Abstract
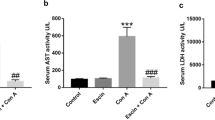
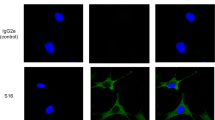
Adult worm extract from Ascaris suum (Asc) has immunosuppressive activity and elicits Th2/IL-4/IL-10 response. This study evaluated the prophylactic and therapeutic effect of Asc in a murine model of concanavalin A (ConA)-induced autoimmune hepatitis (AIH). BALB/c mice received ConA, iv, (20 mg/kg), and three groups of animals were formed: (1) AIH, received only ConA; (2) AIH + Asc prophylactic, treated with Asc (1 mg/ml), ip, 30 min before of the AIH; and (3) AIH + Asc therapeutic, treated with Asc 2 h after the AIH. Plasma transaminase and immunoglobulins (measured at 8 and 24 h and 7 days after treatment) and cytokine production (IL-4, IL-10, IL-13, and IFN-γ) by splenocytes upon ConA and Asc stimulus were compared. The livers were weighed and examined histologically. In the AIH group, there was an increase in liver weight, transaminase levels, and total immunoglobulins. These parameters were reduced by 8–24 h and 7 days in the prophylactic group, but in the therapeutic group, only on day 7. The survival rate of mice in the AIH group was 38.5 %, compared to 67 % in the therapeutic Asc group. The survival rate of the animals with AIH that were prophylactically treated with Asc was 100 %. A decrease of cellular infiltration and high levels of IL-4, IL-10, and IL-13 were induced by Asc. An increase of liver fibrosis was also observed, but with less intensity with prophylactic treatment. Thus, the Ascaris components have an inhibitory effect on AIH, with an intense Th2 immune response.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Araújo CA, Perini A, Martins MA, Macedo MS, Macedo-Soares MF (2008) PAS-1, a protein from Ascaris suum, modulates allergic inflammation via IL-10 and IFN-gamma, but not IL-12. Cytokine 44(3):335–341
Benzel F, Erdur H, Kohler S, Frentsch M, Thiel A, Harms L, Wandinger KP, Rosche B (2012) Immune monitoring of Trichuris suis egg therapy in multiple sclerosis patients. J Helminthol 86(3):339–347
Borkow G, Bentwich Z (2008) Chronic parasite infections cause immune changes that could affect successful vaccination. Trends Parasitol 24(6):243–245
Carambia A, Herkel J (2010) CD4 T cells in hepatic immune tolerance. J Autoimmun 34(1):23–28
Christie JF, Dunbar B, Davidson I, Kennedy MW (1990) N-terminal amino acid sequence identity between a major allergen of Ascaris lumbricoides and Ascaris suum, and MHC-restricted IgE responses to it. Immunology 69(4):596–602
Cooper PJ, Chico ME, Sandoval C, Espinel I, Guevara A, Kennedy MW, Urban JF Jr, Griffin GE, Nutman TB (2000) Human infection with Ascaris lumbricoides is associated with a polarized cytokine response. J Infect Dis 182(4):1207–1213
Czaja AJ (2002) Autoimmune liver disease. Curr Opin Gastroenterol 18(3):334–344
Dawson H, Solano-Aguilar G, Beal M, Beshah E, Vangimalla V, Jones E, Botero S, Urban JF Jr (2009) Localized Th1-, Th2-, T regulatory cell-, and inflammation-associated hepatic and pulmonary immune responses in Ascaris suum-infected swine are increased by retinoic acid. Infect Immun 77(6):2576–2587
de Lima Aires A, de Azevedo Albuquerque MC, Silva RA, Schirato GV, de Pontes Filho NT, de Araújo SB, Souza VM, Costa VM, Malagueño E (2012) Immunohistopathological changes in murine Schistosomiasis mansoni under the influence of N-acetyl-L-cysteine. Parasitol Res 111(4):1569–1578
Elias D, Wolday D, Akuffo H, Petros B, Bronner U, Britton S (2001) Effect of deworming on human T cell responses to mycobacterial antigens in helminth-exposed individuals before and after bacille Calmette–Guerin (BCG) vaccination. Clin Exp Immunol 123(2):219–225
Erb KJ (2009) Can helminths or helminth-derived products be used in humans to prevent or treat allergic diseases? Trends Immunol 30(2):75–82
Faquim-Mauro EL, Macedo MS (1998) The immunosuppressive activity of Ascaris suum is due to high molecular weight components. Clin Exp Immunol 114(2):245–251
Fehér J, Lengyel G (2010) Hepatocellular carcinoma: occurrence, risk factors, biomarkers. Orv Hetil 151(23):933–940
Ferreira AP, Faquim ES, Abrahamsohn IA, Macedo MS (1995) Immunization with Ascaris suum extract impairs T cell functions in mice. Cell Immunol 162(2):202–210
Gove ME, Rhodes DH, Pini M, van Baal JW, Sennello JA, Fayad R, Cabay RJ, Myers MG Jr, Fantuzzi G (2009) Role of leptin receptor-induced STAT3 signaling in modulation of intestinal and hepatic inflammation in mice. J Leukoc Biol 85:491–496
Jonuleit H, Schmitt E (2003) The regulatory T cell family: distinct subsets and their interrelations. J Immunol 171(12):6323–6327
Lemos LVB, Schiavon JLN, Ferraz MLG (2007) Hepatite auto-imune. Prat hosp 9(52):75–80
Lima C, Perini A, Garcia ML, Martins MA, Teixeira MM, Macedo MS (2002) Eosinophilic inflammation and airway hyper-responsiveness are profoundly inhibited by a helminth (Ascaris suum) extract in a murine model of asthma. Clin Exp Allergy 32(11):1659–1666
Liwski R, Zhou J, McAlister V, Lee TD (2000) Prolongation of allograft survival by Nippostrongylus brasiliensis is associated with decreased allospecific cytotoxic T lymphocyte activity and development of T cytotoxic cell type 2 cells. Transplantation 69(9):1912–1922
Longhi MS, Ma Y, Mieli-Vergani G, Vergani D (2010) Aetiopathogenesis of autoimmune hepatitis. J Autoimmun 34(1):7–14
Matera G, Giancotti A, Scalise S, Pulicari MC, Maselli R, Piizzi C, Pelaia G, Tancrè V, Muto V, Doldo P, Cosco V, Cosimo P, Capicotto R, Quirino A, Scalzo R, Liberto MC, Parlato G, Focà A (2008) Ascaris lumbricoides-induced suppression of total and specific IgE responses in atopic subject is interleukin 10-independent and associated with an increase of CD25(+) cells. Diagn Microbiol Infect Dis 62(3):280–286
Miller ML, Sun Y, Fu YX (2009) Cutting edge: B and T lymphocyte attenuator signaling on NKT cells inhibits cytokine release and tissue injury in early immune responses. J Immunol 183:32–36
Oshiro TM, Enobe CS, Araújo CA, Macedo MS, Macedo-Soares MF (2006) PAS-1, a protein affinity purified from Ascaris suum worms, maintains the ability to modulate the immune response to a bystander antigen. Immunol Cell Biol 84(2):138–144
Oshiro TM, Rafael A, Enobe CS, Fernandes I, Macedo-Soares MF (2004) Comparison of different monoclonal antibodies against immunosuppressive proteins of Ascaris suum. Braz J Med Biol Res 37:223–226
Phills JA, Harrold AJ, Whiteman GV, Perelmutter L (1972) Pulmonary infiltrates, asthma and eosinophilia due to Ascaris suum infestation in man. N Engl J Med 286(18):965–970
Rocha FA, Leite AK, Pompeu MM, Cunha TM, Verri WA Jr, Soares FM, Castro RR, Cunha FQ (2008) Protective effect of an extract from Ascaris suum in experimental arthritis models. Infect Immun 76(6):2736–2745
Sabin EA, Araújo MI, Carvalho EM, Pearce EJ (1996) Impairment of tetanus toxoid-specific Th1-like immune responses in humans infected with Schistosoma mansoni. J Infect Dis 173(1):269–272
Sclavons C, Burtea C, Boutry S, Laurent S, Vander Elst L, Muller RN (2013) Phage display screening for tumor necrosis factor-α–binding peptides: detection of inflammation in a mouse model of hepatitis. Int J Pept. doi:10.1155/2013/348409
Silva SR, Jacysyn JF, Macedo MS, Faquim-mauro EL (2006) Immunosuppressive components of Ascaris suum down-regulate expression of costimulatory molecules and function of antigen-presenting cells via an IL-10-mediated mechanism. Eur J Immunol 36:3227–3237
