Translating microfluidics: Cell separation technologies and their barriers to commercialization
- PMID: 27282966
- PMCID: PMC5149119
- DOI: 10.1002/cyto.b.21388
Translating microfluidics: Cell separation technologies and their barriers to commercialization
Abstract
Advances in microfluidic cell sorting have revolutionized the ways in which cell-containing fluids are processed, now providing performances comparable to, or exceeding, traditional systems, but in a vastly miniaturized format. These technologies exploit a wide variety of physical phenomena to manipulate cells and fluid flow, such as magnetic traps, sound waves and flow-altering micropatterns, and they can evaluate single cells by immobilizing them onto surfaces for chemotherapeutic assessment, encapsulate cells into picoliter droplets for toxicity screenings and examine the interactions between pairs of cells in response to new, experimental drugs. However, despite the massive surge of innovation in these high-performance lab-on-a-chip devices, few have undergone successful commercialization, and no device has been translated to a widely distributed clinical commodity to date. Persistent challenges such as an increasingly saturated patent landscape as well as complex user interfaces are among several factors that may contribute to their slowed progress. In this article, we identify several of the leading microfluidic technologies for sorting cells that are poised for clinical translation; we examine the principal barriers preventing their routine clinical use; finally, we provide a prospectus to elucidate the key criteria that must be met to overcome those barriers. Once established, these tools may soon transform how clinical labs study various ailments and diseases by separating cells for downstream sequencing and enabling other forms of advanced cellular or sub-cellular analysis. © 2016 International Clinical Cytometry Society.
Keywords: cell sorting; commercial translation; flow cytometry; lab on a chip; microfluidic.
© 2016 International Clinical Cytometry Society.
Figures
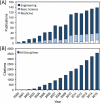


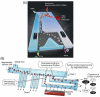

Similar articles
-
Microfluidic cell sorting: a review of the advances in the separation of cells from debulking to rare cell isolation.Lab Chip. 2015 Mar 7;15(5):1230-49. doi: 10.1039/c4lc01246a. Lab Chip. 2015. PMID: 25598308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Developments in label-free microfluidic methods for single-cell analysis and sorting.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2019 Jan;11(1):e1529. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1529. Epub 2018 Apr 24. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2019. PMID: 29687965 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Spark-generated microbubble cell sorter for microfluidic flow cytometry.Cytometry A. 2018 Feb;93(2):222-231. doi: 10.1002/cyto.a.23296. Epub 2018 Jan 18. Cytometry A. 2018. PMID: 29346713
-
Microfluidic chips for cell sorting.Front Biosci. 2008 Jan 1;13:2464-83. doi: 10.2741/2859. Front Biosci. 2008. PMID: 17981727
-
Numerical and experimental evaluation of microfluidic sorting devices.Biotechnol Prog. 2008 Jul-Aug;24(4):981-91. doi: 10.1002/btpr.7. Biotechnol Prog. 2008. PMID: 19194907
Cited by
-
Essential Fluidics for a Flow Cytometer.Curr Protoc. 2024 Oct;4(10):e1124. doi: 10.1002/cpz1.1124. Curr Protoc. 2024. PMID: 39401000
-
A Systematic Analysis of Recent Technology Trends of Microfluidic Medical Devices in the United States.Micromachines (Basel). 2023 Jun 24;14(7):1293. doi: 10.3390/mi14071293. Micromachines (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37512604 Free PMC article.
-
Magnetophoretic circuits: A review of device designs and implementation for precise single-cell manipulation.Anal Chim Acta. 2023 Sep 1;1272:341425. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2023.341425. Epub 2023 May 31. Anal Chim Acta. 2023. PMID: 37355317 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Disposable paper-based microfluidics for fertility testing.iScience. 2022 Aug 18;25(9):104986. doi: 10.1016/j.isci.2022.104986. eCollection 2022 Sep 16. iScience. 2022. PMID: 36105592 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Microfluidics for Neuronal Cell and Circuit Engineering.Chem Rev. 2022 Sep 28;122(18):14842-14880. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00212. Epub 2022 Sep 7. Chem Rev. 2022. PMID: 36070858 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Warkiani ME, Wu L, Tay AK, Han J. Large-volume microfluidic cell sorting for biomedical applications. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2015;17:1, 1–1, 34. - PubMed
-
- El-Ali J, Sorger PK, Jensen KF. Cells on chips. Nature. 2006;442:403–411. - PubMed
-
- Fulwyler M. Electronic separation of biological cells by volume. Science. 1965;150:910–911. - PubMed
-
- Bonner WA, Hulett HR, Sweet RG, Herzenberg LA. Fluorescence activated cell sorting. Review of Scientific Instruments. 1972;43:404–409. - PubMed
-
- Miltenyi S, Muller W, Weichel W, Radbruch A. High gradient magnetic cell separation with MACS. Cytometry. 1990;11:231–238. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous


