Genome analysis of the platypus reveals unique signatures of evolution
- PMID: 18464734
- PMCID: PMC2803040
- DOI: 10.1038/nature06936
Genome analysis of the platypus reveals unique signatures of evolution
Erratum in
- Nature. 2008 Sep 11;455(7210):256. Nefedov, Mikhail [added]; de Jong, Pieter J [added]
Abstract
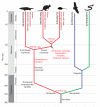
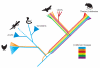
We present a draft genome sequence of the platypus, Ornithorhynchus anatinus. This monotreme exhibits a fascinating combination of reptilian and mammalian characters. For example, platypuses have a coat of fur adapted to an aquatic lifestyle; platypus females lactate, yet lay eggs; and males are equipped with venom similar to that of reptiles. Analysis of the first monotreme genome aligned these features with genetic innovations. We find that reptile and platypus venom proteins have been co-opted independently from the same gene families; milk protein genes are conserved despite platypuses laying eggs; and immune gene family expansions are directly related to platypus biology. Expansions of protein, non-protein-coding RNA and microRNA families, as well as repeat elements, are identified. Sequencing of this genome now provides a valuable resource for deep mammalian comparative analyses, as well as for monotreme biology and conservation.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Defensins and the convergent evolution of platypus and reptile venom genes.Genome Res. 2008 Jun;18(6):986-94. doi: 10.1101/gr.7149808. Epub 2008 May 7. Genome Res. 2008. PMID: 18463304 Free PMC article.
-
Top billing for platypus at end of evolution tree.Nature. 2008 May 8;453(7192):138-9. doi: 10.1038/453138a. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18464700 No abstract available.
-
The mitochondrial genome of a monotreme--the platypus (Ornithorhynchus anatinus).J Mol Evol. 1996 Feb;42(2):153-9. doi: 10.1007/BF02198841. J Mol Evol. 1996. PMID: 8919867
-
Eggs, embryos and the evolution of imprinting: insights from the platypus genome.Reprod Fertil Dev. 2009;21(8):935-42. doi: 10.1071/RD09092. Reprod Fertil Dev. 2009. PMID: 19874717 Review.
-
Tracing monotreme venom evolution in the genomics era.Toxins (Basel). 2014 Apr 2;6(4):1260-73. doi: 10.3390/toxins6041260. Toxins (Basel). 2014. PMID: 24699339 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The evolution of flexibility and function in the Fc domains of IgM, IgY, and IgE.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 9;15:1389494. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1389494. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39445016 Free PMC article.
-
Compensation of gene dosage on the mammalian X.Development. 2024 Aug 1;151(15):dev202891. doi: 10.1242/dev.202891. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Development. 2024. PMID: 39140247 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Body fat and circulating leptin levels in the captive short-beaked echidna (Tachyglossus aculeatus).J Comp Physiol B. 2024 Aug;194(4):457-471. doi: 10.1007/s00360-024-01559-z. Epub 2024 May 15. J Comp Physiol B. 2024. PMID: 38748188 Free PMC article.
-
A conserved NR5A1-responsive enhancer regulates SRY in testis-determination.Nat Commun. 2024 Mar 30;15(1):2796. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-47162-2. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 38555298 Free PMC article.
-
A family of olfactory receptors uniquely expanded in marsupial and monotreme genomes are expressed by a T cell subset also unique to marsupials and monotremes.Dev Comp Immunol. 2024 May;154:105149. doi: 10.1016/j.dci.2024.105149. Epub 2024 Feb 8. Dev Comp Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38340883
References
-
- Home EA. A description of the anatomy of Ornithorynchus paradoxus. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1802;92:67–84.
-
- Bininda-Emonds ORP, et al. The delayed rise of present-day mammals. Nature. 2007;446:507–512. - PubMed
-
- Caldwell H. The embryology of Monotremata and Marsupialia. Phil. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B. 1887;178:463–486.
-
- Griffiths M. Echidnas. Pergamon; Oxford: 1968.
-
- Griffiths M. The Biology of the Monotremes. Academic; New York: 1978.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01 HG004037/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U137761446/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 HG002939/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM059290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG02385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG002385/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG004037-02/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106-37/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM59290/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA013106/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 062023/WT_/Wellcome Trust/United Kingdom
- R01 HG002238/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- HG002238/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases


