Enveloped viruses disable innate immune responses in dendritic cells by direct activation of TAM receptors
- PMID: 23954153
- PMCID: PMC3779433
- DOI: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.005
Enveloped viruses disable innate immune responses in dendritic cells by direct activation of TAM receptors
Abstract
Upon activation by the ligands Gas6 and Protein S, Tyro3/Axl/Mer (TAM) receptor tyrosine kinases promote phagocytic clearance of apoptotic cells and downregulate immune responses initiated by Toll-like receptors and type I interferons (IFNs). Many enveloped viruses display the phospholipid phosphatidylserine on their membranes, through which they bind Gas6 and Protein S and engage TAM receptors. We find that ligand-coated viruses activate TAM receptors on dendritic cells (DCs), dampen type I IFN signaling, and thereby evade host immunity and promote infection. Upon virus challenge, TAM-deficient DCs display type I IFN responses that are elevated in comparison to wild-type cells. As a consequence, TAM-deficient DCs are relatively resistant to infection by flaviviruses and pseudotyped retroviruses, but infection can be restored with neutralizing type I IFN antibodies. Correspondingly, a TAM kinase inhibitor antagonizes the infection of wild-type DCs. Thus, TAM receptors are engaged by viruses in order to attenuate type I IFN signaling and represent potential therapeutic targets.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
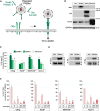
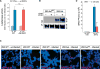

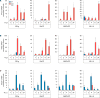
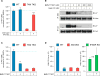
Comment in
-
Viruses PLAY DEAD to TAMe interferon responses.Cell Host Microbe. 2013 Aug 14;14(2):117-8. doi: 10.1016/j.chom.2013.07.014. Cell Host Microbe. 2013. PMID: 23954149 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Receptor tyrosine kinases, TYRO3, AXL, and MER, demonstrate distinct patterns and complex regulation of ligand-induced activation.J Biol Chem. 2014 Sep 12;289(37):25750-63. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M114.569020. Epub 2014 Jul 29. J Biol Chem. 2014. PMID: 25074926 Free PMC article.
-
Differential TAM receptor-ligand-phospholipid interactions delimit differential TAM bioactivities.Elife. 2014 Sep 29;3:e03385. doi: 10.7554/eLife.03385. Elife. 2014. PMID: 25265470 Free PMC article.
-
The TAM receptor Mertk protects against neuroinvasive viral infection by maintaining blood-brain barrier integrity.Nat Med. 2015 Dec;21(12):1464-72. doi: 10.1038/nm.3974. Epub 2015 Nov 2. Nat Med. 2015. PMID: 26523970 Free PMC article.
-
TAM receptors: A phosphatidylserine receptor family and its implications in viral infections.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020;357:81-122. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2020.09.003. Epub 2020 Oct 29. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2020. PMID: 33234246 Review.
-
TAM receptor tyrosine kinase function and the immunopathology of liver disease.Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016 Jun 1;310(11):G899-905. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.00382.2015. Epub 2016 Feb 11. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26867565 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The ability of human TIM1 to bind phosphatidylethanolamine enhances viral uptake and efferocytosis compared to rhesus and mouse orthologs.J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0164924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01649-24. Epub 2024 Oct 30. J Virol. 2024. PMID: 39475278 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular insights into human phosphatidylserine synthase 1 reveal its inhibition promotes LDL uptake.Cell. 2024 Oct 3;187(20):5665-5678.e18. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2024.08.004. Epub 2024 Aug 28. Cell. 2024. PMID: 39208797
-
The ability of human TIM1 to bind phosphatidylethanolamine enhances viral uptake and efferocytosis compared to rhesus and mouse orthologs.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 29:2024.07.29.605603. doi: 10.1101/2024.07.29.605603. bioRxiv. 2024. Update in: J Virol. 2024 Nov 19;98(11):e0164924. doi: 10.1128/jvi.01649-24 PMID: 39131348 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
-
Zika Virus Neuropathogenesis-Research and Understanding.Pathogens. 2024 Jul 2;13(7):555. doi: 10.3390/pathogens13070555. Pathogens. 2024. PMID: 39057782 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In the Eyes of the Beholder-New Mertk Knockout Mouse and Re-Evaluation of Phagocytosis versus Anti-Inflammatory Functions of MERTK.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 13;25(10):5299. doi: 10.3390/ijms25105299. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38791338 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Beasley DW, Li L, Suderman MT, Barrett AD. Mouse neuroinvasive phenotype of West Nile virus strains varies depending upon virus genotype. Virology. 2002;296:17–23. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


