Methylation regulates alpha-synuclein expression and is decreased in Parkinson's disease patients' brains
- PMID: 20445061
- PMCID: PMC6632710
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6119-09.2010
Methylation regulates alpha-synuclein expression and is decreased in Parkinson's disease patients' brains
Abstract
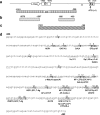
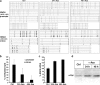
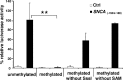
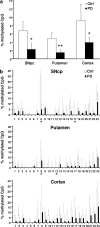
Alpha-synuclein (SNCA) is a major risk gene for Parkinson's disease (PD), and increased SNCA gene dosage results in a parkinsonian syndrome in affected families. We found that methylation of human SNCA intron 1 decreased gene expression, while inhibition of DNA methylation activated SNCA expression. Methylation of SNCA intron 1 was reduced in DNA from sporadic PD patients' substantia nigra, putamen, and cortex, pointing toward a yet unappreciated epigenetic regulation of SNCA expression in PD.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CpG demethylation enhances alpha-synuclein expression and affects the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 24;5(11):e15522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015522. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124796 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomethylation of intron1 of α-synuclein gene does not correlate with Parkinson's disease.Mol Brain. 2017 Feb 7;10(1):6. doi: 10.1186/s13041-017-0285-z. Mol Brain. 2017. PMID: 28173842 Free PMC article.
-
Hypomethylation of SNCA in blood of patients with sporadic Parkinson's disease.J Neurol Sci. 2014 Feb 15;337(1-2):123-8. doi: 10.1016/j.jns.2013.11.033. Epub 2013 Dec 1. J Neurol Sci. 2014. PMID: 24326201
-
[Neurodegeneration and epigenetics].Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2012 Nov;32(5-6):269-73. Nihon Shinkei Seishin Yakurigaku Zasshi. 2012. PMID: 23373314 Review. Japanese.
-
DNA methylation in Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 1:108-120. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13646. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27120258 Review.
Cited by
-
Trends on Novel Targets and Nanotechnology-Based Drug Delivery System in the Treatment of Parkinson's disease: Recent Advancement in Drug Development.Curr Drug Targets. 2024;25(15):987-1011. doi: 10.2174/0113894501312703240826070530. Curr Drug Targets. 2024. PMID: 39313872 Review.
-
The role of gut-derived short-chain fatty acids in Parkinson's disease.Neurogenetics. 2024 Oct;25(4):307-336. doi: 10.1007/s10048-024-00779-3. Epub 2024 Sep 13. Neurogenetics. 2024. PMID: 39266892 Review.
-
Parkinson's disease-associated shifts between DNA methylation and DNA hydroxymethylation in human brain in PD-related genes, including PARK19 (DNAJC6) and PTPRN2 (IA-2β).Res Sq [Preprint]. 2024 Jul 15:rs.3.rs-4572401. doi: 10.21203/rs.3.rs-4572401/v1. Res Sq. 2024. PMID: 39070644 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
Therapeutic Implications and Regulations of Protein Post-translational Modifications in Parkinsons Disease.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Jul 3;44(1):53. doi: 10.1007/s10571-024-01471-8. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38960968 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Neural Stem Cells in Developmental and Adult Stages.Epigenomes. 2024 Jun 4;8(2):22. doi: 10.3390/epigenomes8020022. Epigenomes. 2024. PMID: 38920623 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rüb U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E. Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson's disease. Neurobiol Aging. 2003;24:197–211. - PubMed
-
- Chahrour M, Zoghbi HY. The story of Rett syndrome: from clinic to neurobiology. Neuron. 2007;56:422–437. - PubMed
-
- Chiba-Falek O, Lopez GJ, Nussbaum RL. Levels of alpha-synuclein mRNA in sporadic Parkinson disease patients. Mov Disord. 2006;21:1703–1708. - PubMed
-
- Christensen BC, Houseman EA, Marsit CJ, Zheng S, Wrensch MR, Wiemels JL, Nelson HH, Karagas MR, Padbury JF, Bueno R, Sugarbaker DJ, Yeh RF, Wiencke JK, Kelsey KT. Aging and environmental exposures alter tissue-specific DNA methylation dependent upon CpG island context. PLoS Genet. 2009;5:e1000602. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Clough RL, Stefanis L. A novel pathway for transcriptional regulation of alpha-synuclein. FASEB J. 2007;21:596–607. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

