Blended vs. face-to-face cognitive behavioural treatment for major depression in specialized mental health care: study protocol of a randomized controlled cost-effectiveness trial
- PMID: 25326035
- PMCID: PMC4209039
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-014-0290-z
Blended vs. face-to-face cognitive behavioural treatment for major depression in specialized mental health care: study protocol of a randomized controlled cost-effectiveness trial
Abstract
Background: Depression is a prevalent disorder, associated with a high disease burden and substantial societal, economic and personal costs. Cognitive behavioural treatment has been shown to provide adequate treatment for depression. By offering this treatment in a blended format, in which online and face-to-face treatment are combined, it might be possible to reduce the number of costly face-to-face sessions required to deliver the treatment protocol. This could improve the cost-effectiveness of treatment, while maintaining clinical effects. This protocol describes the design of a pilot study for the evaluation of the feasibility, acceptability and cost-effectiveness of blended cognitive behavioural therapy for patients with major depressive disorder in specialized outpatient mental health care.
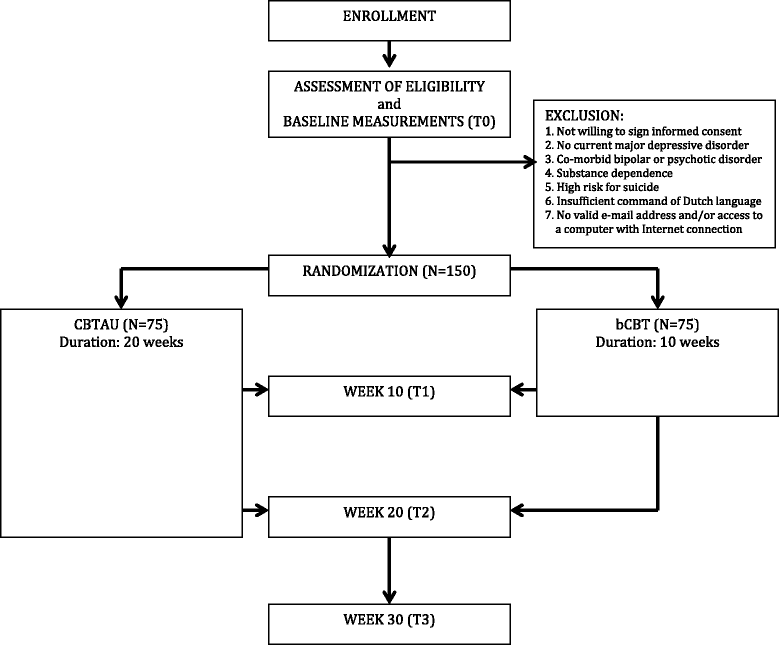
Methods/design: In a randomized controlled trial design, adult patients with major depressive disorder are allocated to either blended cognitive behavioural treatment or traditional face-to-face cognitive behavioural treatment (treatment as usual). We aim to recruit one hundred and fifty patients. Blended treatment will consist of ten face-to-face and nine online sessions provided alternately on a weekly basis. Traditional cognitive behavioural treatment will consist of twenty weekly sessions. Costs and effects are measured at baseline and after 10, 20 and 30 weeks. Evaluations are directed at cost-effectiveness (with depression severity and diagnostic status as outcomes), and cost-utility (with costs per quality adjusted life year, QALY, as outcome). Costs will encompass health care uptake costs and productivity losses due to absence from work and lower levels of efficiency while at work. Other measures of interest are mastery, working alliance, treatment preference at baseline, depressive cognitions, treatment satisfaction and system usability.
Discussion: The results of this pilot study will provide an initial insight into the feasibility and acceptability of blended cognitive behavioural treatment in terms of clinical and economic outcomes (proof of concept) in routine specialized mental health care settings, and an indication as to whether a well-powered clinical trial of blended cognitive behavioural treatment for depression in routine practice would be advisable. This will be determined based on the perspective of various stakeholders including patients, mental health service providers and health insurers. Strengths and limitations of the study are discussed.
Trial registration: Netherlands Trial Register NTR4650 . Registered 18 June 2014.
Similar articles
-
Effectiveness of blended depression treatment for adults in specialised mental healthcare: study protocol for a randomised controlled trial.BMC Psychiatry. 2016 Apr 21;16:113. doi: 10.1186/s12888-016-0818-5. BMC Psychiatry. 2016. PMID: 27102812 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cost-effectiveness of blended vs. face-to-face cognitive behavioural therapy for severe anxiety disorders: study protocol of a randomized controlled trial.BMC Psychiatry. 2015 Dec 12;15:311. doi: 10.1186/s12888-015-0697-1. BMC Psychiatry. 2015. PMID: 26651478 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Cost and Effectiveness of Blended Versus Standard Cognitive Behavioral Therapy for Outpatients With Depression in Routine Specialized Mental Health Care: Pilot Randomized Controlled Trial.J Med Internet Res. 2019 Oct 29;21(10):e14261. doi: 10.2196/14261. J Med Internet Res. 2019. PMID: 31663855 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical efficacy and economic evaluation of online cognitive behavioral therapy for major depressive disorder: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2018 Feb;18(1):25-41. doi: 10.1080/14737167.2018.1407245. Epub 2017 Nov 30. Expert Rev Pharmacoecon Outcomes Res. 2018. PMID: 29145746 Review.
-
Group cognitive behavioural therapy for postnatal depression: a systematic review of clinical effectiveness, cost-effectiveness and value of information analyses.Health Technol Assess. 2010 Sep;14(44):1-107, iii-iv. doi: 10.3310/hta14440. Health Technol Assess. 2010. PMID: 20863477 Review.
Cited by
-
Mapping review of 'proof-of-concept' in mental health implementation research using the TRL framework: a need for a better focus and conceptual clarification.BMJ Open. 2024 Aug 22;14(8):e080078. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2023-080078. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 39179274 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Novel Blended Transdiagnostic Intervention (eOrygen) for Youth Psychosis and Borderline Personality Disorder: Uncontrolled Single-Group Pilot Study.JMIR Ment Health. 2024 Apr 1;11:e49217. doi: 10.2196/49217. JMIR Ment Health. 2024. PMID: 38557432 Free PMC article.
-
An Adjunctive Internet-Based Intervention to Enhance Treatment for Depression in Adults: Randomized Controlled Trial.JMIR Ment Health. 2021 Dec 16;8(12):e26814. doi: 10.2196/26814. JMIR Ment Health. 2021. PMID: 34927594 Free PMC article.
-
Does it blend? Exploring therapist fidelity in blended CBT for anxiety disorders.Internet Interv. 2021 Jun 26;25:100418. doi: 10.1016/j.invent.2021.100418. eCollection 2021 Sep. Internet Interv. 2021. PMID: 34401377 Free PMC article.
-
Pragmatic Quasi-Experimental Controlled Trial Evaluating the Outcomes of Blended CBT Compared to Face-to-Face CBT and Treatment as Usual for Adolescents with Depressive Disorders.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021 Mar 17;18(6):3102. doi: 10.3390/ijerph18063102. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2021. PMID: 33802913 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Smit F, Cuijpers P, Oostenbrink J, Batelaan N, de Graaf R, Beekman A. Costs of nine common mental disorders: implications for curative and preventive psychiatry. J Ment Health Policy Econ. 2006;9:193–200. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources