Anti-inflammatory iridoids of botanical origin
- PMID: 22414102
- PMCID: PMC3873812
- DOI: 10.2174/092986712800229005
Anti-inflammatory iridoids of botanical origin
Abstract
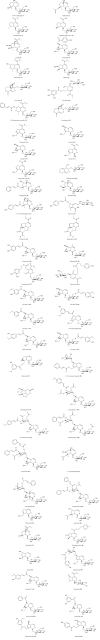
Inflammation is a manifestation of a wide range of disorders which include; arthritis, atherosclerosis, Alzheimer's disease, inflammatory bowel syndrome, physical injury and infection amongst many others. Common treatment modalities are usually nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as aspirin, paracetamol, indomethacin and ibuprofen as well as corticosteroids such as prednisone. These however, may be associated with a host of side effects due to non-selectivity for cyclooxygenase (COX) enzymes involved in inflammation and those with selectivity may be highly priced. Thus, there is a continuing search for safe and effective antiinflammatory molecules from natural sources. Research has confirmed that iridoids exhibit promising anti-inflammatory activity which may be beneficial in the treatment of inflammation. Iridoids are secondary metabolites present in various plants, especially in species belonging to the Apocynaceae, Lamiaceae, Loganiaceae, Rubiaceae, Scrophulariaceae and Verbenaceae families. Many of these ethnobotanicals have an illustrious history of traditional use alluding to their use to treat inflammation. Although iridoids exhibit a wide range of pharmacological activities such as cardiovascular, hepatoprotection, hypoglycaemic, antimutagenic, antispasmodic, anti-tumour, antiviral, immunomodulation and purgative effects this review will acutely focus on their anti-inflammatory properties. The paper aims to present a summary for the most prominent iridoid-containing plants for which anti-inflammatory activity has been demonstrated in vitro and / or in vivo.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Natural iridoids from Patrinia heterophylla showing anti-inflammatory activities in vitro and in vivo.Bioorg Chem. 2020 Nov;104:104331. doi: 10.1016/j.bioorg.2020.104331. Epub 2020 Oct 1. Bioorg Chem. 2020. PMID: 33142407
-
Biological and pharmacological activities of iridoids: recent developments.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008 Apr;8(4):399-420. doi: 10.2174/138955708783955926. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2008. PMID: 18473930 Review.
-
In vitro COX-1 and COX-2 enzyme inhibitory activities of iridoids from Penstemon barbatus, Castilleja tenuiflora, Cresentia alata and Vitex mollis.Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015 Oct 15;25(20):4505-8. doi: 10.1016/j.bmcl.2015.08.075. Epub 2015 Aug 29. Bioorg Med Chem Lett. 2015. PMID: 26351040
-
Exploring the Multitarget Potential of Iridoids: Advances and Applications.Curr Top Med Chem. 2023;23(5):371-388. doi: 10.2174/1568026623666221222142217. Curr Top Med Chem. 2023. PMID: 36567288 Review.
-
Iridoids from Morinda lucida, (Benth.) Rubiaceae, produced analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities via agonism at the kappa and delta opioid receptors, inhibition of COX-2 besides elevation of CAT and SOD activities.J Ethnopharmacol. 2023 Jun 12;309:116355. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2023.116355. Epub 2023 Mar 11. J Ethnopharmacol. 2023. PMID: 36914035
Cited by
-
Phytochemical Compounds as Promising Therapeutics for Intestinal Fibrosis in Inflammatory Bowel Disease: A Critical Review.Nutrients. 2024 Oct 25;16(21):3633. doi: 10.3390/nu16213633. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39519465 Free PMC article. Review.
-
High-Altitude Medicinal Plants as Promising Source of Phytochemical Antioxidants to Combat Lifestyle-Associated Oxidative Stress-Induced Disorders.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jul 23;17(8):975. doi: 10.3390/ph17080975. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39204080 Free PMC article. Review.
-
In vitro study on anti-proliferative and anti-cancer activity of picrosides in triple-negative breast cancer.Med Oncol. 2024 May 8;41(6):143. doi: 10.1007/s12032-024-02397-3. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38717628
-
In vitro and in silico docking and molecular dynamic of antimicrobial activities, alpha-glucosidase, and anti-inflammatory activity of compounds from the aerial parts of Mussaenda saigonensis.RSC Adv. 2024 Apr 16;14(17):12081-12095. doi: 10.1039/d4ra01865f. eCollection 2024 Apr 10. RSC Adv. 2024. PMID: 38628478 Free PMC article.
-
Extract from Aronia melanocarpa, Lonicera caerulea, and Vaccinium myrtillus Improves near Visual Acuity in People with Presbyopia.Nutrients. 2024 Mar 23;16(7):926. doi: 10.3390/nu16070926. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38612968 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
References
-
- Ríos J L, Bas E, Recio M C. Effects of natural products on contact dermatitis. Curr. Med. Chem.: Anti-inflammatory & Anti-allergy Agents. 2005;4:65–80.
-
- Sherwood L. Human Physiology: From cells to systems. 5th ed. California (US): Brooks Cole; 2003.
-
- Rang H P, Dale M M. Rang & Dale’s Pharmacology. 6th ed. Philadelphia (US): Churchill Livingstone; 2007.
-
- Harris S G, Padilla J, Koumas L, Ray D, Phipps R P. l Prostaglandins as modulators of immunity. Trends Immunol. 2002;23:144–150. - PubMed
-
- Moore M L, Peebles R S. Update on the role of prostaglandins in allergic lung inflammation: Separating friends from foes, harder than you might think. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2006;117:1036–1039. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources