Dopamine D4 receptor-knock-out mice exhibit reduced exploration of novel stimuli
- PMID: 10531457
- PMCID: PMC6782928
- DOI: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.19-21-09550.1999
Dopamine D4 receptor-knock-out mice exhibit reduced exploration of novel stimuli
Abstract
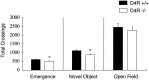
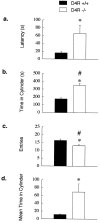
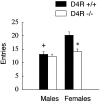
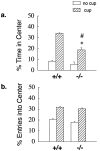
The involvement of dopamine neurotransmission in behavioral responses to novelty is suggested by reports that reward is related to increased dopamine activity, that dopamine modulates exploratory behavior in animals, and that Parkinson's disease patients report diminished responses to novelty. Some studies have reported that polymorphisms of the human dopamine D4 receptor (D4R) gene are associated with personality inventory measures of the trait called "novelty-seeking". To explore a potential role for the D4R in behavioral responses to novelty, we evaluated D4R-knock-out (D4R-/-) and wild-type (D4R+/+) mice in three approach-avoidance paradigms: the open field, emergence, and novel object tests. These three paradigms differ in the degree to which they elicit approach, or exploratory behavior, and avoidance, or anxiety-related behavior. Thus, we used these three tests to determine whether the D4R primarily influences the exploratory or the anxious component of responses to approach-avoidance conflicts. D4R-/- mice were significantly less behaviorally responsive to novelty than D4R+/+ mice in all three tests. The largest phenotypic differences were observed in the novel object test, which maximizes approach behavior, and the smallest phenotypic differences were found in the open field test, which maximizes avoidance behavior. Hence, D4R-/- mice exhibit reductions in behavioral responses to novelty, reflecting a decrease in novelty-related exploration.
Figures
Similar articles
-
RO-10-5824 is a selective dopamine D4 receptor agonist that increases novel object exploration in C57 mice.Neuropharmacology. 2003 Mar;44(4):473-81. doi: 10.1016/s0028-3908(02)00412-4. Neuropharmacology. 2003. PMID: 12646284
-
Dopamine D4 receptor deficiency in mice alters behavioral responses to anxiogenic stimuli and the psychostimulant methylphenidate.Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013 Feb;103(4):831-41. doi: 10.1016/j.pbb.2012.12.006. Epub 2012 Dec 19. Pharmacol Biochem Behav. 2013. PMID: 23262298
-
Absence of dopamine D4 receptors results in enhanced reactivity to unconditioned, but not conditioned, fear.Eur J Neurosci. 2002 Jan;15(1):158-64. doi: 10.1046/j.0953-816x.2001.01842.x. Eur J Neurosci. 2002. PMID: 11860516
-
Dopamine D4 receptor gene: novelty or nonsense?Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999 Jul;21(1):3-16. doi: 10.1016/S0893-133X(98)00115-8. Neuropsychopharmacology. 1999. PMID: 10379515 Review.
-
Dopamine D4 receptor gene (DRD4) is associated with Novelty Seeking (NS) and substance abuse: the saga continues..Mol Psychiatry. 2001 Sep;6(5):497-9. doi: 10.1038/sj.mp.4000918. Mol Psychiatry. 2001. PMID: 11526461 Review. No abstract available.
Cited by
-
Activation of D2-like dopamine receptors improves the neuronal network and cognitive function of PPT1KI mice.Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024 Sep 16. doi: 10.1038/s41401-024-01377-7. Online ahead of print. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 2024. PMID: 39284877
-
Mouse Model of Parkinson's Disease with Bilateral Dorsal Striatum Lesion with 6-Hydroxydopamine Exhibits Cognitive Apathy-like Behavior.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Jul 22;25(14):7993. doi: 10.3390/ijms25147993. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39063235 Free PMC article.
-
Now it's your turn!: Eye blink rate in a Jenga task modulated by interaction of task wait times, effortful control, and internalizing behaviors.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 8;19(3):e0294888. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0294888. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38457390 Free PMC article.
-
Neuropharmacological Evidence Implicating Drug-Induced Glutamate Receptor Dysfunction in Affective and Cognitive Sequelae of Subchronic Methamphetamine Self-Administration in Mice.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Feb 5;25(3):1928. doi: 10.3390/ijms25031928. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38339206 Free PMC article.
-
A Dual Effect of Dopamine on Hippocampal LTP and Cognitive Functions in Control and Kindled Mice.J Neurosci. 2024 Jan 31;44(5):e0926212023. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.0926-21.2023. J Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38124004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Adams LM, Geyer MA. A proposed animal model for hallucinogens based on LSD's effects on patterns of exploration in rats. Behav Neurosci. 1985;99:881–900. - PubMed
-
- Ariano MA, Wang J, Noblett KL, Larson ER, Sibley D. Cellular distribution of the rat D4 dopamine receptor protein in the CNS using anti-receptor antisera. Brain Res. 1997;752:26–34. - PubMed
-
- Asghari V, Sanyal S, Buchwaldt S, Paterson A, Jovanovic V, Van Tol HH. Modulation of intracellular cyclic AMP levels by different human dopamine D4 receptor variants. J Neurochem. 1995;65:1157–1165. - PubMed
-
- Belzung C. Hippocampal mossy fibres: implication in novelty reactions or in anxiety behaviors? Behav Brain Res. 1992;51:149–155. - PubMed
-
- Belzung C, Le Pape G. Comparison of different behavioral test situations used in psychopharmacology for measurement of anxiety. Physiol Behav. 1994;56:623–628. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

