RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation
- PMID: 18342629
- PMCID: PMC2858862
- DOI: 10.1016/j.febslet.2008.03.004
RNA-binding proteins and post-transcriptional gene regulation
Abstract
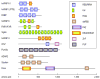
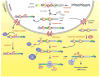
RNAs in cells are associated with RNA-binding proteins (RBPs) to form ribonucleoprotein (RNP) complexes. The RBPs influence the structure and interactions of the RNAs and play critical roles in their biogenesis, stability, function, transport and cellular localization. Eukaryotic cells encode a large number of RBPs (thousands in vertebrates), each of which has unique RNA-binding activity and protein-protein interaction characteristics. The remarkable diversity of RBPs, which appears to have increased during evolution in parallel to the increase in the number of introns, allows eukaryotic cells to utilize them in an enormous array of combinations giving rise to a unique RNP for each RNA. In this short review, we focus on the RBPs that interact with pre-mRNAs and mRNAs and discuss their roles in the regulation of post-transcriptional gene expression.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deciphering the mRNP Code: RNA-Bound Determinants of Post-Transcriptional Gene Regulation.Trends Biochem Sci. 2017 May;42(5):369-382. doi: 10.1016/j.tibs.2017.02.004. Epub 2017 Mar 6. Trends Biochem Sci. 2017. PMID: 28268044 Review.
-
Deciphering human ribonucleoprotein regulatory networks.Nucleic Acids Res. 2019 Jan 25;47(2):570-581. doi: 10.1093/nar/gky1185. Nucleic Acids Res. 2019. PMID: 30517751 Free PMC article.
-
Extensive cross-regulation of post-transcriptional regulatory networks in Drosophila.Genome Res. 2015 Nov;25(11):1692-702. doi: 10.1101/gr.182675.114. Epub 2015 Aug 20. Genome Res. 2015. PMID: 26294687 Free PMC article.
-
PAR-CliP--a method to identify transcriptome-wide the binding sites of RNA binding proteins.J Vis Exp. 2010 Jul 2;(41):2034. doi: 10.3791/2034. J Vis Exp. 2010. PMID: 20644507 Free PMC article.
-
RNA recognition by RNP proteins during RNA processing.Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998;27:407-45. doi: 10.1146/annurev.biophys.27.1.407. Annu Rev Biophys Biomol Struct. 1998. PMID: 9646873 Review.
Cited by
-
Regulating translation in aging: from global to gene-specific mechanisms.EMBO Rep. 2024 Nov 19. doi: 10.1038/s44319-024-00315-2. Online ahead of print. EMBO Rep. 2024. PMID: 39562712 Review.
-
Subcellular mRNA kinetic modeling reveals nuclear retention as rate-limiting.Mol Syst Biol. 2024 Nov 15. doi: 10.1038/s44320-024-00073-2. Online ahead of print. Mol Syst Biol. 2024. PMID: 39548324
-
USP30-AS1 Suppresses Colon Cancer Cell Inflammatory Response Through NF-κB/MYBBP1A Signaling.Inflammation. 2024 Nov 6. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02170-8. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39503963
-
IGF2BP1 phosphorylation in the disordered linkers regulates ribonucleoprotein condensate formation and RNA metabolism.Nat Commun. 2024 Oct 20;15(1):9054. doi: 10.1038/s41467-024-53400-4. Nat Commun. 2024. PMID: 39426983 Free PMC article.
-
CypA/TAF15/STAT5A/miR-514a-3p feedback loop drives ovarian cancer metastasis.Oncogene. 2024 Nov;43(49):3570-3585. doi: 10.1038/s41388-024-03188-w. Epub 2024 Oct 14. Oncogene. 2024. PMID: 39402372
References
-
- Matera AG, Terns RM, Terns MP. Non-coding RNAs: lessons from the small nuclear and small nucleolar RNAs. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2007;8:209–20. - PubMed
-
- Burd CG, Dreyfuss G. Conserved structures and diversity of functions of RNA-binding proteins. Science. 1994;265:615–21. - PubMed
-
- Chen Y, Varani G. Protein families and RNA recognition. FEBS J. 2005;272:2088–97. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


