Ambroxol improves lysosomal biochemistry in glucocerebrosidase mutation-linked Parkinson disease cells
- PMID: 24574503
- PMCID: PMC3999713
- DOI: 10.1093/brain/awu020
Ambroxol improves lysosomal biochemistry in glucocerebrosidase mutation-linked Parkinson disease cells
Abstract
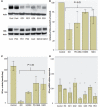
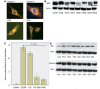
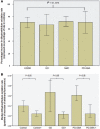
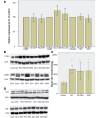
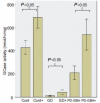
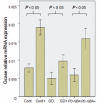
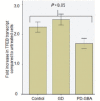
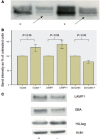
Gaucher disease is caused by mutations in the glucocerebrosidase gene, which encodes the lysosomal hydrolase glucosylceramidase. Patients with Gaucher disease and heterozygous glucocerebrosidase mutation carriers are at increased risk of developing Parkinson's disease. Indeed, glucocerebrosidase mutations are the most frequent risk factor for Parkinson's disease in the general population. Therefore there is an urgent need to understand the mechanisms by which glucocerebrosidase mutations predispose to neurodegeneration to facilitate development of novel treatments. To study this we generated fibroblast lines from skin biopsies of five patients with Gaucher disease and six heterozygous glucocerebrosidase mutation carriers with and without Parkinson's disease. Glucosylceramidase protein and enzyme activity levels were assayed. Oxidative stress was assayed by single cell imaging of dihydroethidium. Glucosylceramidase enzyme activity was significantly reduced in fibroblasts from patients with Gaucher disease (median 5% of controls, P = 0.0001) and heterozygous mutation carriers with (median 59% of controls, P = 0.001) and without (56% of controls, P = 0.001) Parkinson's disease compared with controls. Glucosylceramidase protein levels, assessed by western blot, were significantly reduced in fibroblasts from Gaucher disease (median glucosylceramidase levels 42% of control, P < 0.001) and heterozygous mutation carriers with (median 59% of control, P < 0.001) and without (median 68% of control, P < 0.001) Parkinson's disease. Single cell imaging of dihydroethidium demonstrated increased production of cytosolic reactive oxygen species in fibroblasts from patients with Gaucher disease (dihydroethidium oxidation rate increased by a median of 62% compared to controls, P < 0.001) and heterozygous mutation carriers with (dihydroethidium oxidation rate increased by a median of 68% compared with controls, P < 0.001) and without (dihydroethidium oxidation rate increased by a median of 70% compared with controls, P < 0.001) Parkinson's disease. We hypothesized that treatment with the molecular chaperone ambroxol hydrochloride would improve these biochemical abnormalities. Treatment with ambroxol hydrochloride increased glucosylceramidase activity in fibroblasts from healthy controls, Gaucher disease and heterozygous glucocerebrosidase mutation carriers with and without Parkinson's disease. This was associated with a significant reduction in dihydroethidium oxidation rate of ∼50% (P < 0.05) in fibroblasts from controls, Gaucher disease and heterozygous mutation carriers with and without Parkinson's disease. In conclusion, glucocerebrosidase mutations are associated with reductions in glucosylceramidase activity and evidence of oxidative stress. Ambroxol treatment significantly increases glucosylceramidase activity and reduces markers of oxidative stress in cells bearing glucocerebrosidase mutations. We propose that ambroxol hydrochloride should be further investigated as a potential treatment for Parkinson's disease.
Keywords: Gaucher disease; Parkinson’s disease; ambroxol; glucocerebrosidase; lysosome.
Figures

Comment in
-
Magic shotgun for Parkinson's disease?Brain. 2014 May;137(Pt 5):1274-5. doi: 10.1093/brain/awu076. Brain. 2014. PMID: 24771397 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Parkinson's disease in patients and obligate carriers of Gaucher disease.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013 Jan;19(1):129-31. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2012.06.023. Epub 2012 Aug 31. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2013. PMID: 22940477
-
Ambroxol-induced rescue of defective glucocerebrosidase is associated with increased LIMP-2 and saposin C levels in GBA1 mutant Parkinson's disease cells.Neurobiol Dis. 2015 Oct;82:235-242. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2015.06.008. Epub 2015 Jun 19. Neurobiol Dis. 2015. PMID: 26094596
-
Glucocerebrosidase activity in Parkinson's disease with and without GBA mutations.Brain. 2015 Sep;138(Pt 9):2648-58. doi: 10.1093/brain/awv179. Epub 2015 Jun 27. Brain. 2015. PMID: 26117366 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular mechanisms of the ambroxol action in Gaucher disease and GBA1 mutation-associated Parkinson disease.Neurochem Int. 2024 Sep;178:105774. doi: 10.1016/j.neuint.2024.105774. Epub 2024 May 24. Neurochem Int. 2024. PMID: 38797393 Review.
-
Combined beta-glucosylceramide and ambroxol hydrochloride in patients with Gaucher related Parkinson disease: From clinical observations to drug development.Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2018 Feb;68:117-120. doi: 10.1016/j.bcmd.2016.10.028. Epub 2016 Nov 12. Blood Cells Mol Dis. 2018. PMID: 27866808 Review.
Cited by
-
Clinical, mechanistic, biomarker, and therapeutic advances in GBA1-associated Parkinson's disease.Transl Neurodegener. 2024 Sep 12;13(1):48. doi: 10.1186/s40035-024-00437-6. Transl Neurodegener. 2024. PMID: 39267121 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysosomal dysfunction in α-synuclein pathology: molecular mechanisms and therapeutic strategies.Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024 Sep 3;81(1):382. doi: 10.1007/s00018-024-05419-5. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2024. PMID: 39223418 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A PIKfyve modulator combined with an integrated stress response inhibitor to treat lysosomal storage diseases.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Aug 20;121(34):e2320257121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2320257121. Epub 2024 Aug 16. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39150784
-
GBA1-Associated Parkinson's Disease Is a Distinct Entity.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 28;25(13):7102. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137102. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000225 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Study protocol of the GRoningen early-PD Ambroxol treatment (GREAT) trial: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled, single center trial with ambroxol in Parkinson patients with a GBA mutation.BMC Neurol. 2024 May 1;24(1):146. doi: 10.1186/s12883-024-03629-9. BMC Neurol. 2024. PMID: 38693511 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Alvarez-Erviti L, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Cooper JM, Caballero C, Ferrer I, Obeso JA, et al. Chaperone-mediated autophagy markers in Parkinson disease brains. Arch Neurol. 2010;67:1464–72. - PubMed
-
- Aureli M, Bassi R, Loberto M, Regis S, Prinetti A, Chigorno V, et al. Cell surface associated glycohydrolases in normal and Gaucher disease fibroblasts. J Inherit Metab Dis. 2012;5:1081–91. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases


