Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer
- PMID: 20018552
- PMCID: PMC2834864
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cytogfr.2009.11.005
Dangerous liaisons: STAT3 and NF-kappaB collaboration and crosstalk in cancer
Abstract
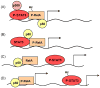
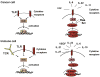
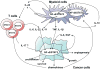
Transcriptional factors of the NF-kappaB family and STAT3 are ubiquitously expressed and control numerous physiological processes including development, differentiation, immunity, metabolism and cancer. Both NF-kappaB and STAT3 are rapidly activated in response to various stimuli including stresses and cytokines, although they are regulated by entirely different signaling mechanisms. Once activated, NF-kappaB and STAT3 control the expression of anti-apoptotic, pro-proliferative and immune response genes. Some of these genes overlap and require transcriptional cooperation between the two factors. The activation of and interaction between STAT3 and NF-kappaB plays a key role in controlling the dialog between the malignant cell and its microenvironment, especially with inflammatory/immune cells that infiltrate tumors. Quite often, cytokines whose expression is induced in response to NF-kappaB in immune cells of the tumor microenvironment lead to STAT3 activation in both malignant and immune cells. While within malignant and pre-malignant cells STAT3 exerts important oncogenic functions, within inflammatory cells it may also suppress tumor promotion through its anti-inflammatory effects. Other interactions and forms of crosstalk between NF-kappaB and STAT3 include physical interaction between the two, cooperation of these factors at gene promoters/enhancers, the NF-kappaB dependent expression of inhibitors of STAT3 activation and the participation of STAT3 in inflammatory cells in the negative regulation NF-kappaB. Despite these versatile and occasionally antagonistic interactions, NF-kappaB and STAT3 cooperate to promote the development and progression of colon, gastric and liver cancers. In addition to explaining the molecular pathogenesis of cancer, these interactions also offer opportunities for the design of new therapeutic interventions.
Conflict of interest statement
Authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Differential expression of miRNAs regulating NF-κB and STAT3 crosstalk during colitis-associated tumorigenesis.Mol Cell Probes. 2019 Oct;47:101442. doi: 10.1016/j.mcp.2019.101442. Epub 2019 Aug 31. Mol Cell Probes. 2019. PMID: 31479716
-
NF-κB and STAT3 signaling pathways collaboratively link inflammation to cancer.Protein Cell. 2013 Mar;4(3):176-85. doi: 10.1007/s13238-013-2084-3. Epub 2013 Mar 13. Protein Cell. 2013. PMID: 23483479 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Rafoxanide negatively modulates STAT3 and NF-κB activity and inflammation-associated colon tumorigenesis.Cancer Sci. 2024 Nov;115(11):3596-3611. doi: 10.1111/cas.16317. Epub 2024 Sep 6. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 39239848 Free PMC article.
-
A requirement of STAT3 DNA binding precludes Th-1 immunostimulatory gene expression by NF-κB in tumors.Cancer Res. 2011 Jun 1;71(11):3772-80. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-10-3304. Epub 2011 Apr 18. Cancer Res. 2011. PMID: 21502401 Free PMC article.
-
IKK/NF-kappaB and STAT3 pathways: central signalling hubs in inflammation-mediated tumour promotion and metastasis.EMBO Rep. 2009 Dec;10(12):1314-9. doi: 10.1038/embor.2009.243. Epub 2009 Nov 6. EMBO Rep. 2009. PMID: 19893576 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Nuclear versus cytoplasmic IKKα signaling in keratinocytes leads to opposite skin phenotypes and inflammatory responses, and a different predisposition to cancer.Oncogene. 2024 Nov 7. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03203-0. Online ahead of print. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39511409
-
NF-κB signaling pathway in tumor microenvironment.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 18;15:1476030. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1476030. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39493763 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TRIM25, TRIM28 and TRIM59 and Their Protein Partners in Cancer Signaling Crosstalk: Potential Novel Therapeutic Targets for Cancer.Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024 Sep 25;46(10):10745-10761. doi: 10.3390/cimb46100638. Curr Issues Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 39451518 Free PMC article. Review.
-
FASN contributes to ADM resistance of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by inhibiting ferroptosis via nf-κB/STAT3/GPX4 axis.Cancer Biol Ther. 2024 Dec 31;25(1):2403197. doi: 10.1080/15384047.2024.2403197. Epub 2024 Sep 30. Cancer Biol Ther. 2024. PMID: 39345091 Free PMC article.
-
Hereditary Colorectal Cancer Syndromes and Inflammatory Bowel Diseases: Risk Management and Surveillance Strategies.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Aug 26;16(17):2967. doi: 10.3390/cancers16172967. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39272825 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Bishop JM. Molecular themes in oncogenesis. Cell. 1991;64:235–248. - PubMed
-
- Bromberg JF, Wrzeszczynska MH, Devgan G, et al. Stat3 as an oncogene. Cell. 1999;98:295–303. - PubMed
-
- Karin M. Nuclear factor-kappaB in cancer development and progression. Nature. 2006;441:431–436. - PubMed
-
- Karin M. NF-kB and cancer: mechanisms and targets. Mol Carcinog. 2006;45:355–361. - PubMed
-
- Yu H, Kortylewski M, Pardoll D. Crosstalk between cancer and immune cells: role of STAT3 in the tumour microenvironment. Nat Rev Immunol. 2007;7:41–51. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous


