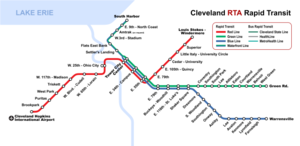
RTA Rapid Transit
RTA Rapid Transit (generally known as The Rapid) is a rapid transit and semi-metro[4] system owned and operated by the Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority (GCRTA).
The system serves Cleveland and surrounding areas in Cuyahoga County. The system currently consists of four total service lines: one rapid transit rail line and three light rail lines.
Rail Lines
[edit]The four rail lines join at Tower City Center in downtown Cleveland, on the platform level of the former Cleveland Union Terminal.
Three rail lines share their tracks at Tri-C–Campus District and East 55th stations. This sharing of one route by light and heavy rail trains is quite unusual. The shared stations have connected platforms of two heights to accommodate the two kinds of trains. And the two types of trains both use the same maintenance facility since they both use the same track gauge and same source of power (overhead catenary).
Red Line
[edit]The Red Line, a heavy-rail route, runs in both directions on fully grade-separated rights-of-way built from 1955 to 1968. It serves Cleveland's southwest suburbs, with its southwestern terminus at Cleveland Hopkins International Airport. Heading northeast, the Red Line serves University Circle before heading to its northeastern terminus at the Louis Stokes Station at Windermere in East Cleveland.
Blue, Green, and Waterfront Lines
[edit]The Blue and Green light-rail lines (alternatively known as the RTA Shaker Rapid) were built from 1913 to 1936 as grade-separated lines closer to downtown and surface lines along street medians in the streetcar suburb of Shaker Heights.
The two lines part ways at Shaker Square, a historic mixed-use community in Cleveland proper, just west of the Shaker Heights border. The Blue Line veers southeast along Van Aken Boulevard until reaching its terminus near the intersection of Warrensville Center Road and Chagrin Boulevard (U.S. Route 422 and State Route 8). The Green line continues due east along Shaker Boulevard (State Route 87) until reaching its terminus at the intersection of Green Road.

The Waterfront Line, opened in 1996, extends the Blue and Green Lines from Tower City north through The Flats. It then travels northeast along the shoreline of Lake Erie, servicing the local Amtrak station and terminates at the Lakefront Municipal lot. The Waterfront light rail line provides access from Tower City Center to the Flats, Cleveland Browns Stadium, the Great Lakes Science Center, the Rock and Roll Hall of Fame, and Burke Lakefront Airport.
Stations
[edit]
The RTA Rapid Transit system consists of a total of 47 stations.[5] The stations are fully or partially within the city limits of Cleveland, Shaker Heights, East Cleveland, and Brook Park.







| †* | Terminus and transfer stations |
| † | Terminal stations |
| * | Transfer stations |
| Closed stations |
| Station | Rapid Transit lines | Jurisdiction | Opened | Rebuilt | ADA access |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Airport† | Red | Cleveland | 1968 | 1994 | 1994 |
| Amtrak | Waterfront | Cleveland | 1997 | ||
| Ashby | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1981 | |
| Attleboro | Green | Shaker Heights | 1913 | 1980 | |
| Avalon | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1981 | |
| Belvoir | Green | Shaker Heights | 1936 | 1980 | |
| Brookpark | Red | Cleveland / Brook Park | 1969 | 2017 | 2003 |
| Buckeye–Woodhill* | Blue Green | Cleveland | 1920 | 1981, 2012 | 2012 |
| Cedar–University | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | 2014 | 2002 |
| Courtland | Green | Shaker Heights | 1915 | 1980 | |
| Coventry | Green | Cleveland / Shaker Heights | 1913 | 1980 | |
| Drexmore | Blue | Cleveland | 1948 | 1981 | |
| East 9th–North Coast | Waterfront | Cleveland | 1996 | 1996 | |
| East 55th* | Red Blue Green | Cleveland | 1920 | 2011 | 2011 |
| East 79th | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | 2021 | 2021 |
| East 79th* | Blue Green | Cleveland | 1920 | 1981 | |
| East 105th–Quincy | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | 2005 | 2005 |
| East 116th–St. Luke's* | Blue Green | Cleveland | 1920 | 1981, 2019 | 2019 |
| Eaton | Green | Shaker Heights | 1915 | 1980 | |
| Euclid–East 120th | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | ||
| Farnsleigh | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1930 | 1981, 2019 | 2019 |
| Flats East Bank | Waterfront | Cleveland | 1996 | 1996 | |
| Green Road† | Green | Shaker Heights | 1936 | 1980, 1988 | 2001 |
| Kenmore | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1981 | |
| Lee–Shaker | Green | Shaker Heights | 1913 | 1980, 2017 | 2017 |
| Lee–Van Aken | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1981, 2015 | 2015 |
| Little Italy–University Circle | Red | Cleveland | 2015 | 2015 | |
| Lynnfield | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1981 | |
| Onaway | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1980 | |
| Puritas–West 150th | Red | Cleveland | 1968 | 2011 | 2011 |
| Settlers Landing | Waterfront | Cleveland | 1996 | 1996 | |
| Shaker Square* | Blue Green | Cleveland | 1920 | 1986 | 2006 |
| South Harbor† | Waterfront | Cleveland | 1996 | 1996 | |
| South Park | Green | Shaker Heights | 1913 | 1980 | |
| South Woodland | Blue | Cleveland / Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1981 | |
| Southington | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1920 | 1980 | |
| Southington | Green | Shaker Heights | 1913 | 1981 | |
| Superior | Red | East Cleveland | 1955 | 1996 | 1996 |
| Tower City†* | Red Blue Green Waterfront | Cleveland | 1930 | 1990 | 1990 |
| Tri-C–Campus District* | Red Blue Green | Cleveland | 1930 | 2003, 2018 | 2018 |
| Triskett | Red | Cleveland | 1958 | 2000 | 2000 |
| Warrensville–Shaker | Green | Shaker Heights | 1928 | 1980, 2016 | 2016 |
| Warrensville–Van Aken† | Blue | Shaker Heights | 1930 | 1981, 1999 | 1999 |
| West 3rd | Waterfront | Cleveland | 1999 | 1999 | |
| West 25th–Ohio City | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | 1992 | 1992 |
| West 65th–Lorain | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | 2004 | 2004 |
| West 117th–Madison | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | 2007 | 2007 |
| West Boulevard–Cudell | Red | Cleveland | 1955 | 1999 | 1999 |
| West Green | Green | Shaker Heights | 1936 | 1980 | |
| West Park | Red | Cleveland | 1958 | 1996 | 1996 |
| Windermere†* | Red | East Cleveland | 1955 | 1997 | 1997 |
Note: Euclid–East 120th Street station closed in 2015 and was replaced by Little Italy–University Circle station.
See also
[edit]- List of metro systems
- List of light rail transit systems
- List of rail transit systems in the United States
- List of Ohio train stations
References
[edit]- ^ a b c d "Overview: Facts about the Greater Cleveland RTA". Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority. 29 November 2014. Retrieved 2018-01-03.
- ^ "Transit Ridership Report Third Quarter 2024" (PDF). American Public Transportation Association. November 20, 2024. Retrieved November 23, 2024.
- ^ "Transit Ridership Report Fourth Quarter 2023" (PDF). American Public Transportation Association. March 4, 2024. Retrieved September 5, 2024.
- ^ Landgraf, Robert J. (1992). "Cleveland's Light Rail System in the 1980s: The Ongoing Revolution". Transportation Research Record (1361): 259. ISSN 0361-1981. Retrieved 7 May 2024.
- ^ RTA system maps
External links
[edit]- Greater Cleveland Regional Transit Authority – Maps and Schedules
- Historic American Engineering Record (HAER) No. OH-4, "Shaker Heights Rapid Transit Line, Cleveland, Cuyahoga County, OH", 18 photos, 15 data pages, 2 photo caption pages
- Jon Bell – Cleveland, Ohio: Transit Links
- Cleveland, Ohio – Rapid Transit (RTA)
- nycsubway.org – Cleveland, Ohio
- RTA Rapid Transit Locations
- Northern Ohio Railway Museum