Exploring the Potential of Spectral Classification in Estimation of Soil Contaminant Elements
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study Area and Soil Sample
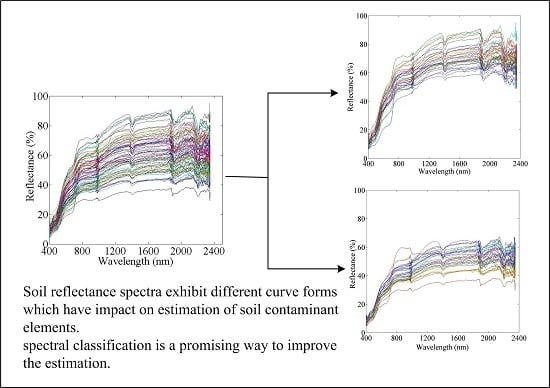
2.2. Spectral Measurement and Pre-processing
2.3. Soil Reflectance Spectra Classification
2.4. Model Construction and Validation
2.4.1. Model Construction
2.4.2. Model Validation
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of Soil Contaminant Elements
3.2. Prediction Accuracy Based on Squared Euclidean Distance
3.3. Prediction Accuracy Based on Cosine of Spectral Angle
3.4. Spatial Distribution Assessment
4. Discussion
4.1. Potential of Spectral Classification in Estimating Soil Contaminant Elements
4.2. Distance Measure Methods of K-means Clustering
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Khlifi, R.; Olmedo, P.; Gil, F.; Hammami, B.; Chakroun, A.; Rebai, A.; Hamza-Chaffai, A. Arsenic, cadmium, chromium and nickel in cancerous and healthy tissues from patients with head and neck cancer. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 452-453, 58–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ikeda, M.; Zhang, Z.W.; Shimbo, S.; Watanabe, T.; Nakatsuka, H.; Moon, C.S.; Matsuda-Inoguchi, N.; Higashikawa, K. Urban population exposure to lead and cadmium in east and south-east Asia. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 373–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iyengar, G.V.; Nair, P.P. Global outlook on nutrition and the environment: Meeting the challenges of the next millennium. Sci. Total Environ. 2000, 249, 331–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steiger, B.V.; Webster, R.; Schulin, R.; Lehmann, R. Mapping heavy metals in polluted soil by disjunctive kriging. Environ. Pollut. 1996, 94, 205–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, S.C.; Li, X.D.; Zhang, G.; Qi, S.H.; Min, Y.S. Heavy metals in agricultural soils of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Environ. Pollut. 2002, 119, 33–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, T.; Chen, Y.; Liu, Y.; Wu, G. Visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy—An alternative for monitoring soil contamination by heavy metals. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 265, 166–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooistra, L.; Wanders, J.; Epema, G.F.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Wehrens, R.; Buydens, L.M.C. The potential of field spectroscopy for the assessment of sediment properties in river floodplains. Anal. Chim. Acta 2003, 484, 189–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, H.; Wu, G.; Wu, X. Feasibility of estimating heavy metal concentrations in phragmites australis using laboratory-based hyperspectral data—A case study along Le’an River, China. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2010, 12, S166–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Walvoort, D.J.J.; McBratney, A.B.; Janik, L.J.; Skjemstad, J.O. Visible, near infrared, mid infrared or combined diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for simultaneous assessment of various soil properties. Geoderma 2006, 131, 59–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; McBratney, A.B. Laboratory evaluation of a proximal sensing technique for simultaneous measurement of soil clay and water content. Geoderma 1998, 85, 19–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Ji, J.; Gong, P.; Liao, Q.; Tian, Q.; Ma, H. A mechanism study of reflectance spectroscopy for investigating heavy metals in soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2007, 71, 918–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellon-Maurel, V.; Fernandez-Ahumada, E.; Palagos, B.; Roger, J.M.; McBratney, A. Critical review of chemometric indicators commonly used for assessing the quality of the prediction of soil attributes by NIR spectroscopy. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2010, 29, 1073–1081. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerrero, C.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Mouazen, A.M. Special issue ‘diffuse reflectance spectroscopy in soil science and land resource assessment’. Geoderma 2010, 158, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burns, R.G. Mineralogical applications of crystal field theory; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1993; p. 575. [Google Scholar]
- Clark, R.N. Spectroscopy of rocks and minerals, and principles of spectroscopy. In Remote Sensing for Earth Science: Manual of Remote Sensing, 3rd ed.; Rencz, A., Ed.; John Wiley and Sons, Inc: New York, NY, US, 1999; pp. 3–58. [Google Scholar]
- Covelo, E.F.; Vega, F.A.; Andrade, M.L. Simultaneous sorption and desorption of Cd, Cr, Cu, Ni, Pb, and Zn in acid soils: II. soil ranking and influence of soil characteristics. J. Hazard. Mater. 2007, 147, 862–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vega, F.A.; Covelo, E.F.; Andrade, M.L. Competitive sorption and desorption of heavy metals in mine soils: Influence of mine soil characteristics. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2006, 298, 582–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kooistra, L.; Wehrens, R.; Leuven, R.S.E.W.; Buydens, L.M.C. Possibilities of visible-near-infrared spectroscopy for the assessment of soil contamination in river floodplains. Anal. Chim. Acta 2001, 446, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malley, D.F.; Williams, P.C. Use of near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy in prediction of heavy metals in freshwater sediment by their association with organic matter. Environ. Sci. Technol. 1997, 31, 3461–3467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sipos, P.; Nemeth, T.; Kis, V.K.; Mohai, I. Association of individual soil mineral constituents and heavy metals as studied by sorption experiments and analytical electron microscopy analyses. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 168, 1512–1520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vohland, M.; Bossung, C.; Fründ, H.C. A spectroscopic approach to assess trace-heavy metal contents in contaminated floodplain soilsviaspectrally active soil components. J. Plant Nutr. Soil Sci. 2009, 172, 201–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, X.Q.; Mao, Y.Q.; Ji, J.; Ma, H.R.; Chen, J.; Liao, Q.L. Reflectance spectroscopy study of Cd contamination in the sediments of the Changjiang River, China. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 3449–3454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kemper, T.; Sommer, S. Estimate of heavy metal contamination in soils after a mining accident using reflectance spectroscopy. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2002, 36, 2742–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, W.; Zhang, X. Estimating soil zinc concentrations using reflectance spectroscopy. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2017, 58, 126–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Boruvka, L.; Vasat, R.; Saberioon, M.; Klement, A.; Kratina, J.; Tejnecky, V.; Drabek, O. Estimation of potentially toxic elements contamination in anthropogenic soils on a brown coal mining dumpsite by reflectance spectroscopy: A case study. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0117457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.; Chang, Q.; Clevers, J.G.; Kooistra, L. Rapid identification of soil cadmium pollution risk at regional scale based on visible and near-infrared spectroscopy. Environ. Pollut. 2015, 206, 217–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.; Li, F.; Yang, Z.; Ayoko, G.A.; Frost, R.L.; Ji, J. Diffuse reflectance spectroscopy for monitoring potentially toxic elements in the agricultural soils of Changjiang River Delta, China. Appl. Clay Sci. 2012, 64, 75–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Y.; Chen, J.; Wu, X.; Tian, Q.; Ji, J.; Qin, Z. Possibilities of reflectance spectroscopy for the assessment of contaminant elements in suburban soils. Appl. Geochem. 2005, 20, 1051–1059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoner, E.R.; Baumgardner, M.F. Characteristic variations in reflectance of surface soils. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 1981, 45, 1161–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cipra, J.E.; Baumgard, M.F.; Stoner, E.R.; Macdonal, R.B. Measuring radiance charasteristics of soil with a field spectroradiometer. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. Proc. 1971, 35, 1014–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, C. Preliminary Research on Spectral Classification of Typical Soils in China and Its Data Processing; Science Press: Beijing, China, 1981; pp. 315–323. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Xu, B.; Ji, G.; Zhu, Y. A preliminary research of geographic regionalization of China land background and spectral reflectance characteristics of soil. Remote Sens. Environ. China 1991, 6, 142–151. (In Chinses) [Google Scholar]
- Awiti, A.O.; Walsh, M.G.; Shepherd, K.D.; Kinyamario, J. Soil condition classification using infrared spectroscopy: A proposition for assessment of soil condition along a tropical forest-cropland chronosequence. Geoderma 2008, 143, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.J.; Zhang, B.; Zhang, Y.Z.; Song, K.S.; Wang, Z.M.; Li, F.; Hu, M.G. Soil taxonomy on the basis of reflectance spectral characteristics. Spectrosc. Spectr. Anal. 2008, 28, 624–628. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, H.; Zhao, J.; Wang, Q.; Sui, Y.; Wang, J.; Yang, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, C. Soil type recognition as improved by genetic algorithm-based variable selection using near infrared spectroscopy and partial least squares discriminant analysis. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 10930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vasques, G.M.; Demattê, J.A.M.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Ramírez-López, L.; Terra, F.S. Soil classification using visible/near-infrared diffuse reflectance spectra from multiple depths. Geoderma 2014, 223-225, 73–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Condit, H.R. Application of characteristic vector analysis to spectral energy distribution of daylight and spectral reflectance of American soils. Appl. Opt. 1972, 11, 74–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, T. Spectral characteristic of main types of soils in southern China and soil classification. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1995, 32, 58–68. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Vasques, G.M.; Grunwald, S.; Sickman, J.O. Comparison of multivariate methods for inferential modeling of soil carbon using visible/near-infrared spectra. Geoderma 2008, 146, 14–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vohland, M.; Besold, J.; Hill, J.; Fründ, H.C. Comparing different multivariate calibration methods for the determination of soil organic carbon pools with visible to near infrared spectroscopy. Geoderma 2011, 166, 198–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholizadeh, A.; Borůvka, L.; Saberioon, M.M.; Kozák, J.; Vašát, R.; Němeček, K. Comparing different data preprocessing methods for monitoring soil heavy metals based on soil spectral features. Soil Water Res. 2016, 10, 218–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Ji, W.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Chen, S.; Zhou, Y. Prediction of soil organic matter using a spatially constrained local partial least squares regression and the Chinese vis-NIR spectral library. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2015, 66, 679–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wetterlind, J.; Stenberg, B. Near-infrared spectroscopy for within-field soil characterization: Small local calibrations compared with national libraries spiked with local samples. Eur. J. Soil Sci. 2010, 61, 823–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Knadel, M.; Gislum, R.; Deng, F.; Norgaard, T.; de Jonge, L.W.; Moldrup, P.; Greve, M.H. Predicting soil organic carbon at field scale using a national soil spectral library. J. Near Infrared Spectrosc. 2013, 21, 213–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Viscarra Rossel, R.A.; Behrens, T. Using data mining to model and interpret soil diffuse reflectance spectra. Geoderma 2010, 158, 46–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, Z.; Wang, Q.; Peng, J.; Ji, W.; Liu, H.; Li, X.; Viscarra Rossel, R.A. Development of a national VNIR soil-spectral library for soil classification and prediction of organic matter concentrations. Sci. China-Earth Sci. 2014, 57, 1671–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Probst, A.; Liao, B. Metal contamination of soils and crops affected by the Chenzhou lead/zinc mine spill (Hunan, China). Sci. Total Environ. 2005, 339, 153–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rinnan, Å.; Berg, F.v.d.; Engelsen, S.B. Review of the most common pre-processing techniques for near-infrared spectra. TrAC Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1201–1222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Pan, T.; Chen, J.; Lu, Q. Waveband selection for NIR spectroscopy analysis of soil organic matter based on SG smoothing and MWPLS methods. Chemom. Intell. Lab. Syst. 2011, 107, 139–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Liu, T. Relationships between spectral reflectance characteristics and soil properite—A case study in southern China. Chin. J. Soil Sci. 1989, 4, 158–160. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Wu, H.; Wang, R. Soil spectral characteristic and its quantitative nalysis in soil classification. Acta Pedol. Sin. 1991, 28, 177–185. (In Chinese) [Google Scholar]