Souza VM, Faquim-Mauro EL, Macedo MS (2002) Extracts of Ascaris suum egg and adult worm share similar immunosuppressive properties. Braz J Med Biol Res 35(1):81–89
Souza VM, Jacysyn JF, Macedo MS (2004) IL-4 and IL-10 are essential for immunosuppression induced by high molecular weight proteins from Ascaris suum. Cytokine 28(2):92–100
Sugawara Y, Azuma N, Onodera S, Tsunoka Y, Morimoto M (2011) Th2 immune responses and alternatively activated macrophages (AAMacs) in helminth infection in aged mice. J Vet Med Sci 73(4):511–516
Tiegs G, Hentschel J, Wendel A (1992) A T cell-dependent experimental liver injury in mice inducible by concanavalin A. J Clin Invest 90(1):196–203
Tu CT, Yao QY, Xu BL, Zhang SC (2013) Curcumin protects against concanavalin A-induced hepatitis in mice through inhibiting the cytoplasmic translocation and expression of high mobility group box 1. Inflammation 36(1):206–215
Urban JF Jr, Steenhard NR, Solano-aguilar GI, Dawson HD, Iweala OI, Nagler CR, Noland GS, Kumar N, Anthony RM, Shea-Donohue T, Weinstock J, Gause WC (2007) Infection with parasitic nematodes confounds vaccination efficacy. Vet Parasitol 148(1):14–20
Wang HX, Liu M, Weng SY, Li JJ, Xie C, He HL, Guan W, Yuan YS, Gao J (2012) Immune mechanisms of concanavalin A model of autoimmune hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 18(2):119–125
Wilson MS, Mentink-Kane MM, Pesce JT, Ramalingam TR, Thompson R, Wynn TA (2007) Immunopathology of schistosomiasis. Immunol Cell Biol 85(2):148–154
Wynn TA (2008) Cellular and molecular mechanisms of fibrosis. J Pathol 214(2):199–210
Wynn TA (2004) Fibrotic disease and the T(H)1/T(H)2 paradigm. Nat Rev Immunol 4(8):583–594
Wynn TA (2003) IL-13 effector functions. Annu Rev Immunol 21:425–456
Xu L, Zhang F, Xu W, Xiong S (2009) Specific antibodies induced by DNA vaccination with extracellular domain of CD25 gene protect against ConA-induced autoimmune hepatitis. Clin Immunol 132(3):412–419
Yamamoto K, Hiura M, Tabaru A, Honma Y, Narita R, Abe S, Shimajiri S, Okamoto K, Yamaguchi K, Harada M (2011) Rapid progression of hepatocellular carcinoma in a patient with autoimmune hepatitis. Intern Med 50(13):1409–1413
Yamashita J, Iwamura C, Sasaki T, Mitsumori K, Ohshima K, Hada K, Hara N, Takahashi M, Kaneshiro Y, Tanaka H, Kaneko K, Nakayama T (2011) Apolipoprotein A-II suppressed concanavalin A-induced hepatitis via the inhibition of CD4 T cell function. J Immunol 186:3410–3420
Yang SH, Park MJ, Yoon IH, Kim SY, Hong SH, Shin JY, Nam HY, Kim YH, Kim B, Park CG (2009) Soluble mediators from mesenchymal stem cells suppress T cell proliferation by inducing IL-10. Exp Mol Med 41(5):315–324
Ye F, Yan S, Xu L, Jiang Z, Liu N, Xiong S, Wang Y, Chu Y (2009) Tr1 regulatory T cells induced by ConA pretreatment prevent mice from ConA-induced hepatitis. Immunol Lett 122(2):198–207
Yin H, Cheng L, Agarwal C, Agarwal R, Ju C (2010) Lactoferrin protects against concanavalin A-induced liver injury in mice. Liver Int 30(4):623–632
Yu Z, Otsuka H, Yamaguchi K, Kuroishi T, Sasano T, Sugawara S, Nakamura M, Endo Y (2011) Roles of platelets and macrophages in the protective effects of lipopolysaccharide against concanavalin A-induced murine hepatitis. Biochim Biophys Acta 1812(9):1069–1079
Conflict of interest
W.R.C. Nascimento was in receipt of a Masters fellowship from Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico (CNPq).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nascimento, W.C., Silva, R.P., Fernandes, E.S. et al. Immunomodulation of liver injury by Ascaris suum extract in an experimental model of autoimmune hepatitis. Parasitol Res 113, 3309–3317 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3994-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00436-014-3994-6