Bioinformatic analysis of the CLE signaling peptide family
- PMID: 18171480
- PMCID: PMC2254619
- DOI: 10.1186/1471-2229-8-1
Bioinformatic analysis of the CLE signaling peptide family
Erratum in
- BMC Plant Biol. 2009;9:17
Abstract
Background: Plants encode a large number of leucine-rich repeat receptor-like kinases. Legumes encode several LRR-RLK linked to the process of root nodule formation, the ligands of which are unknown. To identify ligands for these receptors, we used a combination of profile hidden Markov models and position-specific iterative BLAST, allowing us to detect new members of the CLV3/ESR (CLE) protein family from publicly available sequence databases.
Results: We identified 114 new members of the CLE protein family from various plant species, as well as five protein sequences containing multiple CLE domains. We were able to cluster the CLE domain proteins into 13 distinct groups based on their pairwise similarities in the primary CLE motif. In addition, we identified secondary motifs that coincide with our sequence clusters. The groupings based on the CLE motifs correlate with known biological functions of CLE signaling peptides and are analogous to groupings based on phylogenetic analysis and ectopic overexpression studies. We tested the biological function of two of the predicted CLE signaling peptides in the legume Medicago truncatula. These peptides inhibit the activity of the root apical and lateral root meristems in a manner consistent with our functional predictions based on other CLE signaling peptides clustering in the same groups.
Conclusion: Our analysis provides an identification and classification of a large number of novel potential CLE signaling peptides. The additional motifs we found could lead to future discovery of recognition sites for processing peptidases as well as predictions for receptor binding specificity.
Figures



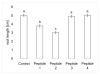
Similar articles
-
Comprehensive identification and clustering of CLV3/ESR-related (CLE) genes in plants finds groups with potentially shared function.New Phytol. 2017 Oct;216(2):605-616. doi: 10.1111/nph.14348. Epub 2016 Dec 1. New Phytol. 2017. PMID: 27911469
-
Identification of potential host plant mimics of CLAVATA3/ESR (CLE)-like peptides from the plant-parasitic nematode Heterodera schachtii.Mol Plant Pathol. 2011 Feb;12(2):177-86. doi: 10.1111/j.1364-3703.2010.00660.x. Epub 2010 Oct 1. Mol Plant Pathol. 2011. PMID: 21199567 Free PMC article.
-
Gain-of-function phenotypes of many CLAVATA3/ESR genes, including four new family members, correlate with tandem variations in the conserved CLAVATA3/ESR domain.Plant Physiol. 2006 Apr;140(4):1331-44. doi: 10.1104/pp.105.075515. Epub 2006 Feb 17. Plant Physiol. 2006. PMID: 16489133 Free PMC article.
-
CLE peptide ligands and their roles in establishing meristems.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007 Feb;10(1):39-43. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2006.11.003. Epub 2006 Nov 28. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2007. PMID: 17129751 Review.
-
CLE peptide signaling during plant development.Protoplasma. 2010 Apr;240(1-4):33-43. doi: 10.1007/s00709-009-0095-y. Epub 2009 Dec 17. Protoplasma. 2010. PMID: 20016993 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
In silico analysis of R2R3-MYB transcription factors in the basal eudicot model, Aquilegia coerulea.3 Biotech. 2024 Nov;14(11):284. doi: 10.1007/s13205-024-04119-y. Epub 2024 Oct 29. 3 Biotech. 2024. PMID: 39479299 Free PMC article.
-
Uncovering PheCLE1 and PheCLE10 Promoting Root Development Based on Genome-Wide Analysis.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jun 29;25(13):7190. doi: 10.3390/ijms25137190. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39000298 Free PMC article.
-
Genome-Wide Identification and Characterization of CLAVATA3/EMBRYO SURROUNDING REGION (CLE) Gene Family in Foxtail Millet (Setaria italica L.).Genes (Basel). 2023 Nov 6;14(11):2046. doi: 10.3390/genes14112046. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38002989 Free PMC article.
-
The CLAVATA3/ESR-related peptide family in the biofuel crop pennycress.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Aug 4;14:1240342. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1240342. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37600169 Free PMC article.
-
Root-knot nematode modulates plant CLE3-CLV1 signaling as a long-distance signal for successful infection.Sci Adv. 2023 Jun 2;9(22):eadf4803. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf4803. Epub 2023 Jun 2. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 37267361 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


