Galactose 6-O-sulfotransferases are not required for the generation of Siglec-F ligands in leukocytes or lung tissue
- PMID: 23880769
- PMCID: PMC3772201
- DOI: 10.1074/jbc.M113.485409
Galactose 6-O-sulfotransferases are not required for the generation of Siglec-F ligands in leukocytes or lung tissue
Abstract
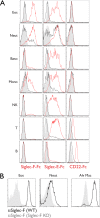
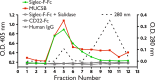
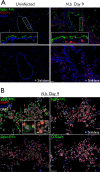
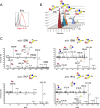
Eosinophil accumulation is a characteristic feature of the immune response to parasitic worms and allergens. The cell surface carbohydrate-binding receptor Siglec-F is highly expressed on eosinophils and negatively regulates their accumulation during inflammation. Although endogenous ligands for Siglec-F have yet to be biochemically defined, binding studies using glycan arrays have implicated galactose 6-O-sulfate (Gal6S) as a partial recognition determinant for this receptor. Only two sulfotransferases are known to generate Gal6S, namely keratan sulfate galactose 6-O-sulfotransferase (KSGal6ST) and chondroitin 6-O-sulfotransferase 1 (C6ST-1). Here we use mice deficient in both KSGal6ST and C6ST-1 to determine whether these sulfotransferases are required for the generation of endogenous Siglec-F ligands. First, we characterize ligand expression on leukocyte populations and find that ligands are predominantly expressed on cell types also expressing Siglec-F, namely eosinophils, neutrophils, and alveolar macrophages. We also detect Siglec-F ligand activity in bronchoalveolar lavage fluid fractions containing polymeric secreted mucins, including MUC5B. Consistent with these observations, ligands in the lung increase dramatically during infection with the parasitic nematode, Nippostrongylus brasiliensis, which is known to induce eosinophil accumulation and mucus production. Surprisingly, Gal6S is undetectable in sialylated glycans from eosinophils and BAL fluid analyzed by mass spectrometry. Furthermore, none of the ligands we describe are diminished in mice lacking KSGal6ST and C6ST-1, indicating that neither of the known galactose 6-O-sulfotransferases is required for ligand synthesis. These results establish that ligands for Siglec-F are present on several cell types that are relevant during allergic lung inflammation and argue against the widely held view that Gal6S is critical for glycan recognition by this receptor.
Keywords: Eosinophils; Galactose-6-O-Sulfate; Lectin; Lung; Mucins; Siglec-F; Sulfotransferase.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Airway glycomic and allergic inflammatory consequences resulting from keratan sulfate galactose 6-O-sulfotransferase (CHST1) deficiency.Glycobiology. 2018 Jun 1;28(6):406-417. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cwy025. Glycobiology. 2018. PMID: 29659839 Free PMC article.
-
KSGal6ST generates galactose-6-O-sulfate in high endothelial venules but does not contribute to L-selectin-dependent lymphocyte homing.Glycobiology. 2013 Mar;23(3):381-94. doi: 10.1093/glycob/cws166. Epub 2012 Dec 18. Glycobiology. 2013. PMID: 23254996 Free PMC article.
-
Endogenous airway mucins carry glycans that bind Siglec-F and induce eosinophil apoptosis.J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015 May;135(5):1329-1340.e9. doi: 10.1016/j.jaci.2014.10.027. Epub 2014 Dec 12. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25497369 Free PMC article.
-
The role of lung epithelial ligands for Siglec-8 and Siglec-F in eosinophilic inflammation.Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013 Feb;13(1):106-11. doi: 10.1097/ACI.0b013e32835b594a. Curr Opin Allergy Clin Immunol. 2013. PMID: 23160308 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Siglec-8 on human eosinophils and mast cells, and Siglec-F on murine eosinophils, are functionally related inhibitory receptors.Clin Exp Allergy. 2009 Mar;39(3):317-24. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.2008.03173.x. Clin Exp Allergy. 2009. PMID: 19178537 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
GlcNAc6ST2/CHST4 Is Essential for the Synthesis of R-10G-Reactive Keratan Sulfate/Sulfated N-Acetyllactosamine Oligosaccharides in Mouse Pleural Mesothelium.Molecules. 2024 Feb 7;29(4):764. doi: 10.3390/molecules29040764. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 38398516 Free PMC article.
-
Complementary Role of GlcNAc6ST2 and GlcNAc6ST3 in Synthesis of CL40-Reactive Sialylated and Sulfated Glycans in the Mouse Pleural Mesothelium.Molecules. 2022 Jul 16;27(14):4543. doi: 10.3390/molecules27144543. Molecules. 2022. PMID: 35889417 Free PMC article.
-
Siglecs in allergy and asthma.Mol Aspects Med. 2023 Apr;90:101104. doi: 10.1016/j.mam.2022.101104. Epub 2022 Jul 11. Mol Aspects Med. 2023. PMID: 35835621 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Human brain sialoglycan ligand for CD33, a microglial inhibitory Siglec implicated in Alzheimer's disease.J Biol Chem. 2022 Jun;298(6):101960. doi: 10.1016/j.jbc.2022.101960. Epub 2022 Apr 20. J Biol Chem. 2022. PMID: 35452678 Free PMC article.
-
Siglec-F Promotes IL-33-Induced Cytokine Release from Bone Marrow-Derived Eosinophils Independently of the ITIM and ITIM-like Motif Phosphorylation.J Immunol. 2022 Feb 1;208(3):732-744. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100184. Epub 2022 Jan 7. J Immunol. 2022. PMID: 34996839 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hogan S. P., Rosenberg H. F., Moqbel R., Phipps S., Foster P. S., Lacy P., Kay A. B., Rothenberg M. E. (2008) Eosinophils. Biological properties and role in health and disease. Clin. Exp. Allergy 38, 709–750 - PubMed
-
- Humbles A. A., Lloyd C. M., McMillan S. J., Friend D. S., Xanthou G., McKenna E. E., Ghiran S., Gerard N. P., Yu C., Orkin S. H., Gerard C. (2004) A critical role for eosinophils in allergic airways remodeling. Science 305, 1776–1779 - PubMed
-
- Oyoshi M. K., He R., Kanaoka Y., ElKhal A., Kawamoto S., Lewis C. N., Austen K. F., Geha R. S. (2012) Eosinophil-derived leukotriene C4 signals via type 2 cysteinyl leukotriene receptor to promote skin fibrosis in a mouse model of atopic dermatitis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 109, 4992–4997 - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ravetch J. V., Lanier L. L. (2000) Immune inhibitory receptors. Science 290, 84–89 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases


