The trace amine associated receptor 1 agonist RO5263397 attenuates the induction of cocaine behavioral sensitization in rats
- PMID: 24561093
- PMCID: PMC3991844
- DOI: 10.1016/j.neulet.2014.02.024
The trace amine associated receptor 1 agonist RO5263397 attenuates the induction of cocaine behavioral sensitization in rats
Abstract
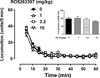
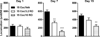
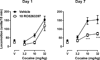
The trace amine associated receptor (TAAR) 1 is a new G protein coupled receptor that critically modulates central dopaminergic system. Recently, several selective TAAR 1 ligands have been described to possess antipsychotic and antidepressant-like activities. However, it is unknown of the role of these ligands in modulating psychostimulant-induced neurobehavioral plasticity. This study examined the effects of a selective TAAR 1 agonist, RO5263397, on cocaine induced behavioral sensitization in rats, a rodent model of drug-induced behavioral plasticity. Daily treatment with 15mg/kg cocaine (i.p., 7 days) induced robust locomotor sensitization in rats. RO5263397 (1-10mg/kg, i.p.) alone did not significantly alter the locomotor activity. Acute treatment with RO5263397 (3.2 and 10mg/kg) did not significantly modify cocaine-induced hyperactivity; however, the induction of locomotor sensitization was significantly blocked after 7 days of daily RO5263397 treatment. More importantly, the expression of locomotor sensitization remained significantly attenuated when rats were re-tested 7 days after the last drug treatment. The marked attenuation of cocaine sensitization was also evidenced by the suppression of the dose-effect function (3.2-32mg/kg) of cocaine sensitization. Together, these data represent the first to report a critical modulatory role of TAAR 1 agonists in cocaine-induced behavioral plasticity, which may be indicative of its potential role for altering other long-lasting behavioral maladaptations of cocaine including drug addiction.
Keywords: Behavioral sensitization; Cocaine; Rats; TAAR 1.
Copyright © 2014 Elsevier Ireland Ltd. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
None.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of the trace amine-associated receptor 1 agonist RO5263397 on abuse-related effects of cocaine in rats.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014 Sep;39(10):2309-16. doi: 10.1038/npp.2014.91. Epub 2014 Apr 18. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2014. PMID: 24743376 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of the trace amine associated receptor 1 agonist RO5263397 on abuse-related behavioral indices of methamphetamine in rats.Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014 Oct 31;18(4):pyu060. doi: 10.1093/ijnp/pyu060. Int J Neuropsychopharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25522401 Free PMC article.
-
Trace amine-associated receptor 1: A promising target for the treatment of psychostimulant addiction.Eur J Pharmacol. 2015 Aug 15;761:345-52. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2015.06.019. Epub 2015 Jun 16. Eur J Pharmacol. 2015. PMID: 26092759 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Dissociable effects of the kappa-opioid receptor agonists bremazocine, U69593, and U50488H on locomotor activity and long-term behavioral sensitization induced by amphetamine and cocaine.Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000 May;150(1):35-44. doi: 10.1007/s002130000424. Psychopharmacology (Berl). 2000. PMID: 10867974
-
Neuropsychotoxicity of abused drugs: effects of serotonin receptor ligands on methamphetamine- and cocaine-induced behavioral sensitization in mice.J Pharmacol Sci. 2008 Jan;106(1):15-21. doi: 10.1254/jphs.fm0070121. Epub 2008 Jan 16. J Pharmacol Sci. 2008. PMID: 18198473 Review.
Cited by
-
Trace amine-associated receptor 1 and drug abuse.Adv Pharmacol. 2022;93:373-401. doi: 10.1016/bs.apha.2021.10.005. Epub 2021 Nov 11. Adv Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35341572 Free PMC article.
-
Therapeutic Potential of TAAR1 Agonists in Schizophrenia: Evidence from Preclinical Models and Clinical Studies.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 Dec 7;22(24):13185. doi: 10.3390/ijms222413185. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34947997 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lateral hypothalamic LEPR neurons drive appetitive but not consummatory behaviors.Cell Rep. 2021 Aug 24;36(8):109615. doi: 10.1016/j.celrep.2021.109615. Cell Rep. 2021. PMID: 34433027 Free PMC article.
-
Activation of trace amine-associated receptor 1 attenuates nicotine withdrawal-related effects.Addict Biol. 2022 Jan;27(1):e13075. doi: 10.1111/adb.13075. Epub 2021 Jun 25. Addict Biol. 2022. PMID: 34170054 Free PMC article.
-
Effects of a trace amine-associated receptor 1 agonist RO 5263397 on ethanol-induced behavioral sensitization.Behav Brain Res. 2020 Jul 15;390:112641. doi: 10.1016/j.bbr.2020.112641. Epub 2020 May 12. Behav Brain Res. 2020. PMID: 32407821 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Baladi MG, Koek W, Aumann M, Velasco F, France CP. Eating high fat chow enhances the locomotor-stimulating effects of cocaine in adolescent and adult female rats. Psychopharmacology (Berl) 2012;222:447–457. - PubMed
-
- Borowsky B, Adham N, Jones KA, Raddatz R, Artymyshyn R, Ogozalek KL, Durkin MM, Lakhlani PP, Bonini JA, Pathirana S, Boyle N, Pu X, Kouranova E, Lichtblau H, Ochoa FY, Branchek TA, Gerald C. Trace amines: identification of a family of mammalian G protein-coupled receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2001;98:8966–8971. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bradaia A, Trube G, Stalder H, Norcross RD, Ozmen L, Wettstein JG, Pinard A, Buchy D, Gassmann M, Hoener MC, Bettler B. The selective antagonist EPPTB reveals TAAR1-mediated regulatory mechanisms in dopaminergic neurons of the mesolimbic system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2009;106:20081–20086. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


