Circulating palmitoleate strongly and independently predicts insulin sensitivity in humans
- PMID: 19889804
- PMCID: PMC2809292
- DOI: 10.2337/dc09-0544
Circulating palmitoleate strongly and independently predicts insulin sensitivity in humans
Abstract
Objective: We investigated whether palmitoleate, which prevents insulin resistance in mice, predicts insulin sensitivity in humans.
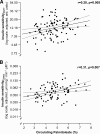
Research design and methods: The fasting fatty acid pattern in the plasma free fatty acid (FFA) fraction was determined in 100 subjects at increased risk for type 2 diabetes. Insulin sensitivity was estimated during an oral glucose tolerance test (OGTT) at baseline and after 9 months of lifestyle intervention and measured during the euglycemic-hyperinsulinemic clamp (n = 79).
Results: Circulating palmitoleate (OGTT:F ratio = 8.2, P = 0.005; clamp:F ratio = 7.8, P = 0.007) but not total FFAs (OGTT:F ratio = 0.6, P = 0.42; clamp:F ratio = 0.7, P = 0.40) correlated positively with insulin sensitivity, independently of age, sex, and adiposity. High baseline palmitoleate predicted a larger increase in insulin sensitivity. For 1-SD increase in palmitoleate, the odds ratio for being in the highest versus the lowest tertile of adjusted change in insulin sensitivity was 2.35 (95% CI 1.16-5.35).
Conclusions: Circulating palmitoleate strongly and independently predicts insulin sensitivity, suggesting that it plays an important role in the pathophysiology of insulin resistance in humans.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Circulating palmitoleic acid is an independent determinant of insulin sensitivity, beta cell function and glucose tolerance in non-diabetic individuals: a longitudinal analysis.Diabetologia. 2020 Jan;63(1):206-218. doi: 10.1007/s00125-019-05013-6. Epub 2019 Nov 1. Diabetologia. 2020. PMID: 31676981
-
Insulin sensitivity is not associated with palmitoleate availability in obese humans.J Lipid Res. 2011 Apr;52(4):808-12. doi: 10.1194/jlr.M013599. Epub 2011 Jan 25. J Lipid Res. 2011. PMID: 21266364 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating palmitoleic acid and risk of metabolic abnormalities and new-onset diabetes.Am J Clin Nutr. 2010 Dec;92(6):1350-8. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.110.003970. Epub 2010 Oct 13. Am J Clin Nutr. 2010. PMID: 20943795 Free PMC article.
-
Trans-palmitoleic acid, metabolic risk factors, and new-onset diabetes in U.S. adults: a cohort study.Ann Intern Med. 2010 Dec 21;153(12):790-9. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-153-12-201012210-00005. Ann Intern Med. 2010. PMID: 21173413 Free PMC article.
-
The Role of the Novel Lipokine Palmitoleic Acid in Health and Disease.Adv Nutr. 2017 Jan 17;8(1):173S-181S. doi: 10.3945/an.115.011130. Print 2017 Jan. Adv Nutr. 2017. PMID: 28096141 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
High-Fat Feeding Alters Circulating Triglyceride Composition: Roles of FFA Desaturation and ω-3 Fatty Acid Availability.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 13;25(16):8810. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168810. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201497 Free PMC article.
-
Short leukocyte telomere length and high plasma phospholipid fatty acids increase the risk of type 2 diabetes.Endocr Connect. 2024 Oct 13;13(9):e240033. doi: 10.1530/EC-24-0033. Print 2024 Sep 1. Endocr Connect. 2024. PMID: 39045889 Free PMC article.
-
The role of adipose tissue dysfunction in hepatic insulin resistance and T2D.J Endocrinol. 2024 Aug 2;262(3):e240115. doi: 10.1530/JOE-24-0115. Print 2024 Sep 1. J Endocrinol. 2024. PMID: 38967989 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Protocol for a randomized placebo-controlled clinical trial using pure palmitoleic acid to ameliorate insulin resistance and lipogenesis in overweight and obese subjects with prediabetes.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Jan 19;14:1306528. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1306528. eCollection 2023. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 38313838 Free PMC article.
-
Metabolomic signatures associated with weight gain and psychosis spectrum diagnoses: A pilot study.Front Psychiatry. 2023 Apr 24;14:1169787. doi: 10.3389/fpsyt.2023.1169787. eCollection 2023. Front Psychiatry. 2023. PMID: 37168086 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Perseghin G, Scifo P, De Cobelli F, Pagliato E, Battezzati A, Arcelloni C, Vanzulli A, Testolin G, Pozza G, Del Maschio A, Luzi L. Intramyocellular triglyceride content is a determinant of in vivo insulin resistance in humans: a 1H-13C nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy assessment in offspring of type 2 diabetic parents. Diabetes 1999; 48: 1600– 1606 - PubMed
-
- Stefan N, Kantartzis K, Machann J, Schick F, Thamer C, Rittig K, Balletshofer B, Machicao F, Fritsche A, Häring HU. Identification and characterization of metabolically benign obesity in humans. Arch Intern Med 2008; 168: 1609– 1616 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


