Overview of the voltage-gated sodium channel family
- PMID: 12620097
- PMCID: PMC153452
- DOI: 10.1186/gb-2003-4-3-207
Overview of the voltage-gated sodium channel family
Abstract
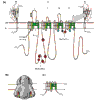
Selective permeation of sodium ions through voltage-dependent sodium channels is fundamental to the generation of action potentials in excitable cells such as neurons. These channels are large integral membrane proteins and are encoded by at least ten genes in mammals. The different sodium channels have remarkably similar functional properties, but small changes in sodium-channel function are biologically relevant, as underscored by mutations that cause several human diseases of hyperexcitability.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Voltage-gated sodium channel modulation by scorpion alpha-toxins.Toxicon. 2007 Feb;49(2):142-58. doi: 10.1016/j.toxicon.2006.09.023. Epub 2006 Sep 28. Toxicon. 2007. PMID: 17087986 Free PMC article. Review.
-
International Union of Pharmacology. XLVII. Nomenclature and structure-function relationships of voltage-gated sodium channels.Pharmacol Rev. 2005 Dec;57(4):397-409. doi: 10.1124/pr.57.4.4. Pharmacol Rev. 2005. PMID: 16382098 Review.
-
Voltage-gated sodium channels: action players with many faces.Ann Med. 2006;38(7):472-82. doi: 10.1080/07853890600969072. Ann Med. 2006. PMID: 17101538 Review.
-
Ion permeation through a voltage- sensitive gating pore in brain sodium channels having voltage sensor mutations.Neuron. 2005 Jul 21;47(2):183-9. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2005.06.012. Neuron. 2005. PMID: 16039561
-
Voltage-gated sodium channels in pain states: role in pathophysiology and targets for treatment.Brain Res Rev. 2009 Apr;60(1):65-83. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresrev.2008.12.005. Epub 2008 Dec 25. Brain Res Rev. 2009. PMID: 19150627 Review.
Cited by
-
Higher sodium in older individuals or after stroke/reperfusion, but not in migraine or Alzheimer's disease - a study in different preclinical models.Sci Rep. 2024 Sep 16;14(1):21636. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-72280-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39284837 Free PMC article.
-
Potential roles of voltage-gated ion channel disruption in Tuberous Sclerosis Complex.Front Mol Neurosci. 2024 Aug 26;17:1404884. doi: 10.3389/fnmol.2024.1404884. eCollection 2024. Front Mol Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39253727 Free PMC article.
-
Voltage-Gated K+ Channel Modulation by Marine Toxins: Pharmacological Innovations and Therapeutic Opportunities.Mar Drugs. 2024 Jul 29;22(8):350. doi: 10.3390/md22080350. Mar Drugs. 2024. PMID: 39195466 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genomic analysis of an Ecuadorian individual carrying an SCN5A rare variant.BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024 Jul 27;24(1):388. doi: 10.1186/s12872-024-04049-w. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2024. PMID: 39068398 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into the voltage-gated sodium channel, NaV1.8, and its role in visceral pain perception.Front Pharmacol. 2024 May 23;15:1398409. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2024.1398409. eCollection 2024. Front Pharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38855747 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Hille B. Ion Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates Inc; 2001.
-
- Catterall WA. From ionic currents to molecular mechanisms: the structure and function of voltage-gated sodium channels. Neuron. 2000;26:13–25. - PubMed
-
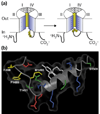
- Rohl CA, Boeckman FA, Baker C, Scheuer T, Catterall WA, Klevit RE. Solution structure of the sodium channel inactivation gate. Biochemistry. 1999;38:855–861. - PubMed
-
- Doyle DA, Cabral JM, Pfuetzner RA, Gulbis JM, Cohen SL, Chait BT, MacKinnon R. The structure of the potassium channel: molecular basis of K+ conduction and selectivity. Science. 1988;280:69–77. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


