Interferon gamma contributes to initiation of uterine vascular modification, decidual integrity, and uterine natural killer cell maturation during normal murine pregnancy
- PMID: 10899912
- PMCID: PMC2193246
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.192.2.259
Interferon gamma contributes to initiation of uterine vascular modification, decidual integrity, and uterine natural killer cell maturation during normal murine pregnancy
Abstract
The dominant lymphocytes in human and murine implantation sites are transient, pregnancy-associated uterine natural killer (uNK) cells. These cells are a major source of interferon (IFN)-gamma. Implantation sites in mice lacking uNK cells (alymphoid recombinase activating gene [RAG]-2(-/)- common cytokine receptor chain gamma [gamma(c)](-/)-) or IFN-gamma signaling (IFN-gamma(-/)- or IFN-gammaRalpha(-/)-) fail to initiate normal pregnancy-induced modification of decidual arteries and display hypocellularity or necrosis of decidua. To investigate the functions of uNK cell-derived IFN-gamma during pregnancy, RAG-2(-/)-gamma(c)(-/)- females were engrafted with bone marrow from IFN-gamma(-/)- mice, IFN-gamma signal-disrupted mice (IFN-gammaRalpha(-/)- or signal transducer and activator of transcription [Stat]-1(-/)-), or from mice able to establish normal uNK cells (severe combined immunodeficient [SCID] or C57BL/6). Mated recipients were analyzed at midgestation. All grafts established uNK cells. Grafts from IFN-gamma(-/)- mice did not reverse host vascular or decidual pathology. Grafts from all other donors promoted modification of decidual arteries and decidual cellularity. Grafts from IFN-gammaRalpha(-/)- or Stat-1(-/)- mice overproduced uNK cells, all of which were immature. Grafts from IFN-gamma(-/)-, SCID, or C57BL/6 mice produced normal, mature uNK cells. Administration of murine recombinant IFN-gamma to pregnant RAG-2(-/)-gamma(c)(-/)- mice initiated decidual vessel modification and promoted decidual cellularity in the absence of uNK cells. These in vivo findings strongly suggest that uNK cell-derived IFN-gamma modifies the expression of genes in the uterine vasculature and stroma, which initiates vessel instability and facilitates pregnancy-induced remodeling of decidual arteries.
Figures
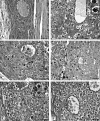
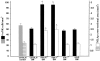
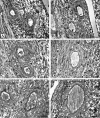
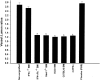
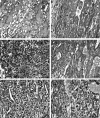

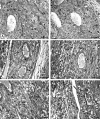
Comment in
-
Role of uterine natural killer cells and interferon gamma in placental development.J Exp Med. 2000 Jul 17;192(2):F1-4. doi: 10.1084/jem.192.2.f1. J Exp Med. 2000. PMID: 10939888 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
Assessment of requirements for IL-15 and IFN regulatory factors in uterine NK cell differentiation and function during pregnancy.J Immunol. 2003 Sep 15;171(6):2937-44. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.171.6.2937. J Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12960317
-
Functions of uterine natural killer cells are mediated by interferon gamma production during murine pregnancy.Semin Immunol. 2001 Aug;13(4):235-41. doi: 10.1006/smim.2000.0319. Semin Immunol. 2001. PMID: 11437631 Review.
-
Interferon-gamma contributes to the normalcy of murine pregnancy.Biol Reprod. 1999 Aug;61(2):493-502. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod61.2.493. Biol Reprod. 1999. PMID: 10411532
-
Pathways participating in activation of mouse uterine natural killer cells during pregnancy.Biol Reprod. 2005 Sep;73(3):510-8. doi: 10.1095/biolreprod.104.033951. Epub 2005 May 4. Biol Reprod. 2005. PMID: 15878887
-
Update on pathways regulating the activation of uterine Natural Killer cells, their interactions with decidual spiral arteries and homing of their precursors to the uterus.J Reprod Immunol. 2003 Aug;59(2):175-91. doi: 10.1016/s0165-0378(03)00046-9. J Reprod Immunol. 2003. PMID: 12896821 Review.
Cited by
-
A New Look at Immunogenetics of Pregnancy: Maternal Major Histocompatibility Complex Class I Educates Uterine Natural Killer Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 15;25(16):8869. doi: 10.3390/ijms25168869. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39201555 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Association between endometrial protein expression of IFN-γ and delayed conception after parturition in dairy cows.Vet Res Commun. 2024 Oct;48(5):3187-3196. doi: 10.1007/s11259-024-10490-1. Epub 2024 Aug 14. Vet Res Commun. 2024. PMID: 39141287
-
Emerging role of C5aR2: novel insights into the regulation of uterine immune cells during pregnancy.Front Immunol. 2024 Jun 20;15:1411315. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1411315. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38979410 Free PMC article.
-
Murine modeling of menstruation identifies immune correlates of protection during Chlamydia muridarum challenge.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2024 May 23:2024.05.21.595090. doi: 10.1101/2024.05.21.595090. bioRxiv. 2024. PMID: 38826233 Free PMC article. Preprint.
-
High amniotic fluid fractalkine and MIP-1β levels are associated with intrauterine growth restriction: a prospective cohort study.Turk J Med Sci. 2023 Dec 16;54(1):280-290. doi: 10.55730/1300-0144.5789. eCollection 2024. Turk J Med Sci. 2023. PMID: 38812616 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kurago Z.B., Lutz C.T., Smith K.D., Colonna M. NK cell natural cytotoxicity and IFN-gamma production are not always coordinately regulatedengagement of DX9 KIR+ NK cells by HLA-B7 variants and target cells. J. Immunol. 1998;160:1573–1580. - PubMed
-
- Boehm U., Klamp T., Groot M., Howard J.C. Cellular responses to interferon-gamma. Annu. Rev. Immunol. 1997;15:749–795. - PubMed
-
- King A., Loke Y.W. On the nature and function of human uterine granular lymphocytes. Immunol. Today. 1991;12:432–435. - PubMed
-
- Croy B.A., Kiso Y. Granulated metrial gland cellsa natural killer cell subset of the pregnant murine uterus. Microsc. Res. Tech. 1993;25:189–200. - PubMed
-
- Jokhi P.P., King A., Sharkey A.M., Smith S.K., Loke Y.W. Screening for cytokine messenger ribonucleic acids in purified human decidual lymphocyte populations by the reverse-transcriptase polymerase chain reaction. J. Immunol. 1994;153:4427–4435. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous


