Leptin, the obesity-associated hormone, exhibits direct cardioprotective effects
- PMID: 16847434
- PMCID: PMC1629412
- DOI: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706834
Leptin, the obesity-associated hormone, exhibits direct cardioprotective effects
Abstract
Background and purpose: Protection against ischaemia-reperfusion (I/R) injury involves PI3K-Akt and p44/42 MAPK activation. Leptin which regulates appetite and energy balance also promotes myocyte proliferation via PI3K-Akt and p44/42 MAPK activation. We, therefore, hypothesized that leptin may also exhibit cardioprotective activity.
Experimental approach: The influence of leptin on I/R injury was examined in perfused hearts from C57Bl/6 J mice that underwent 35 min global ischaemia and 35 min reperfusion, infarct size being assessed by triphenyltetrazolium chloride staining. The concomitant activation of cell-signalling pathways was investigated by Western blotting. The effect of leptin on mitochondrial permeability transition pore (MPTP) opening was studied in rat cardiomyocytes.
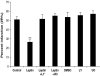
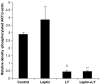
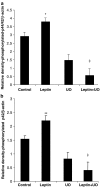
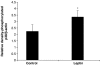
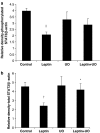
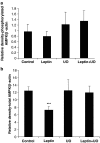
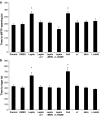
Key results: Leptin (10 nM) administered during reperfusion reduced infarct size significantly. Protection was blocked by either LY294002 or UO126, inhibitors of Akt and p44/42 MAPK, respectively. Western blotting confirmed that leptin stimulated p44/42 MAPK phosphorylation significantly. Akt phosphorylation was also enhanced but did not achieve statistical significance. Additionally, leptin treatment was associated with a significant increase in p38 phosphorylation. By contrast, leptin caused downregulation of phosphorylated and non-phosphorylated STAT3, and of total AMP-activated kinase. Cardiomyocytes responded to leptin with delayed opening of the MPTP and delayed time until contracture.
Conclusions and implications: Our data indicate for the first time that the adipocytokine, leptin, has direct cardioprotective properties which may involve the PI3-Akt and p44/42 MAPK pathways.
Figures
Comment in
-
Obesity--a risk factor or a RISK factor for myocardial infarction?Br J Pharmacol. 2006 Sep;149(1):1-3. doi: 10.1038/sj.bjp.0706833. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Br J Pharmacol. 2006. PMID: 16894350 Free PMC article.
Similar articles
-
Apelin-13 and apelin-36 exhibit direct cardioprotective activity against ischemia-reperfusion injury.Basic Res Cardiol. 2007 Nov;102(6):518-28. doi: 10.1007/s00395-007-0671-2. Epub 2007 Aug 13. Basic Res Cardiol. 2007. PMID: 17694254
-
Evidence that hydroxysafflor yellow A protects the heart against ischaemia-reperfusion injury by inhibiting mitochondrial permeability transition pore opening.Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008 Feb;35(2):211-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1440-1681.2007.04814.x. Epub 2007 Oct 17. Clin Exp Pharmacol Physiol. 2008. PMID: 17941891
-
The cardioprotective actions of leptin are lost in the Zucker obese (fa/fa) rat.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009 Apr;53(4):311-7. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0b013e31819d6152. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2009. PMID: 19390347
-
Adipocytokines, cardiovascular pathophysiology and myocardial protection.Pharmacol Ther. 2011 Feb;129(2):206-19. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2010.09.003. Epub 2010 Oct 16. Pharmacol Ther. 2011. PMID: 20920528 Review.
-
Signaling pathways involved in the cardioprotective effects of cannabinoids.J Pharmacol Sci. 2006 Oct;102(2):155-66. doi: 10.1254/jphs.crj06011x. Epub 2006 Oct 7. J Pharmacol Sci. 2006. PMID: 17031075 Review.
Cited by
-
Adipokines and their potential impacts on susceptibility to myocardial ischemia/reperfusion injury in diabetes.Lipids Health Dis. 2024 Nov 13;23(1):372. doi: 10.1186/s12944-024-02357-w. Lipids Health Dis. 2024. PMID: 39538244 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association of attenuated leptin signaling pathways with impaired cardiac function under prolonged high-altitude hypoxia.Sci Rep. 2024 May 3;14(1):10206. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-59559-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38702334 Free PMC article.
-
Adipsin inhibits Irak2 mitochondrial translocation and improves fatty acid β-oxidation to alleviate diabetic cardiomyopathy.Mil Med Res. 2023 Dec 11;10(1):63. doi: 10.1186/s40779-023-00493-5. Mil Med Res. 2023. PMID: 38072993 Free PMC article.
-
A potential adverse role for leptin and cardiac leptin receptor in the right ventricle in pulmonary arterial hypertension: effect of metformin is BMPR2 mutation-specific.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 Oct 5;10:1276422. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1276422. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37869164 Free PMC article.
-
Body fat percentage and infarct size in patients with non-ST segment elevation myocardial infarction.North Clin Istanb. 2023 Sep 13;10(5):567-574. doi: 10.14744/nci.2023.87259. eCollection 2023. North Clin Istanb. 2023. PMID: 37829751 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bose AK, Mocanu MM, Carr RD, Brand CL, Yellon DM. Glucagon-like peptide 1 can directly protect the heart against ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Diabetes. 2005;54:146–151. - PubMed
-
- Bruno A, Conus S, Schmid I, Simon HU. Apoptotic pathways are inhibited by leptin receptor activation in neutrophils. J Immunol. 2005;174:8090–8096. - PubMed
-
- Brzozowski T, Konturek PC, Pajdo R, Kwicien S, Ptak A, Sliwowski Z, et al. Brain–gut axis in gastroprotection by leptin and cholecystokinin against ischaemia–reperfusion induced gastric lesions. J Physiol Pharmacol. 2001;52:583–602. - PubMed
-
- Bullard AJ, Govewalla P, Yellon DM. Erythropoietin protects the myocardium against reperfusion injury in vitro and in vivo. Basic Res Cardiol. 2005;100:397–403. - PubMed
-
- Considine RV, Sinha MK, Heiman ML, Kriauciunas A, Stephens TW, Nyce MR, et al. Serum immunoreactive-leptin concentrations in normal-weight and obese humans. N Engl J Med. 1996;334:292–295. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous


