Measuring the burden of disease in Korea
- PMID: 17596664
- PMCID: PMC2693648
- DOI: 10.3346/jkms.2007.22.3.518
Measuring the burden of disease in Korea
Abstract
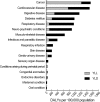
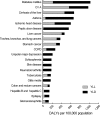
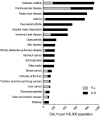
This paper provides an overview of the Korean Burden of Disease (KBoD) study, which was the first such study to assess the national burden of disease using disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) in an advanced Asian country. The KBoD study generally followed the approach utilized in the original Global Burden of Disease study (GBD), with the exception of the disease classification and epidemiological data estimation methods used, and the relative weightings of disabilities. The results of the present study reveal that the burden of disease per 100,000 of the Korean population originates primarily from; cancer (1,525 Person Years, PYs), cardiovascular disease (1,492 PYs), digestive disease (1,140 PYs), diabetes mellitus (990 PYs), and certain neuro-psychiatric conditions (883 PYs). These results are largely consistent with those of developed countries, but also represent uniquely Korean characteristics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Disability-Adjusted Life Years (DALYs) for Injuries Using Death Certificates and Hospital Discharge Survey by the Korean Burden of Disease Study 2012.J Korean Med Sci. 2016 Nov;31 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S200-S207. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S2.S200. J Korean Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27775258 Free PMC article.
-
Disability-adjusted Life Years for 313 Diseases and Injuries: the 2012 Korean Burden of Disease Study.J Korean Med Sci. 2016 Nov;31 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S146-S157. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S2.S146. J Korean Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27775252 Free PMC article.
-
The state of health in the Arab world, 1990-2010: an analysis of the burden of diseases, injuries, and risk factors.Lancet. 2014 Jan 25;383(9914):309-20. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)62189-3. Epub 2014 Jan 20. Lancet. 2014. PMID: 24452042
-
Quantifying Burden of Disease to Measure Population Health in Korea.J Korean Med Sci. 2016 Nov;31 Suppl 2(Suppl 2):S101-S107. doi: 10.3346/jkms.2016.31.S2.S101. J Korean Med Sci. 2016. PMID: 27775246 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Global burden of disease in young people aged 10-24 years: a systematic analysis.Lancet. 2011 Jun 18;377(9783):2093-102. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60512-6. Epub 2011 Jun 7. Lancet. 2011. PMID: 21652063 Review.
Cited by
-
Korean National Burden of Disease: The Importance of Diabetes Management.Diabetes Metab J. 2024 Jul;48(4):518-530. doi: 10.4093/dmj.2024.0087. Epub 2024 Jul 26. Diabetes Metab J. 2024. PMID: 39091003 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Population health outcomes in South Korea 1990-2019, and projections up to 2040: a systematic analysis for the Global Burden of Disease Study 2019.Lancet Public Health. 2023 Aug;8(8):e639-e650. doi: 10.1016/S2468-2667(23)00122-6. Lancet Public Health. 2023. PMID: 37516480 Free PMC article.
-
Epidemiology of patients with asthma in Korea: Analysis of the NHISS database 2006-2015.World Allergy Organ J. 2023 Apr 19;16(4):100768. doi: 10.1016/j.waojou.2023.100768. eCollection 2023 Apr. World Allergy Organ J. 2023. PMID: 37128250 Free PMC article.
-
Increased Risk of Developing Depression in Disability after Stroke: A Korean Nationwide Study.Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023 Jan 2;20(1):842. doi: 10.3390/ijerph20010842. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2023. PMID: 36613164 Free PMC article.
-
A systematic literature review of disability weights measurement studies: evolution of methodological choices.Arch Public Health. 2022 Mar 24;80(1):91. doi: 10.1186/s13690-022-00860-z. Arch Public Health. 2022. PMID: 35331325 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Global burden of disease 2002 estimates. World Health Organization. 2002. [Sep, 2006]. Available from: http://www3.who.int/whosis/menu.cfm?path=evidence,burden,burden_estimate....
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources


