Regression of fibrosis after chronic stimulation of cannabinoid CB2 receptor in cirrhotic rats
- PMID: 18029545
- PMCID: PMC2887659
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.107.131896
Regression of fibrosis after chronic stimulation of cannabinoid CB2 receptor in cirrhotic rats
Abstract
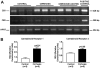
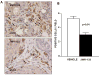
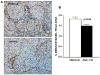
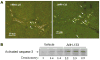
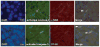
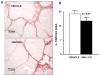
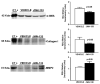
Two cannabinoid (CB) receptor subtypes, CB1 and CB2, have been cloned and characterized. Among other activities, receptor activation by cannabinoid ligands may result in pro- or antifibrogenic effects depending on their interaction with CB1 or CB2, respectively. In the current study, we investigated whether selective activation of hepatic CB2 modifies collagen abundance in cirrhotic rats with ascites. mRNA and protein expression of CB receptors in the liver of control and cirrhotic rats was assessed by reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction, Western blot, and immunohistochemistry. The effect of chronically activating the CB2 receptor was investigated in cirrhotic rats with ascites treated daily (9 days) with the CB2 receptor-selective agonist 3-(1,1-dimethylbutyl)-1-deoxy-Delta(8)-tetrahydrocannabinol (JWH-133). At the end of treatment, mean arterial pressure and portal pressure were measured, and liver samples were obtained to evaluate infiltrate of mononuclear cells, hepatic apoptosis, alpha-smooth muscle actin (SMA) expression, collagen content, and matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-2 abundance in all animals. JWH-133 improved arterial pressure, decreased the inflammatory infiltrate, reduced the number of activated stellate cells, increased apoptosis in nonparenchymal cells located in the margin of the septa, and decreased fibrosis compared with cirrhotic rats treated with vehicle. This was associated with decreased alpha-SMA and collagen I and increased MMP-2 in the hepatic tissue of cirrhotic rats treated with the CB2 agonist compared with untreated cirrhotic animals. Therefore, selective activation of hepatic CB2 receptors significantly reduces hepatic collagen content in rats with pre-existing cirrhosis, thus raising the possibility of using selective CB2 agonists for the treatment of hepatic fibrosis in human cirrhosis.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Antifibrogenic role of the cannabinoid receptor CB2 in the liver.Gastroenterology. 2005 Mar;128(3):742-55. doi: 10.1053/j.gastro.2004.12.050. Gastroenterology. 2005. PMID: 15765409
-
Hepatic expression of cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2 correlate with fibrogenesis in patients with chronic hepatitis B.Int J Infect Dis. 2017 Jun;59:124-130. doi: 10.1016/j.ijid.2017.03.008. Epub 2017 Mar 15. Int J Infect Dis. 2017. PMID: 28315398
-
Role of cannabinoid receptors in hepatic fibrosis and apoptosis associated with bile duct ligation in rats.Eur J Pharmacol. 2014 Nov 5;742:118-24. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2014.08.021. Epub 2014 Aug 30. Eur J Pharmacol. 2014. PMID: 25179573
-
[The endocannabinoid system as a novel target for the treatment of liver fibrosis].Pathol Biol (Paris). 2008 Feb;56(1):36-8. doi: 10.1016/j.patbio.2007.01.001. Epub 2007 Apr 6. Pathol Biol (Paris). 2008. PMID: 17412522 Review. French.
-
Role of cannabinoids in chronic liver diseases.World J Gastroenterol. 2008 Oct 28;14(40):6109-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.14.6109. World J Gastroenterol. 2008. PMID: 18985799 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic potential of agents targeting cannabinoid type 2 receptors in organ fibrosis.Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024 Dec;12(6):e1219. doi: 10.1002/prp2.1219. Pharmacol Res Perspect. 2024. PMID: 39425446 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Impact of the CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor in Inflammatory Diseases: An Update.Molecules. 2024 Jul 18;29(14):3381. doi: 10.3390/molecules29143381. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39064959 Free PMC article. Review.
-
CB2 Cannabinoid Receptor as a Potential Target in Myocardial Infarction: Exploration of Molecular Pathogenesis and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jan 30;25(3):1683. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031683. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38338960 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Acute and subacute toxic effects of CUMYL-4CN-BINACA on male albino rats.Forensic Toxicol. 2024 Jul;42(2):125-141. doi: 10.1007/s11419-023-00676-8. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Forensic Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38102417
-
Exploring the therapeutic potential of natural compounds modulating the endocannabinoid system in various diseases and disorders: review.Pharmacol Rep. 2023 Dec;75(6):1410-1444. doi: 10.1007/s43440-023-00544-7. Epub 2023 Oct 31. Pharmacol Rep. 2023. PMID: 37906390 Review.
References
-
- Bátkai S, Jarai Z, Wagner JA, Goparaju SK, Varga K, Liu J, Wang L, Mirshahi F, Khanolkar AD, Makriyannis A, et al. Endocannabinoids acting at vascular CB1 receptors mediate the vasodilated state in advanced liver cirrhosis. Nat Med. 2001;7:827–832. - PubMed
-
- Begg M, Pacher P, Batkai S, Osei-Hyiaman D, Offertaler L, Mo FM, Liu J, Kunos G. Evidence for novel cannabinoid receptors. Pharmacol Ther. 2005;106:133–145. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

