The landscape of recombination in African Americans
- PMID: 21775986
- PMCID: PMC3154982
- DOI: 10.1038/nature10336
The landscape of recombination in African Americans
Abstract
Recombination, together with mutation, gives rise to genetic variation in populations. Here we leverage the recent mixture of people of African and European ancestry in the Americas to build a genetic map measuring the probability of crossing over at each position in the genome, based on about 2.1 million crossovers in 30,000 unrelated African Americans. At intervals of more than three megabases it is nearly identical to a map built in Europeans. At finer scales it differs significantly, and we identify about 2,500 recombination hotspots that are active in people of West African ancestry but nearly inactive in Europeans. The probability of a crossover at these hotspots is almost fully controlled by the alleles an individual carries at PRDM9 (P value < 10(-245)). We identify a 17-base-pair DNA sequence motif that is enriched in these hotspots, and is an excellent match to the predicted binding target of PRDM9 alleles common in West Africans and rare in Europeans. Sites of this motif are predicted to be risk loci for disease-causing genomic rearrangements in individuals carrying these alleles. More generally, this map provides a resource for research in human genetic variation and evolution.
Figures
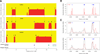
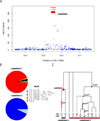
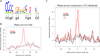
Comment in
-
Human genetics: Recombination diversified.Nat Rev Genet. 2011 Aug 2;12(9):585. doi: 10.1038/nrg3056. Nat Rev Genet. 2011. PMID: 21808263 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Variants of the protein PRDM9 differentially regulate a set of human meiotic recombination hotspots highly active in African populations.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011 Jul 26;108(30):12378-83. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1109531108. Epub 2011 Jul 12. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011. PMID: 21750151 Free PMC article.
-
A high-density admixture map for disease gene discovery in african americans.Am J Hum Genet. 2004 May;74(5):1001-13. doi: 10.1086/420856. Epub 2004 Apr 14. Am J Hum Genet. 2004. PMID: 15088270 Free PMC article.
-
Fine-scale recombination rate differences between sexes, populations and individuals.Nature. 2010 Oct 28;467(7319):1099-103. doi: 10.1038/nature09525. Nature. 2010. PMID: 20981099
-
Drive against hotspot motifs in primates implicates the PRDM9 gene in meiotic recombination.Science. 2010 Feb 12;327(5967):876-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1182363. Epub 2009 Dec 31. Science. 2010. PMID: 20044541 Free PMC article.
-
The genomic landscape of African populations in health and disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2017 Oct 1;26(R2):R225-R236. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddx253. Hum Mol Genet. 2017. PMID: 28977439 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A Minimal Hybrid Sterility Genome Assembled by Chromosome Swapping Between Mouse Subspecies (Mus musculus).Mol Biol Evol. 2024 Oct 4;41(10):msae211. doi: 10.1093/molbev/msae211. Mol Biol Evol. 2024. PMID: 39404090 Free PMC article.
-
Life history and ancestry of the late Upper Palaeolithic infant from Grotta delle Mura, Italy.Nat Commun. 2024 Sep 20;15(1):8248. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-51150-x. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39304646 Free PMC article.
-
Predicting Differentially Methylated Cytosines in TET and DNMT3 Knockout Mutants via a Large Language Model.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 Sep 4:2024.05.02.592257. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.02.592257. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 39282350 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Structural variants in linkage disequilibrium with GWAS-significant SNPs.Heliyon. 2024 May 28;10(11):e32053. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e32053. eCollection 2024 Jun 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 38882374 Free PMC article.
-
Neandertal ancestry through time: Insights from genomes of ancient and present-day humans.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 13:2024.05.13.593955. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.13.593955. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38798350 Free PMC article. Preprint.
References
-
- Jeffreys AJ, Kauppi L, Neumann R. Intensely punctate meiotic recombination in the class II region of the major histocompatibility complex. Nat. Genet. 2001;29:217–212. - PubMed
-
- McVean GA, et al. The fine-scale structure of recombination rate variation in the human genome. Science. 2004;304:581–584. - PubMed
-
- Myers S, Bottolo L, Freeman C, McVean G, Donnelly P. A fine-scale map of recombination rates and hotspots across the human genome. Science. 2005;310:321–324. - PubMed
-
- Kong A, et al. Fine-scale recombination rate differences between sexes, populations and individuals. Nature. 2010;467:1099–1103. - PubMed
-
- Kong A, et al. A high-resolution recombination map of the human genome. Nature Genetics. 2002;31:241–247. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- CA148127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA87895/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA055769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES011126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA54281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA55769/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES06717/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U19 CA148127/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01-CA73629/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA77305/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004168-03/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087895/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES010126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- RC2 CA148085/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA060691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01 HD033175/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- CA88164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES006717/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004168/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- CA1326792/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA140388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA1116460/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA121197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- RC1 GM091332/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA141716/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA121197S2/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HL084107-04/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA092447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA073629/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA127219/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA127219/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG006399/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- GM08016/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- CA121197/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ES10126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 CA058223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA068578/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100374/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HHSN268200960009C/PHS HHS/United States
- CA63464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA22453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U58 DP000807/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- R01 HL084107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA060691/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA141716/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 090532/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- CA100374/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01HC65226/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 ES007784/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA022453/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 CA063464/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- ImNIH/Intramural NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA068485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA088164/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA140388/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01PC35145/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA092447/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA100598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA1116460S1/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA68485/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- S06 GM008016/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- HL084107/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 ES011126/ES/NIEHS NIH HHS/United States
- CA58223/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01PC35139/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM091332/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA054281/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA052689/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- N01-HC-65226/HC/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- U01 HG004726/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA100598/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


