Obligatory heterotetramerization of three previously uncharacterized Kv channel alpha-subunits identified in the human genome
- PMID: 12060745
- PMCID: PMC123007
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.122617999
Obligatory heterotetramerization of three previously uncharacterized Kv channel alpha-subunits identified in the human genome
Abstract
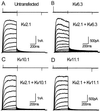
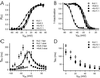
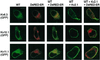
Voltage-gated K(+) channels control excitability in neuronal and various other tissues. We identified three unique alpha-subunits of voltage-gated K(+)-channels in the human genome. Analysis of the full-length sequences indicated that one represents a previously uncharacterized member of the Kv6 subfamily, Kv6.3, whereas the others are the first members of two unique subfamilies, Kv10.1 and Kv11.1. Although they have all of the hallmarks of voltage-gated K(+) channel subunits, they did not produce K(+) currents when expressed in mammalian cells. Confocal microscopy showed that Kv6.3, Kv10.1, and Kv11.1 alone did not reach the plasma membrane, but were retained in the endoplasmic reticulum. Yeast two-hybrid experiments failed to show homotetrameric interactions, but showed interactions with Kv2.1, Kv3.1, and Kv5.1. Co-expression of each of the previously uncharacterized subunits with Kv2.1 resulted in plasma membrane localization with currents that differed from typical Kv2.1 currents. This heteromerization was confirmed by co-immunoprecipitation. The Kv2 subfamily consists of only two members and uses interaction with "silent subunits" to diversify its function. Including the subunits described here, the "silent subunits" represent one-third of all Kv subunits, suggesting that obligatory heterotetramer formation is more widespread than previously thought.
Figures



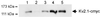
Similar articles
-
Conserved negative charges in the N-terminal tetramerization domain mediate efficient assembly of Kv2.1 and Kv2.1/Kv6.4 channels.J Biol Chem. 2009 Nov 13;284(46):31625-34. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M109.039479. Epub 2009 Aug 28. J Biol Chem. 2009. PMID: 19717558 Free PMC article.
-
The subfamily-specific interaction between Kv2.1 and Kv6.4 subunits is determined by interactions between the N- and C-termini.PLoS One. 2014 Jun 5;9(6):e98960. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0098960. eCollection 2014. PLoS One. 2014. PMID: 24901643 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of Kv6.2 a new gamma-subunit of voltage-gated potassium channel.Recept Channels. 1999;6(5):337-50. Recept Channels. 1999. PMID: 10551266
-
Kv5, Kv6, Kv8, and Kv9 subunits: No simple silent bystanders.J Gen Physiol. 2016 Feb;147(2):105-25. doi: 10.1085/jgp.201511507. Epub 2016 Jan 11. J Gen Physiol. 2016. PMID: 26755771 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular diversity and function of voltage-gated (Kv) potassium channels in epithelial cells.Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005 Aug;37(8):1578-94. doi: 10.1016/j.biocel.2005.04.002. Epub 2005 Apr 26. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 2005. PMID: 15882958 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel loss-of-function KCNB1 gene variant in a twin with global developmental delay and seizures.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Oct 14;18:1477989. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1477989. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39469306 Free PMC article.
-
KCNG4 Genetic Variant Linked to Migraine Prevents Expression of KCNB1.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 17;25(16):8960. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168960. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201645 Free PMC article.
-
A novel autism-associated KCNB1 mutation dramatically slows Kv2.1 potassium channel activation, deactivation and inactivation.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jul 29;18:1438101. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2024.1438101. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39135902 Free PMC article.
-
Structural and functional characterization of an individual with the M285R KCNV2 hypomorphic allele.Ophthalmic Genet. 2024 Aug;45(4):425-434. doi: 10.1080/13816810.2024.2324046. Epub 2024 Mar 8. Ophthalmic Genet. 2024. PMID: 38454848 Free PMC article.
-
All-potassium channel CRISPR screening reveals a lysine-specific pathway of insulin secretion.Mol Metab. 2024 Feb;80:101885. doi: 10.1016/j.molmet.2024.101885. Epub 2024 Jan 19. Mol Metab. 2024. PMID: 38246588 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hille B. Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes. Sunderland, MA: Sinauer; 1991.
-
- Barry D M, Nerbonne J M. Annu Rev Physiol. 1996;58:363–394. - PubMed
-
- Pongs O. FEBS Lett. 1999;452:31–35. - PubMed
-
- Pongs O. Physiol Rev. 1992;72:S69–S88. - PubMed
-
- Zhao B, Rassendren F, Kaang B K, Furukawa Y, Kubo T, Kandel E R. Neuron. 1994;13:1205–1213. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases


