Ryanodine receptor phosphorylation at Serine 2030, 2808 and 2814 in rat cardiomyocytes
- PMID: 18755143
- PMCID: PMC2581610
- DOI: 10.1016/j.bbrc.2008.08.084
Ryanodine receptor phosphorylation at Serine 2030, 2808 and 2814 in rat cardiomyocytes
Abstract
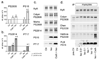
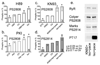
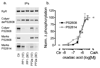
The cardiac ryanodine receptor (RyR) controls Ca2+ release from the sarcoplasmic reticulum (SR) during excitation-contraction coupling. Three phosphorylation sites have been identified: Serine-(S)2808, S2814 and recently S2030. We measured phosphorylation with at least two different antibodies per site and demonstrate that for S2808 results were highly antibody-dependent and two out of three S2808 antibodies did not accurately report phosphorylation level. The RyR was substantially phosphorylated in quiescent rat cardiomyocytes at S2808 and less so at S2814, but appeared to be unphosphorylated at S2030. Basal phosphorylation at S2808/S2814 was maintained by a Ca2+ dependent kinase other than Ca2+/Calmodulin-dependent kinase (CaMKII). During stimulation with Isoproterenol S2808 was phosphorylated by protein kinase A (PKA) and S2814 was phosphorylated by CaMKII. Phosphatase 1 appears to be the main phosphatase dephosphorylating S2808/S2814, but phosphatase 2a may also dephosphorylate S2814. RyR phosphorylation is complex, but important in understanding RyR functional modulation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
A Single Protein Kinase A or Calmodulin Kinase II Site Does Not Control the Cardiac Pacemaker Ca2+ Clock.Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016 Feb;9(2):e003180. doi: 10.1161/CIRCEP.115.003180. Circ Arrhythm Electrophysiol. 2016. PMID: 26857906 Free PMC article.
-
Phosphorylation of the ryanodine receptor 2 at serine 2030 is required for a complete β-adrenergic response.J Gen Physiol. 2019 Feb 4;151(2):131-145. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201812155. Epub 2018 Dec 12. J Gen Physiol. 2019. PMID: 30541771 Free PMC article.
-
Maximal acceleration of Ca2+ release refractoriness by β-adrenergic stimulation requires dual activation of kinases PKA and CaMKII in mouse ventricular myocytes.J Physiol. 2015 Mar 15;593(6):1495-507. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.2014.278051. Epub 2014 Oct 7. J Physiol. 2015. PMID: 25772298 Free PMC article.
-
Toward biologically targeted therapy of calcium cycling defects in heart failure.Physiology (Bethesda). 2008 Feb;23:6-16. doi: 10.1152/physiol.00033.2007. Physiology (Bethesda). 2008. PMID: 18268360 Review.
-
Epac in cardiac calcium signaling.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013 May;58:162-71. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2012.11.021. Epub 2012 Dec 7. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2013. PMID: 23220153 Review.
Cited by
-
β-adrenergic regulation of Ca2+ signaling in heart cells.Biophys Rep. 2024 Oct 31;10(5):274-282. doi: 10.52601/bpr.2024.240906. Biophys Rep. 2024. PMID: 39539286 Free PMC article.
-
Dual ablation of the RyR2-Ser2808 and RyR2-Ser2814 sites increases propensity for pro-arrhythmic spontaneous Ca2+ releases.J Physiol. 2024 Oct;602(20):5179-5201. doi: 10.1113/JP286453. Epub 2024 Sep 24. J Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39316734
-
Chai-Hu-San-Shen Capsule Ameliorates Ventricular Arrhythmia Through Inhibition of the CaMKII/FKBP12.6/RyR2/Ca2+ Signaling Pathway in Rats with Myocardial Ischemia.Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022 Oct 3;2022:2670473. doi: 10.1155/2022/2670473. eCollection 2022. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022. PMID: 36225189 Free PMC article.
-
Preserved cardiac performance and adrenergic response in a rabbit model with decreased ryanodine receptor 2 expression.J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022 Jun;167:118-128. doi: 10.1016/j.yjmcc.2022.04.004. Epub 2022 Apr 9. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 2022. PMID: 35413295 Free PMC article.
-
Regulation of cardiac ryanodine receptor function by the cyclic-GMP dependent protein kinase G.Curr Res Physiol. 2022 Mar 23;5:171-178. doi: 10.1016/j.crphys.2022.03.004. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35356048 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bers DM. Macromolecular complexes regulating cardiac ryanodine receptor function. J. Mol. Cell. Cardiol. 2004;37:417–429. - PubMed
-
- Marx SO, Reiken S, Hisamatsu Y, Jayaraman T, Burkhoff D, Rosemblit N, Marks AR. PKA phosphorylation dissociates FKBP12.6 from the calcium release channel (ryanodine receptor): defective regulation in failing hearts. Cell. 2000;101:365–376. - PubMed
-
- Ai X, Curran JW, Shannon TR, Bers DM, Pogwizd SM. Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase modulates cardiac ryanodine receptor phosphorylation and sarcoplasmic reticulum Ca2+ leak in heart failure. Circ. Res. 2005;97:1314–1322. - PubMed
-
- Wehrens XH, Lehnart SE, Marks AR. Ryanodine receptor-targeted anti-arrhythmic therapy. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci. 2005;1047:366–375. - PubMed
-
- Witcher DR, Kovacs RJ, Schulman H, Cefali DC, Jones LR. Unique phosphorylation site on the cardiac ryanodine receptor regulates calcium channel activity. J. Biol. Chem. 1991;266:11144–11152. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