- Shao, X.; Bian, X.; Liu, J.; Zhang, M.; Cai, W. Multivariate calibration methods in near infrared spectroscopic analysis. Anal. Methods 2010, 2, 1662–1666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thomas, E.V. A primer on multivariate calibration. Anal. Chem. 1994, 66, A795–A804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leardi, R.; Gonzalez, A.L. Genetic algorithms applied to feature selection in PLS regression: How and when to use them. Chemom. Intel. Lab. Syst. 1998, 41, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Cui, L.; Gao, W.; Shi, T.; Chen, Y.; Gao, Y. Prediction of low heavy metal concentrations in agricultural soils using visible and near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Geoderma 2014, 216, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, C.W.; Laird, D.A.; Mausbach, M.J.; Hurburgh, C.R. Near-infrared reflectance spectroscopy-principal components regression analyses of soil properties. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 2001, 65, 480–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saeys, W.; Mouazen, A.M.; Ramon, H. Potential for onsite and online analysis of pig manure using visible and near infrared reflectance spectroscopy. Biosyst. Eng. 2005, 91, 393–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Liu, X.M.; Li, X.; Zhao, K.L.; Zhang, J.B.; Xu, J.M.; Shi, J.C.; Dahlgren, R.A. Heavy metal sources identification and sampling uncertainty analysis in a field-scale vegetable soil of Hangzhou, China. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Goovaerts, P. Geostatistics in soil science: State-of-the-art and perspectives. Geoderma 1999, 89, 1–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Wu, J.; Xu, J. Characterizing the risk assessment of heavy metals and sampling uncertainty analysis in paddy field by geostatistics and GIS. Environ. Pollut. 2006, 141, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]










| Metal | Minimum | Maximum | Mean | Std 1 | CV 2 | BV 3 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | 10.17 | 59.85 | 25.86 | 6.80 | 0.26 | 40 |
| Zn | 60.44 | 4946.60 | 679.42 | 868.61 | 1.25 | 100 |
| Spectra | Metal | PCs 1 | RMSEP (mg·kg−1) | RPD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 74 soil spectra | Ni | 8 | 4.56 | 1.83 | 0.69 |
| Zn | 7 | 341 | 1.89 | 0.71 | |
| Group E1 | Ni | 10 | 4.36 | 2.70 | 0.85 |
| Zn | 4 | 344 | 1.66 | 0.60 | |
| Group E2 | Ni | 5 | 0.91 | 3.28 | 0.90 |
| Zn | 8 | 174 | 4.02 | 0.93 |
| Spectra | Metal | PCs 1 | RMSEP (mg·kg−1) | RPD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 74 soil spectra | Ni | 8 | 4.56 | 1.83 | 0.69 |
| Zn | 7 | 342 | 1.89 | 0.71 | |
| Group C1 | Ni | 3 | 9.66 | 1.12 | 0.11 |
| Zn | 7 | 568 | 1.42 | 0.44 | |
| Group C2 | Ni | 7 | 2.22 | 2.63 | 0.84 |
| Zn | 5 | 312 | 1.96 | 0.72 |
| Group | PCs 1 | RMSEP (mg·kg−1) | RPD | R2 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Slected subset of the 74 spectra | 9 | 330 | 1.96 | 0.73 |
| Group DE1 | 11 | 55 | 4.88 | 0.95 |
| Group DE2 | 11 | 147 | 5.12 | 0.96 |
| Group DC1 | 2 | 119 | 2.21 | 0.77 |
| Group DC2 | 12 | 382 | 1.92 | 0.71 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Sun, W.; Zhang, X.; Zou, B.; Wu, T. Exploring the Potential of Spectral Classification in Estimation of Soil Contaminant Elements. Remote Sens. 2017, 9, 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060632
Sun W, Zhang X, Zou B, Wu T. Exploring the Potential of Spectral Classification in Estimation of Soil Contaminant Elements. Remote Sensing. 2017; 9(6):632. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060632
Chicago/Turabian StyleSun, Weichao, Xia Zhang, Bin Zou, and Taixia Wu. 2017. "Exploring the Potential of Spectral Classification in Estimation of Soil Contaminant Elements" Remote Sensing 9, no. 6: 632. https://doi.org/10.3390/rs9060632