Biologic functions of the IFN-gamma receptors
- PMID: 10688427
- PMCID: PMC4154595
- DOI: 10.1034/j.1398-9995.1999.00099.x
Biologic functions of the IFN-gamma receptors
Abstract
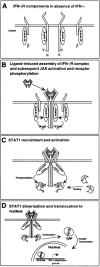
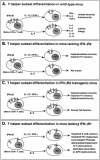
Interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma) is a cytokine that plays an important role in inducing and modulating an array of immune responses. Cellular responses to IFN-gamma are mediated by its heterodimeric cell-surface receptor (IFN-gammaR), which activates downstream signal transduction cascades, ultimately leading to the regulation of gene expression. In order to study the role of IFN-gamma in a number of immune responses and pathways, researchers have generated mice with altered patterns of IFN-gammaR gene expression. These studies, together with analyses of naturally occurring mutations of the IFN-gammaR in man, have been instrumental in elucidating the diverse functions of IFN-gamma, and are the subject of this review.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Regulation of interferon-gamma receptor (INF-gammaR) chains: a peculiar way to rule the life and death of human lymphocytes.Eur Cytokine Netw. 2001 Mar;12(1):6-14. Eur Cytokine Netw. 2001. PMID: 11282540 Review.
-
Adenovirus-mediated murine interferon-gamma receptor transfer enhances the efficacy of IFN-gamma in vivo.Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002 Jan 25;290(3):1042-7. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.2001.6298. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2002. PMID: 11798180
-
Regulation of IFN-gamma production by B effector 1 cells: essential roles for T-bet and the IFN-gamma receptor.J Immunol. 2005 Jun 1;174(11):6781-90. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.174.11.6781. J Immunol. 2005. PMID: 15905519
-
Mice with IFN-gamma receptor deficiency are less susceptible to experimental autoimmune myasthenia gravis.J Immunol. 1999 Apr 1;162(7):3775-81. J Immunol. 1999. PMID: 10201893
-
The IFN gamma receptor: a paradigm for cytokine receptor signaling.Annu Rev Immunol. 1997;15:563-91. doi: 10.1146/annurev.immunol.15.1.563. Annu Rev Immunol. 1997. PMID: 9143700 Review.
Cited by
-
Inflammation in atherosclerosis: pathophysiology and mechanisms.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Nov 11;15(11):817. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-07166-8. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 39528464 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Interactions between the human milk oligosaccharide 2'-fucosyllactose and Bifidobacterium longum subspecies infantis in influencing systemic immune development and function in piglets.Front Nutr. 2024 Oct 25;11:1444594. doi: 10.3389/fnut.2024.1444594. eCollection 2024. Front Nutr. 2024. PMID: 39525504 Free PMC article.
-
In silico assessment of CAR macrophages activity against SARS-CoV-2 infection.Heliyon. 2024 Oct 23;10(21):e39689. doi: 10.1016/j.heliyon.2024.e39689. eCollection 2024 Nov 15. Heliyon. 2024. PMID: 39524874 Free PMC article.
-
A hybrid method for discovering interferon-gamma inducing peptides in human and mouse.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 6;14(1):26859. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-77957-8. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39501025 Free PMC article.
-
Leveraging a comprehensive unbiased RNAseq database to characterize human monocyte-derived macrophage gene expression profiles within commonly employed in vitro polarization methods.Sci Rep. 2024 Nov 5;14(1):26753. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-78000-6. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 39500943 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Billiau A. Interferon‐gamma: biology and role in pathogenesis. Adv Immunol 1996;62:61 130 - PubMed
-
- Boehm U, Klamp T, Groot M, Howard JC. Cellular responses to interferon‐gamma. Annu Rev Immunol 1997;15:749 795 - PubMed
-
- Wheelock EF. Interferon‐like virus‐inhibitor induced in human leukocytes by phytohemagglutinin. Science 1965;149:310 311 - PubMed
-
- Farrar MA & Schreiber RD. The molecular cell biology of interferon‐gamma and its receptor. Annu Rev Immunol 1993;11:571 611 - PubMed
-
- Novick D, Orchansky P, Revel M, Rubinstein M. The human interferon‐gamma receptor. Purification, characterization, and preparation of antibodies. J Biol Chem 1987;262:8483 8487 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources


