Initiation and termination of DNA replication during S phase in relation to cyclins D1, E and A, p21WAF1, Cdt1 and the p12 subunit of DNA polymerase δ revealed in individual cells by cytometry
- PMID: 26059433
- PMCID: PMC4494901
- DOI: 10.18632/oncotarget.4149
Initiation and termination of DNA replication during S phase in relation to cyclins D1, E and A, p21WAF1, Cdt1 and the p12 subunit of DNA polymerase δ revealed in individual cells by cytometry
Abstract
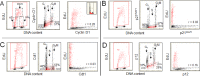
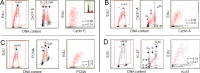
During our recent studies on mechanism of the regulation of human DNA polymerase δ in preparation for DNA replication or repair, multiparameter imaging cytometry as exemplified by laser scanning cytometry (LSC) has been used to assess changes in expression of the following nuclear proteins associated with initiation of DNA replication: cyclin A, PCNA, Ki-67, p21(WAF1), DNA replication factor Cdt1 and the smallest subunit of DNA polymerase δ, p12. In the present review, rather than focusing on Pol δ, we emphasize the application of LSC in these studies and outline possibilities offered by the concurrent differential analysis of DNA replication in conjunction with expression of the nuclear proteins. A more extensive analysis of the data on a correlation between rates of EdU incorporation, likely reporting DNA replication, and expression of these proteins, is presently provided. New data, specifically on the expression of cyclin D1 and cyclin E with respect to EdU incorporation as well as on a relationship between expression of cyclin A vs. p21(WAF1) and Ki-67 vs. Cdt1, are also reported. Of particular interest is the observation that this approach makes it possible to assess the temporal sequence of degradation of cyclin D1, p21(WAF1), Cdt1 and p12, each with respect to initiation of DNA replication and with respect to each other. Also the sequence or reappearance of these proteins in G2 after termination of DNA replication is assessed. The reviewed data provide a more comprehensive presentation of potential markers, whose presence or absence marks the DNA replicating cells. Discussed is also usefulness of these markers as indicators of proliferative activity in cancer tissues that may bear information on tumor progression and have a prognostic value.
Keywords: DNA replication; EdU labeling; S-phase; cell cycle; cell proliferation; laser scanning cytometry; polymerase δ.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Expression of the p12 subunit of human DNA polymerase δ (Pol δ), CDK inhibitor p21(WAF1), Cdt1, cyclin A, PCNA and Ki-67 in relation to DNA replication in individual cells.Cell Cycle. 2014;13(22):3529-40. doi: 10.4161/15384101.2014.958910. Cell Cycle. 2014. PMID: 25483089 Free PMC article.
-
p21CDKN1A does not interfere with loading of PCNA at DNA replication sites, but inhibits subsequent binding of DNA polymerase delta at the G1/S phase transition.Cell Cycle. 2003 Nov-Dec;2(6):596-603. Cell Cycle. 2003. PMID: 14504476
-
Expression patterns of cyclins D1, E and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors p21waf1/cip1, p27kip1 in colorectal carcinoma: correlation with other cell cycle regulators (pRb, p53 and Ki-67 and PCNA) and clinicopathological features.Int J Clin Pract. 2008 Nov;62(11):1736-43. doi: 10.1111/j.1742-1241.2006.01105.x. Int J Clin Pract. 2008. PMID: 19143860
-
Estrogen and antiestrogen regulation of cell cycle progression in breast cancer cells.Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003 Jun;10(2):179-86. doi: 10.1677/erc.0.0100179. Endocr Relat Cancer. 2003. PMID: 12790780 Review.
-
Regulation of DNA Replication Licensing and Re-Replication by Cdt1.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 14;22(10):5195. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105195. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34068957 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Exploring the role of YBX3 in PEDV infection through the utilization of YBX3 knockout and overexpression cell lines.Virus Genes. 2024 Dec;60(6):667-673. doi: 10.1007/s11262-024-02109-z. Epub 2024 Sep 23. Virus Genes. 2024. PMID: 39312036
-
CDK-independent role of D-type cyclins in regulating DNA mismatch repair.Mol Cell. 2024 Apr 4;84(7):1224-1242.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.02.010. Epub 2024 Mar 7. Mol Cell. 2024. PMID: 38458201
-
D-type cyclins regulate DNA mismatch repair in the G1 and S phases of the cell cycle, maintaining genome stability.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jan 13:2024.01.12.575420. doi: 10.1101/2024.01.12.575420. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: Mol Cell. 2024 Apr 4;84(7):1224-1242.e13. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2024.02.010 PMID: 38260436 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
CDKs Functional Analysis in Low Proliferating Early-Stage Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma.J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2023;6(3):187-200. doi: 10.26502/jbsb.5107060. Epub 2023 Aug 16. J Bioinform Syst Biol. 2023. PMID: 37744402 Free PMC article.
-
Docking and simulation studies on cyclin D/CDK4 complex for targeting cell cycle arrest in cancer using flavanone and its congener.J Mol Model. 2023 Mar 7;29(4):90. doi: 10.1007/s00894-023-05496-6. J Mol Model. 2023. PMID: 36881272
References
-
- Dolbeare F, Gray JW. Use of restriction endonucleases and exonuclease III to expose halogenated pyrimidines for immunochemical staining. Cytometry. 1988;9:631–635. - PubMed
-
- Li X, Traganos F, Melamed MR, Darzynkiewicz Z. Single step procedure for DNA strand-breaks labeling. Detection of apoptosis and DNA replication. Cytometry. 1995;20:172–180. - PubMed
-
- Sun Y, Sun Y, Lin G, Zhang R, Zhang K, Xie J, Wang L, Li J. Multicolor flow cytometry analysis of the proliferations of T-lymphocyte subsets in vitro by EdU incorporation. Cytometry A. 2012;81:901–909. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


