The effect of stress on genome regulation and structure
- PMID: 15319229
- PMCID: PMC4242226
- DOI: 10.1093/aob/mch172
The effect of stress on genome regulation and structure
Abstract
Background: Stresses exert evolutionary pressures on all organisms, which have developed sophisticated responses to cope and survive. These responses involve cellular physiology, gene regulation and genome remodelling.
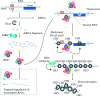
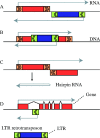
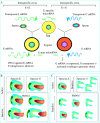
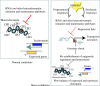
Scope: In this review, the effects of stress on genomes and the connected responses are considered. Recent developments in our understanding of epigenetic genome regulation, including the role of RNA interference (RNAi), suggest a function for this in stress initiation and response. We review our knowledge of how different stresses, tissue culture, pathogen attack, abiotic stress, and hybridization, affect genomes. Using allopolyploid hybridization as an example, we examine mechanisms that may mediate genomic responses, focusing on RNAi-mediated perturbations.
Conclusions: A common response to stresses may be the relaxation of epigenetic regulation, leading to activation of suppressed sequences and secondary effects as regulatory systems attempt to re-establish genomic order.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genetic and epigenetic aspects of polyploid evolution in plants.Cytogenet Genome Res. 2013;140(2-4):270-85. doi: 10.1159/000351430. Epub 2013 Jun 8. Cytogenet Genome Res. 2013. PMID: 23751292 Review.
-
A vicious cycle: RNA silencing and DNA methylation in plants.Cell. 2001 Jul 27;106(2):129-32. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(01)00441-x. Cell. 2001. PMID: 11511339 Review. No abstract available.
-
In situ hybridization to plant tissues and chromosomes.Methods Mol Biol. 2006;326:203-18. doi: 10.1385/1-59745-007-3:203. Methods Mol Biol. 2006. PMID: 16780203 Review.
-
RNA-directed DNA methylation mediated by DRD1 and Pol IVb: a versatile pathway for transcriptional gene silencing in plants.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 May-Jun;1769(5-6):358-74. doi: 10.1016/j.bbaexp.2007.03.001. Epub 2007 Mar 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17449119 Review.
-
Research on plant abiotic stress responses in the post-genome era: past, present and future.Plant J. 2010 Mar;61(6):1041-52. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-313X.2010.04124.x. Plant J. 2010. PMID: 20409277 Review.
Cited by
-
Genome-wide identification, phylogenetic classification of histone acetyltransferase genes, and their expression analysis in sugar beet (Beta vulgaris L.) under salt stress.Planta. 2024 Mar 6;259(4):85. doi: 10.1007/s00425-024-04361-x. Planta. 2024. PMID: 38448714 Free PMC article.
-
m6A RNA demethylase AtALKBH9B promotes mobilization of a heat-activated long terminal repeat retrotransposon in Arabidopsis.Sci Adv. 2023 Dec;9(48):eadf3292. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.adf3292. Epub 2023 Nov 29. Sci Adv. 2023. PMID: 38019921 Free PMC article.
-
Growth and DNA Methylation Alteration in Rice (Oryza sativa L.) in Response to Ozone Stress.Genes (Basel). 2023 Sep 28;14(10):1888. doi: 10.3390/genes14101888. Genes (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37895237 Free PMC article.
-
Methylome changes in Lolium perenne associated with long-term colonisation by the endophytic fungus Epichloë sp. LpTG-3 strain AR37.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Sep 22;14:1258100. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1258100. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37810388 Free PMC article.
-
Active in vivo translocation of the Methanosarcina mazei Gö1 Casposon.Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jul 21;51(13):6927-6943. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkad474. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023. PMID: 37254817 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Aagaard L, Laible G, Selenko P, Schmid M, Dorn R, Schotta G, Kuhfittig S, Wolf A, Lebersorger A, Singh PB, et al. 1999. Functional mammalian homologues of the Drosophila PEV-modifier Su(var)3–9 encode centromere-associated proteins which complex with the heterochromatin component M31. EMBO Journal 18: 1923–1938. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Agrawal RK, Linde J, Sengupta J, Nierhaus KH, Frank J. 2001. Localization of L11 protein on the ribosome and elucidation of its involvement in EF-G-dependent translocation. Journal of Molecular Biology 311: 777–787. - PubMed
-
- Almeida J, Carpenter R, Robbins TP, Martin C, Coen ES. 1989. Genetic interactions underlying flower color patterns in Antirrhinum majus Genes and Development 3: 1758–1767. - PubMed
-
- Bannister AJ, Zegerman P, Partridge JF, Miska EA, Thomas JO, Allshire RC, Kouzarides T. 2001. Selective recognition of methylated lysine 9 on histone H3 by the HP1 chromo domain. Nature 410: 120–124. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


