Hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes mellitus
- PMID: 20723825
- PMCID: PMC2923455
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ecl.2010.05.003
Hypoglycemia in type 1 diabetes mellitus
Abstract
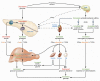
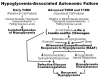
Iatrogenic hypoglycemia, typically the result of the interplay of therapeutic hyperinsulinemia and compromised defenses resulting in hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure (HAAF) in diabetes, is a problem for people with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM). It causes recurrent morbidity is sometimes fatal, leads to recurrent hypoglycemia, and precludes euglycemia over a lifetime of T1DM. Risk factors include those that result in relative or absolute insulin excess and those indicative of HAAF in diabetes. Elimination of hypoglycemia from the lives of people with T1DM will likely be accomplished by new treatment methods that provide plasma glucose-regulated insulin replacement or secretion.
Copyright 2010 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Hypoglycemia in diabetes.Diabetes Care. 2003 Jun;26(6):1902-12. doi: 10.2337/diacare.26.6.1902. Diabetes Care. 2003. PMID: 12766131 Review.
-
Mechanisms of hypoglycemia-associated autonomic failure and its component syndromes in diabetes.Diabetes. 2005 Dec;54(12):3592-601. doi: 10.2337/diabetes.54.12.3592. Diabetes. 2005. PMID: 16306382 Review.
-
Hypoglycemia in diabetes: pathophysiological mechanisms and diurnal variation.Prog Brain Res. 2006;153:361-5. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(06)53021-3. Prog Brain Res. 2006. PMID: 16876586 Review.
-
The science of hypoglycemia in patients with diabetes.Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013 May;9(3):195-208. doi: 10.2174/15733998113099990059. Curr Diabetes Rev. 2013. PMID: 23506375 Review.
-
Hypoglycemia risk reduction in type 1 diabetes.Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001;109 Suppl 2:S412-23. doi: 10.1055/s-2001-18599. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 2001. PMID: 11460588 Review.
Cited by
-
Assessing the influence of insulin type (ultra-rapid vs rapid insulin) and exercise timing on postprandial exercise-induced hypoglycaemia risk in individuals with type 1 diabetes: a randomised controlled trial.Diabetologia. 2024 Nov;67(11):2408-2419. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06234-0. Epub 2024 Jul 29. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 39069599 Clinical Trial.
-
Estimating risk of consequences following hypoglycaemia exposure using the Hypo-RESOLVE cohort: a secondary analysis of pooled data from insulin clinical trials.Diabetologia. 2024 Oct;67(10):2210-2224. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06225-1. Epub 2024 Jul 22. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 39037602 Free PMC article.
-
Recommendations for recognizing, risk stratifying, treating, and managing children and adolescents with hypoglycemia.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jun 4;15:1387537. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1387537. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38894740 Free PMC article.
-
Comparison between a tubeless, on-body automated insulin delivery system and a tubeless, on-body sensor-augmented pump in type 1 diabetes: a multicentre randomised controlled trial.Diabetologia. 2024 Jul;67(7):1235-1244. doi: 10.1007/s00125-024-06155-y. Epub 2024 Apr 18. Diabetologia. 2024. PMID: 38634887 Clinical Trial.
-
Role of the Adrenal Medulla in Hypoglycaemia-Associated Autonomic Failure-A Diabetic Perspective.Metabolites. 2024 Jan 31;14(2):100. doi: 10.3390/metabo14020100. Metabolites. 2024. PMID: 38392992 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cryer PE. Pathophysiology, Prevalence and Prevention. American Diabetes Association; Alexandria, VA: 2009. Hypoglycemia in Diabetes.
-
- The Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329(14):977–86. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- P60 DK20579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK027085/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR000036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR024992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- P60 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK27085/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- M01 RR00036/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 RR24992/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000448/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK007120/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- T32 DK07120/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK027085-29/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical


