BRD4 Regulates Breast Cancer Dissemination through Jagged1/Notch1 Signaling
- PMID: 27651315
- PMCID: PMC5290198
- DOI: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-16-0559
BRD4 Regulates Breast Cancer Dissemination through Jagged1/Notch1 Signaling
Abstract
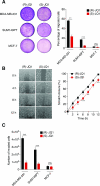
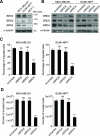
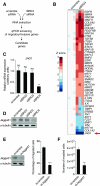
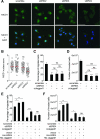
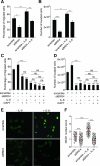
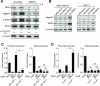
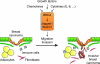
The bromodomain and extraterminal (BET) proteins are epigenetic "readers" of acetylated histones in chromatin and have been identified as promising therapeutic targets in diverse cancers. However, it remains unclear how individual family members participate in cancer progression and small molecule inhibitors such as JQ1 can target functionally independent BET proteins. Here, we report a signaling pathway involving BRD4 and the ligand/receptor pair Jagged1/Notch1 that sustains triple-negative breast cancer migration and invasion. BRD4, but not BRD2 or BRD3, regulated Jagged1 expression and Notch1 signaling. BRD4-selective knockdown suppressed Notch1 activity and impeded breast cancer migration and invasion. BRD4 was required for IL6-stimulated, Notch1-induced migration and invasion, coupling microenvironment inflammation with cancer propagation. Moreover, in patients, BRD4 and Jagged1 expression positively correlated with the presence of distant metastases. These results identify a BRD4/Jagged1/Notch1 signaling pathway that is critical for dissemination of triple-negative breast cancer. Cancer Res; 76(22); 6555-67. ©2016 AACR.
©2016 American Association for Cancer Research.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Notch1 signaling regulates the epithelial-mesenchymal transition and invasion of breast cancer in a Slug-dependent manner.Mol Cancer. 2015 Feb 3;14(1):28. doi: 10.1186/s12943-015-0295-3. Mol Cancer. 2015. PMID: 25645291 Free PMC article.
-
Tumoral BRD4 expression in lymph node-negative breast cancer: association with T-bet+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and disease-free survival.BMC Cancer. 2018 Jul 20;18(1):750. doi: 10.1186/s12885-018-4653-6. BMC Cancer. 2018. PMID: 30029633 Free PMC article.
-
Hsa-miR-599 inhibits breast cancer progression via BRD4/Jagged1/Notch1 axis.J Cell Physiol. 2022 Jan;237(1):523-531. doi: 10.1002/jcp.30548. Epub 2021 Aug 20. J Cell Physiol. 2022. PMID: 34415065
-
BRD4: New hope in the battle against glioblastoma.Pharmacol Res. 2023 May;191:106767. doi: 10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106767. Epub 2023 Apr 13. Pharmacol Res. 2023. PMID: 37061146 Review.
-
BET Inhibitors as Anticancer Agents: A Patent Review.Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2017 Nov 20;12(4):340-364. doi: 10.2174/1574892812666170808121228. Recent Pat Anticancer Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28786345 Review.
Cited by
-
BRD4: an effective target for organ fibrosis.Biomark Res. 2024 Aug 30;12(1):92. doi: 10.1186/s40364-024-00641-6. Biomark Res. 2024. PMID: 39215370 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BRD4-specific PROTAC inhibits basal-like breast cancer partially through downregulating KLF5 expression.Oncogene. 2024 Sep;43(39):2914-2926. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03121-1. Epub 2024 Aug 20. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39164524 Free PMC article.
-
Prioritizing drug targets by perturbing biological network response functions.PLoS Comput Biol. 2024 Jun 27;20(6):e1012195. doi: 10.1371/journal.pcbi.1012195. eCollection 2024 Jun. PLoS Comput Biol. 2024. PMID: 38935814 Free PMC article.
-
Sequential Inhibition of PARP and BET as a Rational Therapeutic Strategy for Glioblastoma.Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024 Aug;11(30):e2307747. doi: 10.1002/advs.202307747. Epub 2024 Jun 19. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024. PMID: 38896791 Free PMC article.
-
Suppression of lysosome metabolism-meditated GARP/TGF-β1 complexes specifically depletes regulatory T cells to inhibit breast cancer metastasis.Oncogene. 2024 Jun;43(25):1930-1940. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03043-y. Epub 2024 May 2. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 38698265
References
-
- Wu SY, Chiang CM. The double bromodomain-containing chromatin adaptor Brd4 and transcriptional regulation. J Biol Chem. 2007;282(18):13141–5. - PubMed
-
- Denis GV, Green MR. A novel, mitogen-activated nuclear kinase is related to a Drosophila developmental regulator. Genes Dev. 1996;10(3):261–71. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous


