Pharmacognostic and phytochemical studies on Ficus Microcarpa L. fil
- PMID: 24167337
- PMCID: PMC3807953
- DOI: 10.4103/0257-7941.118550
Pharmacognostic and phytochemical studies on Ficus Microcarpa L. fil
Abstract
Background: Ficus microcarpa L. fil. (Syn: Ficus retusa) (Moraceae) is well-known traditional medicinal plant. The bark is used for diverse health ailments in traditional and folklore remedies.
Aims: The present study was undertaken to lay down pharmacognostical and phytochemical standards.
Materials and methods: Pharmacognostic studies on fresh, dried and powdered bark was carried out to determine it's morphological, anatomical, and phytochemical diagnostic features. Furthermore, major phytoconstituents were identified from the extracts with the help of high performance liquid chromatography (HPLC) study.
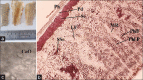
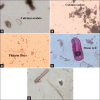
Results: The morphology showed to be soft, brittle, rough, shallow vertical, irregularly oriented fissures, curved surface; with splintering, laminated fracture. Microscopically F. microcarpa showed all general characteristics of bark with some distinct differentiation. The phellem is thin and even, phelloderm few cell and rectangular and followed by smaller sclerides, the phloem rays are broad, multi-serrate and showed the scattered bundles of sclerides. The fluorescence and physicochemical standards for bark were established. HPLC analysis showed the predominant presence of therapeutically important phytoconstituents such as oleanolic, betulinic acid, lupeol, β-sitosterol, catechin, and gallic acid.
Conclusion: The bark of F. microcarpa considered equivalent to other Ficus species, such as Ficus virens, Ficus infectoria, Ficus arnottiana, Ficus lacor, and Ficus talboti. However, there is no pharmacognostical and phytochemical reports on F. microcarpa to authenticate and differentiate it from similar species. Present work has described pharmacognostical and phytochemical characteristics of F. microcarpa and diagnostic features to differentiate it.
Keywords: Ficus microcarpa; Ficus retusa; pharmacognostic; phytochemical study.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Pharmacognostic study and development of quality control parameters for fruit, bark and leaf of Zanthoxylum armatum (Rutaceae).Anc Sci Life. 2015 Jan-Mar;34(3):147-55. doi: 10.4103/0257-7941.157159. Anc Sci Life. 2015. PMID: 26120229 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacognostic standardization and preliminary phytochemical studies of Gaultheria trichophylla.Pharm Biol. 2015;53(12):1711-8. doi: 10.3109/13880209.2014.1003355. Epub 2015 Apr 13. Pharm Biol. 2015. PMID: 25865038
-
Isolation and identification of antioxidant and hyaluronidase inhibitory compounds from Ficus microcarpa L. fil. bark.J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2010 Jun;25(3):406-13. doi: 10.3109/14756360903213473. J Enzyme Inhib Med Chem. 2010. PMID: 20233084
-
Phytochemistry, pharmacology and ethnomedicinal uses of Ficus thonningii (Blume Moraceae): a review.Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012 Dec 31;10(2):203-12. doi: 10.4314/ajtcam.v10i2.4. eCollection 2013. Afr J Tradit Complement Altern Med. 2012. PMID: 24146443 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Review on fresh and dried figs: Chemical analysis and occurrence of phytochemical compounds, antioxidant capacity and health effects.Food Res Int. 2019 May;119:244-267. doi: 10.1016/j.foodres.2019.01.055. Epub 2019 Jan 24. Food Res Int. 2019. PMID: 30884655 Review.
Cited by
-
DNA barcoding, micromorphology and metabolic traits of selected Ficus L. (Moraceae) species from Egypt.BMC Plant Biol. 2024 Nov 13;24(1):1067. doi: 10.1186/s12870-024-05683-4. BMC Plant Biol. 2024. PMID: 39538137 Free PMC article.
-
Antibacterial potential of chalcones and its derivatives against Staphylococcus aureus.3 Biotech. 2023 Jan;13(1):1. doi: 10.1007/s13205-022-03398-7. Epub 2022 Dec 1. 3 Biotech. 2023. PMID: 36466769 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Kuo YH, Li YC. Constituents of the bark of Ficus microcarpa L. f. J Chin Chem Soc. 1997;44:321–5.
-
- Ao C, Li A, Elzaawely AA, Xuan TD, Tawata S. Evaluation of antioxidant and antibacterial activities of Ficus microcarpa L. fil. Extract. Food Control. 2008;19:940–8.
-
- Taira T, Ohdomari A, Nakama N, Shimoji M, Ishihara M. Characterization and antifungal activity of gazyumaru (Ficus microcarpa) latex chitinases: Both the chitin-binding and the antifungal activities of class I chitinase are reinforced with increasing ionic strength. Biosci Biotechnol Biochem. 2005;69:811–8. - PubMed
-
- Liu LH, Wang LS, Liu XM. Comparison of antitussive, expectorant and antiasthmatic activities of different extracts from Ficus microcarpa. J Med Plant Res. 2009;8:596–9.
-
- Kirtikar KR, Basu BD. 2nd ed. II. Deharadun, India: International Book Distribution; 1987. Indian Medicinal Plants.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous


