Local potentiation of excitatory synapses by serotonin and its alteration in rodent models of depression
- PMID: 23502536
- PMCID: PMC3609911
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3355
Local potentiation of excitatory synapses by serotonin and its alteration in rodent models of depression
Abstract
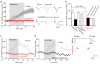
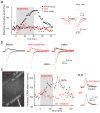
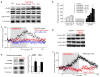
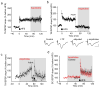
The causes of major depression remain unknown. Antidepressants elevate concentrations of monoamines, particularly serotonin, but it remains uncertain which downstream events are critical to their therapeutic effects. We found that endogenous serotonin selectively potentiated excitatory synapses formed by the temporoammonic pathway with CA1 pyramidal cells via activation of serotonin receptors (5-HT(1B)Rs), without affecting nearby Schaffer collateral synapses. This potentiation was expressed postsynaptically by AMPA-type glutamate receptors and required calmodulin-dependent protein kinase-mediated phosphorylation of GluA1 subunits. Because they share common expression mechanisms, long-term potentiation and serotonin-induced potentiation occluded each other. Long-term consolidation of spatial learning, a function of temporoammonic-CA1 synapses, was enhanced by 5-HT(1B)R antagonists. Serotonin-induced potentiation was quantitatively and qualitatively altered in a rat model of depression, restored by chronic antidepressants, and required for the ability of chronic antidepressants to reverse stress-induced anhedonia. Changes in serotonin-mediated potentiation, and its recovery by antidepressants, implicate excitatory synapses as a locus of plasticity in depression.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare they have no conflicting financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor-dependent long-term potentiation in CA1 region affects synaptic expression of glutamate receptor subunits and associated proteins in the whole hippocampus.Neuroscience. 2006 Sep 1;141(3):1399-413. doi: 10.1016/j.neuroscience.2006.04.070. Epub 2006 Jun 12. Neuroscience. 2006. PMID: 16766131
-
A role for extracellular adenosine in time-dependent reversal of long-term potentiation by low-frequency stimulation at hippocampal CA1 synapses.J Neurosci. 1999 Nov 15;19(22):9728-38. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-22-09728.1999. J Neurosci. 1999. PMID: 10559382 Free PMC article.
-
Postsynaptic induction and presynaptic expression of group 1 mGluR-dependent LTD in the hippocampal CA1 region.J Neurophysiol. 2002 Mar;87(3):1395-403. doi: 10.1152/jn.00723.2001. J Neurophysiol. 2002. PMID: 11877514
-
Masking of forskolin-induced long-term potentiation by adenosine accumulation in area CA1 of the rat hippocampus.Neuroscience. 1999 Jan;88(1):69-78. doi: 10.1016/s0306-4522(98)00200-0. Neuroscience. 1999. PMID: 10051190
-
Plasticity of synapses and reward circuit function in the genesis and treatment of depression.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023 Jan;48(1):90-103. doi: 10.1038/s41386-022-01422-1. Epub 2022 Sep 3. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2023. PMID: 36057649 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
AMPA receptors modulate enhanced dopamine neuronal activity induced by the combined administration of venlafaxine and brexpiprazole.Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024 Dec;49(13):2042-2051. doi: 10.1038/s41386-024-01958-4. Epub 2024 Aug 15. Neuropsychopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39147870 Free PMC article.
-
Fluoxetine Rescues Excessive Myelin Formation and Psychological Behaviors in a Murine PTSD Model.Neurosci Bull. 2024 Aug;40(8):1037-1052. doi: 10.1007/s12264-024-01249-4. Epub 2024 Jul 16. Neurosci Bull. 2024. PMID: 39014176
-
Serotonin Signaling in Hippocampus during Initial Cocaine Abstinence Drives Persistent Drug Seeking.J Neurosci. 2024 Apr 24;44(17):e1505212024. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1505-21.2024. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38514181 Free PMC article.
-
Single-nucleus transcriptomic analysis reveals the relationship between gene expression in oligodendrocyte lineage and major depressive disorder.J Transl Med. 2024 Jan 27;22(1):109. doi: 10.1186/s12967-023-04727-x. J Transl Med. 2024. PMID: 38281050 Free PMC article.
-
Neuronal atg1 Coordinates Autophagy Induction and Physiological Adaptations to Balance mTORC1 Signalling.Cells. 2023 Aug 8;12(16):2024. doi: 10.3390/cells12162024. Cells. 2023. PMID: 37626835 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Cai X, Liang CW, Muralidharan S, Kao JPY, Tang CM, Thompson SM. Unique roles of SK and Kv4.2 potassium channels in dendritic integration. Neuron. 2004;44:351–364. - PubMed
-
- Dewar KM, Grondin L, Carli M, Lima L, Reader TA. [3H]paroxetine binding and serotonin content of rat cortical areas, hippocampus, neostriatum, ventral mesencephalic tegmentum, and midbrain raphe nuclei region following p-chlorophenylalanine and p-chloroamphetamine treatment. J Neurochem. 1992;58:250–257. - PubMed
-
- Remondes M, Schuman EM. Role for a cortical input to hippocampal area CA1 in the consolidation of a long-term memory. Nature. 2004;431:699–703. - PubMed
-
- Santarelli L, Saxe M, Gross C, Surget A, Battaglia F, Dulawa S, Weisstaub N, Lee J, Duman R, Arancio O, Belzung C, Hen R. Requirement of hippocampal neurogenesis for the behavioral effects of antidepressants. Science. 2003;301:805–809. - PubMed
Reference List
-
- Billings AG, Cronkite RC, Moos RH. Social-environmental factors in unipolar depression: comparisons of depressed patients and nondepressed controls. J Abnorm Psychol. 1983;92:119–133. - PubMed
-
- Heninger GR, Delgado PL, Charney DS. The revised monoamine theory of depression: a modulatory role for monoamines, based on new findings from monoamine depletion experiments in humans. Pharmacopsychiatry. 1996;29:2–11. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous


