Intraspecific evolution of human RCCX copy number variation traced by haplotypes of the CYP21A2 gene
- PMID: 23241443
- PMCID: PMC3595039
- DOI: 10.1093/gbe/evs121
Intraspecific evolution of human RCCX copy number variation traced by haplotypes of the CYP21A2 gene
Abstract
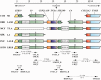
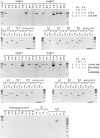
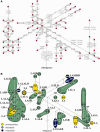
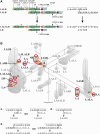
The RCCX region is a complex, multiallelic, tandem copy number variation (CNV). Two complete genes, complement component 4 (C4) and steroid 21-hydroxylase (CYP21A2, formerly CYP21B), reside in its variable region. RCCX is prone to nonallelic homologous recombination (NAHR) such as unequal crossover, generating duplications and deletions of RCCX modules, and gene conversion. A series of allele-specific long-range polymerase chain reaction coupled to the whole-gene sequencing of CYP21A2 was developed for molecular haplotyping. By means of the developed techniques, 35 different kinds of CYP21A2 haplotype variant were experimentally determined from 112 unrelated European subjects. The number of the resolved CYP21A2 haplotype variants was increased to 61 by bioinformatic haplotype reconstruction. The CYP21A2 haplotype variants could be assigned to the haplotypic RCCX CNV structures (the copy number of RCCX modules) in most cases. The genealogy network constructed from the CYP21A2 haplotype variants delineated the origin of RCCX structures. The different RCCX structures were located in tight groups. The minority of groups with identical RCCX structure occurred once in the network, implying monophyletic origin, but the majority of groups occurred several times and in different locations, indicating polyphyletic origin. The monophyletic groups were often created by single unequal crossover, whereas recurrent unequal crossover events generated some of the polyphyletic groups. As a result of recurrent NAHR events, more CYP21A2 haplotype variants with different allele patterns belonged to the same RCCX structure. The intraspecific evolution of RCCX CNV described here has provided a reasonable expectation for that of complex, multiallelic, tandem CNVs in humans.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Genes and Pseudogenes: Complexity of the RCCX Locus and Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 30;12:709758. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.709758. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34394006 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A unique haplotype of RCCX copy number variation: from the clinics of congenital adrenal hyperplasia to evolutionary genetics.Eur J Hum Genet. 2017 Jun;25(6):702-710. doi: 10.1038/ejhg.2017.38. Epub 2017 Apr 12. Eur J Hum Genet. 2017. PMID: 28401898 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-tuned characterization of RCCX copy number variants and their relationship with extended MHC haplotypes.Genes Immun. 2012 Oct;13(7):530-5. doi: 10.1038/gene.2012.29. Epub 2012 Jul 12. Genes Immun. 2012. PMID: 22785613
-
The pathogenic p.Gln319Ter variant is not causing congenital adrenal hyperplasia when inherited in one of the duplicated CYP21A2 genes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023 May 31;14:1156616. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1156616. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37324257 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular genetics of 21-hydroxylase deficiency.Endocr Dev. 2011;20:80-87. doi: 10.1159/000321223. Epub 2010 Dec 16. Endocr Dev. 2011. PMID: 21164261 Review.
Cited by
-
Genomic complexity and clinical significance of the RCCX locus.PeerJ. 2024 Nov 4;12:e18243. doi: 10.7717/peerj.18243. eCollection 2024. PeerJ. 2024. PMID: 39512309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Complex genetic variation in nearly complete human genomes.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 25:2024.09.24.614721. doi: 10.1101/2024.09.24.614721. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39372794 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Quantitative PCR from human genomic DNA: The determination of gene copy numbers for congenital adrenal hyperplasia and RCCX copy number variation.PLoS One. 2022 Dec 1;17(12):e0277299. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277299. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 36454796 Free PMC article.
-
Capturing SNP Association across the NK Receptor and HLA Gene Regions in Multiple Sclerosis by Targeted Penalised Regression Models.Genes (Basel). 2021 Dec 29;13(1):87. doi: 10.3390/genes13010087. Genes (Basel). 2021. PMID: 35052430 Free PMC article.
-
Genes and Pseudogenes: Complexity of the RCCX Locus and Disease.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021 Jul 30;12:709758. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2021.709758. eCollection 2021. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2021. PMID: 34394006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bandelt HJ, Forster P, Rohl A. Median-joining networks for inferring intraspecific phylogenies. Mol Biol Evol. 1999;16:37–48. - PubMed
-
- Banlaki Z, Doleschall M, Rajczy K, Fust G, Szilagyi A. Fine-tuned characterization of RCCX copy number variants and their relationship with extended MHC haplotypes. Genes Immun. 2012;13:530–535. - PubMed
-
- Banlaki Z, et al. ACTH-induced cortisol release is related to the copy number of the C4B gene encoding the fourth component of complement in patients with non-functional adrenal incidentaloma. Clin Endocrinol. 2012;76:478–484. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


