Automated 3-D segmentation of lungs with lung cancer in CT data using a novel robust active shape model approach
- PMID: 21997248
- PMCID: PMC3657761
- DOI: 10.1109/TMI.2011.2171357
Automated 3-D segmentation of lungs with lung cancer in CT data using a novel robust active shape model approach
Abstract
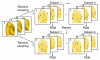
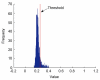
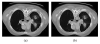
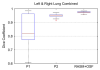
Segmentation of lungs with (large) lung cancer regions is a nontrivial problem. We present a new fully automated approach for segmentation of lungs with such high-density pathologies. Our method consists of two main processing steps. First, a novel robust active shape model (RASM) matching method is utilized to roughly segment the outline of the lungs. The initial position of the RASM is found by means of a rib cage detection method. Second, an optimal surface finding approach is utilized to further adapt the initial segmentation result to the lung. Left and right lungs are segmented individually. An evaluation on 30 data sets with 40 abnormal (lung cancer) and 20 normal left/right lungs resulted in an average Dice coefficient of 0.975±0.006 and a mean absolute surface distance error of 0.84±0.23 mm, respectively. Experiments on the same 30 data sets showed that our methods delivered statistically significant better segmentation results, compared to two commercially available lung segmentation approaches. In addition, our RASM approach is generally applicable and suitable for large shape models.
Figures
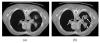
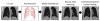
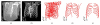
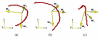


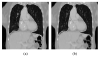
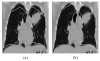
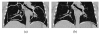
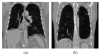

Similar articles
-
A 4D statistical shape model for automated segmentation of lungs with large tumors.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2012;15(Pt 2):347-54. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-33418-4_43. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2012. PMID: 23286067
-
Automated lung segmentation in digital chest tomosynthesis.Med Phys. 2012 Feb;39(2):732-41. doi: 10.1118/1.3671939. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22320783 Free PMC article.
-
Automated model-based rib cage segmentation and labeling in CT images.Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2007;10(Pt 2):195-202. doi: 10.1007/978-3-540-75759-7_24. Med Image Comput Comput Assist Interv. 2007. PMID: 18044569
-
Three-dimensional lung tumor segmentation from x-ray computed tomography using sparse field active models.Med Phys. 2012 Feb;39(2):851-65. doi: 10.1118/1.3676687. Med Phys. 2012. PMID: 22320795
-
Segmentation of airways in lungs using projections in 3-D CT angiography images.Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010;2010:3162-5. doi: 10.1109/IEMBS.2010.5627401. Annu Int Conf IEEE Eng Med Biol Soc. 2010. PMID: 21096807
Cited by
-
Advances in Medical Image Segmentation: A Comprehensive Review of Traditional, Deep Learning and Hybrid Approaches.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Oct 16;11(10):1034. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11101034. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39451409 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Artificial intelligence tool for the study of COVID-19 microdroplet spread across the human diameter and airborne space.PLoS One. 2023 Jul 19;18(7):e0269905. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0269905. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 37467202 Free PMC article.
-
SIFT-GVF-based lung edge correction method for correcting the lung region in CT images.PLoS One. 2023 Feb 28;18(2):e0282107. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0282107. eCollection 2023. PLoS One. 2023. PMID: 36854040 Free PMC article.
-
A Comprehensive Survey on the Progress, Process, and Challenges of Lung Cancer Detection and Classification.J Healthc Eng. 2022 Dec 16;2022:5905230. doi: 10.1155/2022/5905230. eCollection 2022. J Healthc Eng. 2022. PMID: 36569180 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Systematic Review of Automated Segmentation Methods and Public Datasets for the Lung and its Lobes and Findings on Computed Tomography Images.Yearb Med Inform. 2022 Aug;31(1):277-295. doi: 10.1055/s-0042-1742517. Epub 2022 Dec 4. Yearb Med Inform. 2022. PMID: 36463886 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Armato SG, Sensakovic WF. Automated lung segmentation for thoracic CT. Acad. Radiol. 2004;vol. 11(no. 9):1011–1021. - PubMed
-
- Leader JK, Zheng B, Rogers RM, Sciurba FC, Perez A, Chapman BE, Patel S, Fuhrman CR, Gur D. Automated lung segmentation in X-ray computed tomography. Acad. Radiol. 2003;vol. 10(no. 11):1224–1236. - PubMed
-
- Silva A, Silva JS, Santos BS, Ferreira C. Fast pulmonary contour extraction in X-ray CT images: A methodology and quality assessment. Proc. SPIE Med. Imag. 2001;vol. 4321:216–224.
-
- Hu S, Hoffman EA, Reinhardt JM. Automatic lung segmentation for accurate quantitation of volumetric X-ray CT image. IEEE Trans. Med. Imag. 2001 Jun.vol. 20(no. 6):490–498. - PubMed
-
- Hoffman EA, Ritman EL. Effect of body orientation on regional lung expansion in dog and sloth. J. Appl. Physiol. 1985;vol. 59(no. 2):481–491. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


