Identification of benzothiazoles as potential polyglutamine aggregation inhibitors of Huntington's disease by using an automated filter retardation assay
- PMID: 12200548
- PMCID: PMC139900
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.182426599
Identification of benzothiazoles as potential polyglutamine aggregation inhibitors of Huntington's disease by using an automated filter retardation assay
Abstract
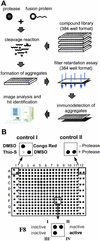
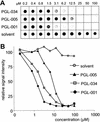
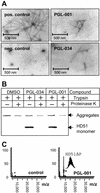
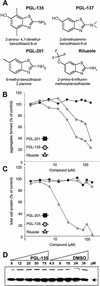
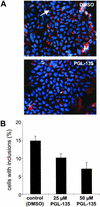
Preventing the formation of insoluble polyglutamine containing protein aggregates in neurons may represent an attractive therapeutic strategy to ameliorate Huntington's disease (HD). Therefore, the ability to screen for small molecules that suppress the self-assembly of huntingtin would have potential clinical and significant research applications. We have developed an automated filter retardation assay for the rapid identification of chemical compounds that prevent HD exon 1 protein aggregation in vitro. Using this method, a total of 25 benzothiazole derivatives that inhibit huntingtin fibrillogenesis in a dose-dependent manner were discovered from a library of approximately 184,000 small molecules. The results obtained by the filter assay were confirmed by immunoblotting, electron microscopy, and mass spectrometry. Furthermore, cell culture studies revealed that 2-amino-4,7-dimethyl-benzothiazol-6-ol, a chemical compound similar to riluzole, significantly inhibits HD exon 1 aggregation in vivo. These findings may provide the basis for a new therapeutic approach to prevent the accumulation of insoluble protein aggregates in Huntington's disease and related glutamine repeat disorders.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Inhibition of huntingtin fibrillogenesis by specific antibodies and small molecules: implications for Huntington's disease therapy.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000 Jun 6;97(12):6739-44. doi: 10.1073/pnas.110138997. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2000. PMID: 10829068 Free PMC article.
-
Green tea (-)-epigallocatechin-gallate modulates early events in huntingtin misfolding and reduces toxicity in Huntington's disease models.Hum Mol Genet. 2006 Sep 15;15(18):2743-51. doi: 10.1093/hmg/ddl210. Epub 2006 Aug 7. Hum Mol Genet. 2006. PMID: 16893904
-
Geldanamycin activates a heat shock response and inhibits huntingtin aggregation in a cell culture model of Huntington's disease.Hum Mol Genet. 2001 Jun 1;10(12):1307-15. doi: 10.1093/hmg/10.12.1307. Hum Mol Genet. 2001. PMID: 11406612
-
Nucleocytoplasmic trafficking and transcription effects of huntingtin in Huntington's disease.Prog Neurobiol. 2007 Nov;83(4):211-27. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2006.11.004. Epub 2007 Jan 22. Prog Neurobiol. 2007. PMID: 17240517 Review.
-
Proteomic Analysis of Huntington's Disease.Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020;21(12):1218-1222. doi: 10.2174/1389203721666201006160327. Curr Protein Pept Sci. 2020. PMID: 33023443 Review.
Cited by
-
Why Is Arginine the Only Amino Acid That Inhibits Polyglutamine Monomers from Taking on Toxic Conformations?ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024 Aug 7;15(15):2925-2935. doi: 10.1021/acschemneuro.4c00276. Epub 2024 Jul 15. ACS Chem Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39009034 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacotherapies for the Treatment of Progressive Supranuclear Palsy: A Narrative Review.Neurol Ther. 2024 Aug;13(4):975-1013. doi: 10.1007/s40120-024-00614-9. Epub 2024 May 14. Neurol Ther. 2024. PMID: 38743312 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Metal-Complexes Bearing Releasable CO Differently Modulate Amyloid Aggregation.Inorg Chem. 2023 Jul 3;62(26):10470-10480. doi: 10.1021/acs.inorgchem.3c01522. Epub 2023 Jun 20. Inorg Chem. 2023. PMID: 37338927 Free PMC article.
-
The role of the glycerol transporter channel Fps1p in cellular proteostasis during enhanced proteotoxic stress.Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022 Sep;106(18):6169-6180. doi: 10.1007/s00253-022-12118-3. Epub 2022 Aug 10. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35945363
-
Pharmacological characterization of mutant huntingtin aggregate-directed PET imaging tracer candidates.Sci Rep. 2021 Sep 9;11(1):17977. doi: 10.1038/s41598-021-97334-z. Sci Rep. 2021. PMID: 34504195 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical


