A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity
- PMID: 17434869
- PMCID: PMC2646098
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1141634
A common variant in the FTO gene is associated with body mass index and predisposes to childhood and adult obesity
Abstract
Obesity is a serious international health problem that increases the risk of several common diseases. The genetic factors predisposing to obesity are poorly understood. A genome-wide search for type 2 diabetes-susceptibility genes identified a common variant in the FTO (fat mass and obesity associated) gene that predisposes to diabetes through an effect on body mass index (BMI). An additive association of the variant with BMI was replicated in 13 cohorts with 38,759 participants. The 16% of adults who are homozygous for the risk allele weighed about 3 kilograms more and had 1.67-fold increased odds of obesity when compared with those not inheriting a risk allele. This association was observed from age 7 years upward and reflects a specific increase in fat mass.
Figures
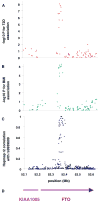
Comment in
-
Obesity genetics and epigenetics: dissecting causality.Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014 Jun;7(3):395-6. doi: 10.1161/CIRCGENETICS.114.000698. Circ Cardiovasc Genet. 2014. PMID: 24951667 No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Combined effects of MC4R and FTO common genetic variants on obesity in European general populations.J Mol Med (Berl). 2009 May;87(5):537-46. doi: 10.1007/s00109-009-0451-6. Epub 2009 Mar 3. J Mol Med (Berl). 2009. PMID: 19255736
-
Risk of type 2 diabetes and obesity is differentially associated with variation in FTO in whites and African-Americans in the ARIC study.PLoS One. 2010 May 20;5(5):e10521. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0010521. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 20502638 Free PMC article.
-
Body mass index and obesity- and diabetes-associated genotypes and risk for pancreatic cancer.Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011 May;20(5):779-92. doi: 10.1158/1055-9965.EPI-10-0845. Epub 2011 Feb 25. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 2011. PMID: 21357378 Free PMC article.
-
Association of FTO common variant (rs9939609) with body fat in Turkish individuals.Lipids Health Dis. 2019 Dec 6;18(1):212. doi: 10.1186/s12944-019-1160-y. Lipids Health Dis. 2019. PMID: 31810473 Free PMC article.
-
The common rs9939609 variant of the fat mass and obesity-associated gene is associated with obesity risk in children and adolescents of Beijing, China.BMC Med Genet. 2010 Jul 5;11:107. doi: 10.1186/1471-2350-11-107. BMC Med Genet. 2010. PMID: 20598163 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Ubiquitination and Metabolic Disease.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024;1466:47-79. doi: 10.1007/978-981-97-7288-9_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2024. PMID: 39546135 Review.
-
Genetic insights into endurance athlete status: A meta-analysis of ACVR1B, AGT, FTO, IL-6, and NRF2 gene polymorphisms.J Biol Methods. 2024 Sep 6;11(3):e99010021. doi: 10.14440/jbm.2024.0013. eCollection 2024. J Biol Methods. 2024. PMID: 39544188 Free PMC article.
-
Integrating Genetic Insights, Technological Advancements, Screening, and Personalized Pharmacological Interventions in Childhood Obesity.Adv Ther. 2024 Nov 13. doi: 10.1007/s12325-024-03057-8. Online ahead of print. Adv Ther. 2024. PMID: 39535684 Review.
-
Dynamic multilayered control of m6A RNA demethylase activity.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024 Nov 12;121(46):e2317847121. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2317847121. Epub 2024 Nov 4. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2024. PMID: 39495907 Free PMC article.
-
Integrative analysis of transcriptome and proteome wide association studies prioritized functional genes for obesity.Hum Genet. 2024 Nov 4. doi: 10.1007/s00439-024-02714-w. Online ahead of print. Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 39495296
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials


