MiR-33 contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis
- PMID: 20466885
- PMCID: PMC3114628
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1189862
MiR-33 contributes to the regulation of cholesterol homeostasis
Abstract
Cholesterol metabolism is tightly regulated at the cellular level. Here we show that miR-33, an intronic microRNA (miRNA) located within the gene encoding sterol-regulatory element-binding factor-2 (SREBF-2), a transcriptional regulator of cholesterol synthesis, modulates the expression of genes involved in cellular cholesterol transport. In mouse and human cells, miR-33 inhibits the expression of the adenosine triphosphate-binding cassette (ABC) transporter, ABCA1, thereby attenuating cholesterol efflux to apolipoprotein A1. In mouse macrophages, miR-33 also targets ABCG1, reducing cholesterol efflux to nascent high-density lipoprotein (HDL). Lentiviral delivery of miR-33 to mice represses ABCA1 expression in the liver, reducing circulating HDL levels. Conversely, silencing of miR-33 in vivo increases hepatic expression of ABCA1 and plasma HDL levels. Thus, miR-33 appears to regulate both HDL biogenesis in the liver and cellular cholesterol efflux.
Figures
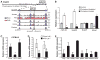

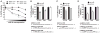
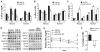
Comment in
-
Medicine. HDL miR-ed down by SREBP introns.Science. 2010 Jun 18;328(5985):1495-6. doi: 10.1126/science.1192409. Science. 2010. PMID: 20558698 Free PMC article.
-
Cardiovascular disorders: MicroRNA modulation of cholesterol.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010 Jul;9(7):515. doi: 10.1038/nrd3208. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2010. PMID: 20592742 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Control of cholesterol metabolism and plasma high-density lipoprotein levels by microRNA-144.Circ Res. 2013 Jun 7;112(12):1592-601. doi: 10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.112.300626. Epub 2013 Mar 21. Circ Res. 2013. PMID: 23519695 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNA-33 and the SREBP host genes cooperate to control cholesterol homeostasis.Science. 2010 Jun 18;328(5985):1566-9. doi: 10.1126/science.1189123. Epub 2010 May 13. Science. 2010. PMID: 20466882 Free PMC article.
-
Pro-apoptotic miRNA-128-2 modulates ABCA1, ABCG1 and RXRα expression and cholesterol homeostasis.Cell Death Dis. 2013 Aug 29;4(8):e780. doi: 10.1038/cddis.2013.301. Cell Death Dis. 2013. PMID: 23990020 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid efflux by the ATP-binding cassette transporters ABCA1 and ABCG1.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006 Jul;1761(7):655-66. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2006.04.012. Epub 2006 May 4. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2006. PMID: 16798073 Review.
-
ATP-binding cassette transporters A1 and G1, HDL metabolism, cholesterol efflux, and inflammation: important targets for the treatment of atherosclerosis.Curr Drug Targets. 2011 May;12(5):647-60. doi: 10.2174/138945011795378522. Curr Drug Targets. 2011. PMID: 21039336 Review.
Cited by
-
Deletion of miR-33, a regulator of the ABCA1-APOE pathway, ameliorates neuropathological phenotypes in APP/PS1 mice.Alzheimers Dement. 2024 Nov;20(11):7805-7818. doi: 10.1002/alz.14243. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Alzheimers Dement. 2024. PMID: 39345217 Free PMC article.
-
Emerging Trends and Innovations in the Treatment and Diagnosis of Atherosclerosis and Cardiovascular Disease: A Comprehensive Review towards Healthier Aging.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Aug 3;16(8):1037. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16081037. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39204382 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immunometabolism in atherosclerotic disorders.Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024 Jun;3(6):637-650. doi: 10.1038/s44161-024-00473-5. Epub 2024 May 23. Nat Cardiovasc Res. 2024. PMID: 39196223 Review.
-
miR-33 deletion in hepatocytes attenuates MASLD-MASH-HCC progression.JCI Insight. 2024 Aug 27;9(19):e168476. doi: 10.1172/jci.insight.168476. JCI Insight. 2024. PMID: 39190492 Free PMC article.
-
Lipid homeostasis in diabetic kidney disease.Int J Biol Sci. 2024 Jul 2;20(10):3710-3724. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.95216. eCollection 2024. Int J Biol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39113692 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous


