atmospheric Ionization and Clouds as Links Between Solar Activity and Climate. Solar Variability and Its Effects on the Earth's Atmospheric and Climate System. in press in forthcoming AGU monograph.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


