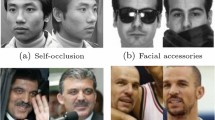
Abstract
This paper investigates the main reason for the obtained low performance when the face recognition algorithms are tested on partially occluded face images. It has been observed that in the case of upper face occlusion, missing discriminative information due to occlusion only accounts for a very small part of the performance drop. The main factor is found to be the registration errors due to erroneous facial feature localization. It has been shown that by solving the misalignment problem, very high correct recognition rates can be achieved with a generic local appearance-based face recognition algorithm. In the case of a lower face occlusion, only a slight decrease in the performance is observed, when a local appearance-based face representation approach is used. This indicates the importance of local processing when dealing with partial face occlusion. Moreover, improved alignment increases the correct recognition rate also in the experiments against the lower face occlusion, which shows that face registration plays a key role on face recognition performance.
Chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Martinez, A.M.: Recognizing imprecisely localized, partially occluded and expression variant faces from a single sample per class. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 24(6), 748–763 (2002)
Tan, X., Chen, S., Zhou, Z.H., Zhang, F.: Recognizing partially occluded, expression variant faces from single training image per person with SOM and soft k-NN ensemble. IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks 16(4), 875–886 (2005)
Park, B.G., Lee, K.M., Lee, S.U.: Face recognition using face-ARG matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 27(12), 1982–1988 (2005)
Fidler, S., Skočaj, D., Leonardis, A.: Combining reconstructive and discriminative subspace methods for robust classification and regression by subsampling. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 28(3), 337–350 (2006)
Wright, J., Ganesh, A., Yang, A., Ma, Y.: Robust face recognition via sparse representation. Technical report, University of Illinois, USA (2007)
Jia, H., Martinez, A.M.: Face recognition with occlusions in the training and testing sets. In: Proceedings of IEEE Int’l. Conf. on Automatic Face and Gesture Recognition (2008)
Ekenel, H.K., Stiefelhagen, R.: Local appearance-based face recognition using discrete cosine transform. In: Proc. of 13th European Signal Processing Conf. (EUSIPCO 2005) (2005)
Ekenel, H.K., Stiefelhagen, R.: Analysis of local appearance-based face recognition: Effects of feature selection and feature normalization. In: Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshop 2006, p. 34 (2006)
Turk, M., Pentland, A.: Eigenfaces for recognition. Journal of Cognitive Neuroscience 3(1), 71–86 (1991)
Belhumeur, P.N., Hespanha, J.P., Kriegman, D.J.: Eigenfaces vs. Fisherfaces: Recognition using class-specific linear projection. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 19(7), 711–720 (1997)
Ekenel, H.K., Sankur, B.: Feature selection in the independent component subspace for face recognition. Pattern Recognition Letters 25(12), 1377–1388 (2004)
Gross, R., Shi, J., Cohn, J.F.: Que vadis face recognition? In: Proceedings of Workshop on Empirical Evaluation Methods in Computer Vision (2001)
Martinez, A.M., Benavente, R.: The AR face database. Technical Report 24, CVC (1998)
Penev, P.S., Atick, J.: Local feature analysis: a general statistical theory for object represntation. Network: Computation in Neural Systems 7, 477–500 (1996)
Phillips, P.J., Flynn, P.J., Scruggs, T., Bowyer, K.W., Chang, J., Hoffman, K., Marques, J., Min, J., Worek, W.: Overview of the Face Recognition Grand Challenge. In: Proc. 2005 IEEE Computer Society Conf. on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Los Alamitos, CA, USA, vol. 1, pp. 947–954 (2005)
Lemieux, A., Parizeau, M.: Experiments on eigenfaces robustness. In: Proc. Int’l. Conf. on Pattern Recognition, vol. 1, pp. 421–424 (2002)
Rentzeperis, E., Stergiou, A., Pnevmatikakis, A., Polymenakos, L.: Impact of face registration errors on recognition. In: Maglogiannis, I., Karpouzis, K., Bramer, M. (eds.) Artificial Intelligence Applications and Innovations (AIAI 2006), pp. 187–194. Springer, Heidelberg (2006)
Wiskott, L., Fellous, J.M., Kruger, N., Malsburg, C.: Face recognition by elastic bunch graph matching. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 19(7), 775–779 (1997)
He, X., Yan, S., Hu, Y., Niyogi, P., Zhang, H.J.: Face recognition using Laplacianfaces. IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence 27(3), 328–340 (2005)
Xie, C., Kumar, B.V.K.V., Palanivel, S., Yegnanarayana, B.: A still-to-video face verification system using advanced correlation filters. In: Zhang, D., Jain, A.K. (eds.) ICBA 2004. LNCS, vol. 3072, pp. 102–108. Springer, Heidelberg (2004)
Samaria, F.S., Harter, A.C.: Parameterisation of a stochastic model for human face identification. In: Proceedings of the Second IEEE Workshop on Applications of Computer Vision, pp. 138–142 (1994)
Ekenel, H.K.: A Robust Face Recognition Algorithm for Real-World Applications. PhD thesis, Universität Karlsruhe (TH), Germany (2009)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2009 Springer-Verlag Berlin Heidelberg
About this paper
Cite this paper
Ekenel, H.K., Stiefelhagen, R. (2009). Why Is Facial Occlusion a Challenging Problem?. In: Tistarelli, M., Nixon, M.S. (eds) Advances in Biometrics. ICB 2009. Lecture Notes in Computer Science, vol 5558. Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01793-3_31
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-642-01793-3_31
Publisher Name: Springer, Berlin, Heidelberg
Print ISBN: 978-3-642-01792-6
Online ISBN: 978-3-642-01793-3
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)