Organophosphate-sensitive lipases modulate brain lysophospholipids, ether lipids and endocannabinoids
- PMID: 18495101
- PMCID: PMC2582404
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cbi.2008.04.008
Organophosphate-sensitive lipases modulate brain lysophospholipids, ether lipids and endocannabinoids
Abstract
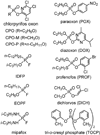
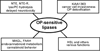
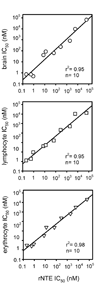
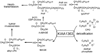
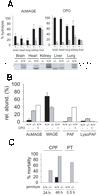
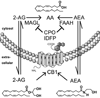
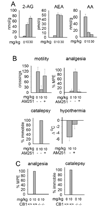
Lipases play key roles in nearly all cells and organisms. Potent and selective inhibitors help to elucidate their physiological functions and associated metabolic pathways. Organophosphorus (OP) compounds are best known for their anticholinesterase properties but selectivity for lipases and other targets can also be achieved through structural optimization. This review considers several lipid systems in brain modulated by highly OP-sensitive lipases. Neuropathy target esterase (NTE) hydrolyzes lysophosphatidylcholine (lysoPC) as a preferred substrate. Gene deletion of NTE in mice is embryo lethal and the heterozygotes are hyperactive. NTE is very sensitive in vitro and in vivo to direct-acting OP delayed neurotoxicants and the related NTE-related esterase (NTE-R) is also inhibited in vivo. KIAA1363 hydrolyzes acetyl monoalkylglycerol ether (AcMAGE) of the platelet-activating factor (PAF) de novo biosynthetic pathway and is a marker of cancer cell invasiveness. It is also a detoxifying enzyme that hydrolyzes chlorpyrifos oxon (CPO) and some other potent insecticide metabolites. Monoacylglycerol lipase and fatty acid amide hydrolase regulate endocannabinoid levels with roles in motility, pain and memory. Inhibition of these enzymes in mice by OPs, such as isopropyl dodecylfluorophosphonate (IDFP), leads to dramatic elevation of brain endocannabinoids and distinct cannabinoid-dependent behavior. Hormone-sensitive lipase that hydrolyzes cholesteryl esters and diacylglycerols is a newly recognized in vivo CPO- and IDFP-target in brain. The OP chemotype can therefore be used in proteomic and metabolomic studies to further elucidate the biological function and toxicological significance of lipases in lipid metabolism. Only the first steps have been taken to achieve appropriate selective action for OP therapeutic agents.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Dual roles of brain serine hydrolase KIAA1363 in ether lipid metabolism and organophosphate detoxification.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008 Apr 1;228(1):42-8. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2007.11.021. Epub 2007 Dec 3. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2008. PMID: 18164358 Free PMC article.
-
Monoacylglycerol lipase inhibition by organophosphorus compounds leads to elevation of brain 2-arachidonoylglycerol and the associated hypomotility in mice.Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006 Feb 15;211(1):78-83. doi: 10.1016/j.taap.2005.10.007. Epub 2005 Nov 28. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16310817
-
The cannabinoid receptor antagonist AM251 increases paraoxon and chlorpyrifos oxon toxicity in rats.Neurotoxicology. 2015 Jan;46:12-8. doi: 10.1016/j.neuro.2014.11.001. Epub 2014 Nov 20. Neurotoxicology. 2015. PMID: 25447325 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibitors of the endocannabinoid-degrading enzymes, or how to increase endocannabinoid's activity by preventing their hydrolysis.Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 2012 Apr 1;7(1):49-70. doi: 10.2174/157488912798842223. Recent Pat CNS Drug Discov. 2012. PMID: 22280341 Review.
-
The contribution of cyclooxygenase-2 to endocannabinoid metabolism and action.Br J Pharmacol. 2007 Nov;152(5):594-601. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0707379. Epub 2007 Jul 9. Br J Pharmacol. 2007. PMID: 17618306 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Developmental brain lipidomics is influenced by postnatal chlorpyrifos exposure and APOE genetic background in mice.Arch Toxicol. 2023 Sep;97(9):2463-2475. doi: 10.1007/s00204-023-03555-8. Epub 2023 Jul 13. Arch Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37439814 Free PMC article.
-
Review: Organophosphorus toxicants, in addition to inhibiting acetylcholinesterase activity, make covalent adducts on multiple proteins and promote protein crosslinking into high molecular weight aggregates.Chem Biol Interact. 2023 May 1;376:110460. doi: 10.1016/j.cbi.2023.110460. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Chem Biol Interact. 2023. PMID: 36963650 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of computational toxicology tools to predict in vivo endpoints associated with Mode of Action and the endocannabinoid system: A case study with chlorpyrifos, chlorpyrifos-oxon and Δ9Tetrahydrocannabinol.Curr Res Toxicol. 2022 Feb 7;3:100064. doi: 10.1016/j.crtox.2022.100064. eCollection 2022. Curr Res Toxicol. 2022. PMID: 35243363 Free PMC article.
-
High-Resolution Confocal Fluorescence Imaging of Serine Hydrolase Activity in Cryosections - Application to Glioma Brain Unveils Activity Hotspots Originating from Tumor-Associated Neutrophils.Biol Proced Online. 2020 Mar 15;22:6. doi: 10.1186/s12575-020-00118-4. eCollection 2020. Biol Proced Online. 2020. PMID: 32190011 Free PMC article.
-
Structure Dependent Determination of Organophosphate Targets in Mammalian Tissues Using Activity-Based Protein Profiling.Chem Res Toxicol. 2020 Feb 17;33(2):414-425. doi: 10.1021/acs.chemrestox.9b00344. Epub 2020 Jan 10. Chem Res Toxicol. 2020. PMID: 31872761 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Chiang KP, Niessen S, Saghatelian A, Cravatt BF. An enzyme that regulates ether lipid signaling pathways in cancer annotated by multidimensional profiling. Chem. Biol. 2006;13:1041–1050. - PubMed
-
- Shi Y, Burn P. Lipid metabolic enzymes: emerging drug targets for the treatment of obesity. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2004;3:695–710. - PubMed
-
- Macphee CH, Nelson J, Zalewski A. Role of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 in atherosclerosis and its potential as a therapeutic target. Curr. Opin. Pharmacol. 2006;7:154–161. - PubMed
-
- Casida JE, Quistad GB. Serine hydrolase targets of organophosphorus toxicants. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2005;157–158:277–283. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


