The gut hormones PYY 3-36 and GLP-1 7-36 amide reduce food intake and modulate brain activity in appetite centers in humans
- PMID: 22000927
- PMCID: PMC3267038
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2011.09.010
The gut hormones PYY 3-36 and GLP-1 7-36 amide reduce food intake and modulate brain activity in appetite centers in humans
Abstract
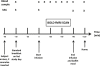
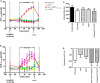
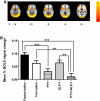
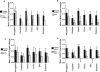
Obesity is a major public health issue worldwide. Understanding how the brain controls appetite offers promising inroads toward new therapies for obesity. Peptide YY (PYY) and glucagon-like peptide 1 (GLP-1) are coreleased postprandially and reduce appetite and inhibit food intake when administered to humans. However, the effects of GLP-1 and the ways in which PYY and GLP-1 act together to modulate brain activity in humans are unknown. Here, we have used functional MRI to determine these effects in healthy, normal-weight human subjects and compared them to those seen physiologically following a meal. We provide a demonstration that the combined administration of PYY(3-36) and GLP-1(7-36 amide) to fasted human subjects leads to similar reductions in subsequent energy intake and brain activity, as observed physiologically following feeding.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Peptide YY3-36 and glucagon-like peptide-17-36 inhibit food intake additively.Endocrinology. 2005 Dec;146(12):5120-7. doi: 10.1210/en.2005-0237. Epub 2005 Sep 8. Endocrinology. 2005. PMID: 16150917 Clinical Trial.
-
Effect of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor antagonism on appetite and food intake in healthy men.Am J Clin Nutr. 2014 Aug;100(2):514-23. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.114.083246. Epub 2014 Jun 25. Am J Clin Nutr. 2014. PMID: 24965303 Clinical Trial.
-
Mycoprotein reduces energy intake and postprandial insulin release without altering glucagon-like peptide-1 and peptide tyrosine-tyrosine concentrations in healthy overweight and obese adults: a randomised-controlled trial.Br J Nutr. 2016 Jul;116(2):360-74. doi: 10.1017/S0007114516001872. Epub 2016 May 20. Br J Nutr. 2016. PMID: 27198187 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Gut hormones as peripheral anti obesity targets.Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004 Oct;3(5):379-88. doi: 10.2174/1568007043336950. Curr Drug Targets CNS Neurol Disord. 2004. PMID: 15544446 Review.
-
Peptide YY, appetite and food intake.Proc Nutr Soc. 2005 May;64(2):213-6. doi: 10.1079/pns2005427. Proc Nutr Soc. 2005. PMID: 15960866 Review.
Cited by
-
Trends on Novel Targets and Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Parkinson's disease: Recent Advancement in Drug Development.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(15):987-1011. doi: 10.2174/0113894501312703240826070530. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 39313872 Review.
-
Improved leptin sensitivity and increased soluble leptin receptor concentrations may underlie the additive effects of combining PYY [, , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , ] and exendin-4 on body weight lowering in diet-induced obese mice.Heliyon. 2024 Jun 3;10(12):e32009. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32009. eCollection 2024 Jun 30. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39183855 Free PMC article.
-
Semaglutide treatment of hypothalamic obesity - a real-life data study.Pituitary. 2024 Oct;27(5):685-692. doi: 10.1007/s11102-024-01429-5. Epub 2024 Aug 9. Pituitary. 2024. PMID: 39120810 Free PMC article.
-
Neuroimaging and neuroendocrine insights into food cravings and appetite interventions in obesity.Psychoradiology. 2023 Oct 14;3:kkad023. doi: 10.1093/psyrad/kkad023. eCollection 2023. Psychoradiology. 2023. PMID: 38666104 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting the incretin system in obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus.Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024 Aug;20(8):447-459. doi: 10.1038/s41574-024-00979-9. Epub 2024 Apr 17. Nat Rev Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38632474 Review.
References
-
- Adam T.C.M., Jocken J., Westerterp-Plantenga M.S. Decreased glucagon-like peptide 1 release after weight loss in overweight/obese subjects. Obes. Res. 2005;13:710–716. - PubMed
-
- Batterham R.L., Cowley M.A., Small C.J., Herzog H., Cohen M.A., Dakin C.L., Wren A.M., Brynes A.E., Low M.J., Ghatei M.A. Gut hormone PYY(3-36) physiologically inhibits food intake. Nature. 2002;418:650–654. - PubMed
-
- Batterham R.L., ffytche D.H., Rosenthal J.M., Zelaya F.O., Barker G.J., Withers D.J., Williams S.C. PYY modulation of cortical and hypothalamic brain areas predicts feeding behaviour in humans. Nature. 2007;450:106–109. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


